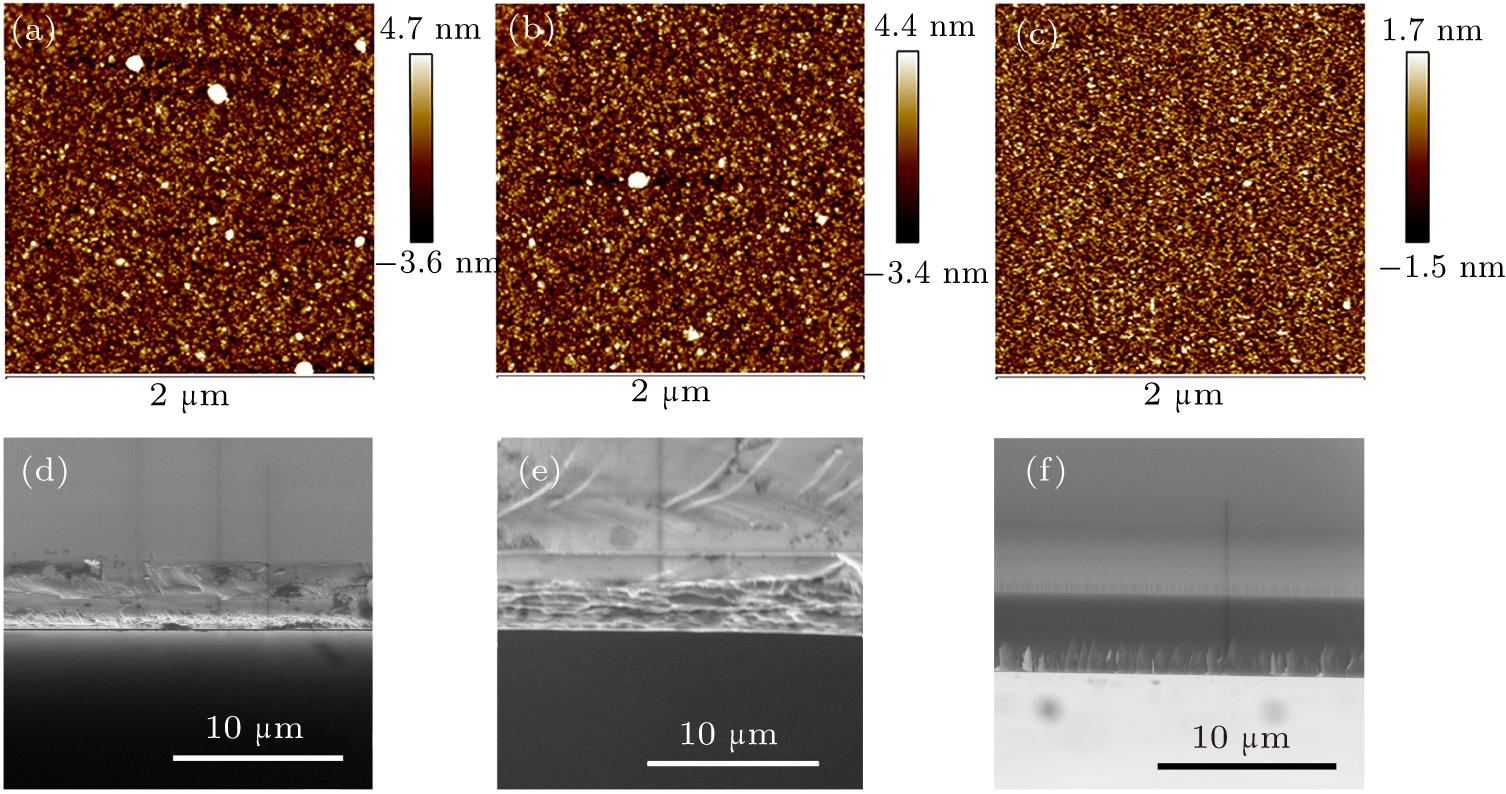
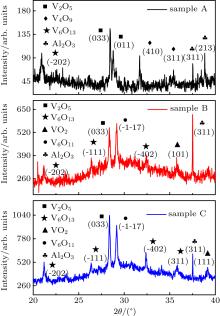
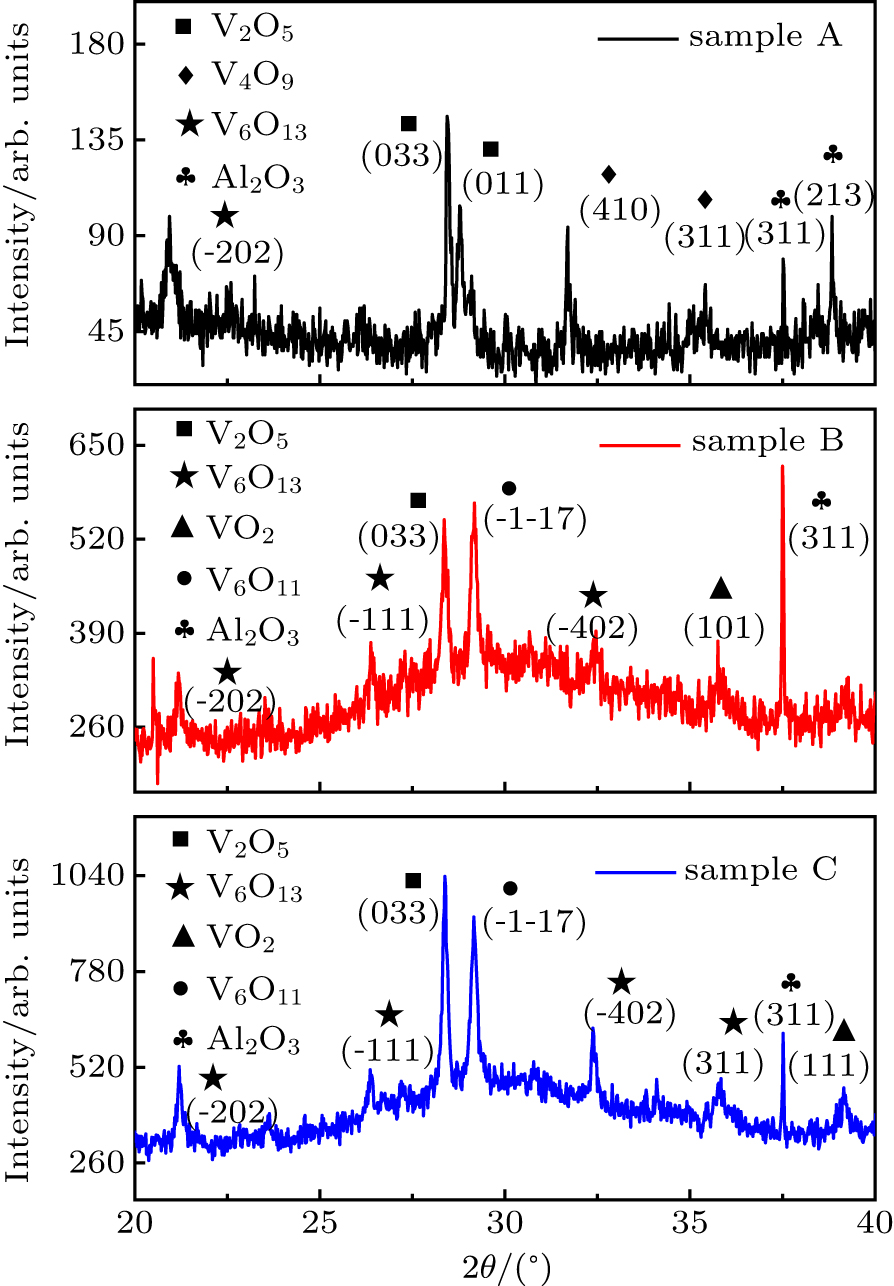
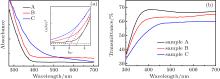
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
Shao Z W, Cao X, Zhang Q X, Long S W, Chang T C, Xu F, Yang Y, Jin P 2019 Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C 200 110044 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.110044 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
Son M, Lee J, Park J, Shin J, Choi G, Jung S, Lee W, Kim S, Park S, Hwang H 2011 IEEE Electr. Device L. 32 1579 DOI: 10.1109/LED.2011.2163697 |
| [6] |
Wang Z L, Zhang Z H, Zhao Z, Shao R W, Sui M L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 177201 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.67.177201 |
| [7] |
Sun X N, Qu Z M, Wang Q G, Yuan Y, Liu S H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 107201 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.107201 |
| [8] |
Chen X Y, Pomerantseva E, Banerjee P, Gregorczyk K, Ghodssi R, Rubloff G 2012 Chem. Mater. 24 1255 DOI: 10.1021/cm202901z |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
Shin S, Suga S, Taniguchi M, Fujisawa M, Kanzaki H, Fujimori A, Daimon H, Ueda Y, Kosuge K, Kachi S 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 4993 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.4993 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
Yun S J, Lim J W, Noh J S, Chae B G, Kim H T 2008 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47 3067 DOI: 10.1143/JJAP.47.3067 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
Blanquart T, Niinistö J, Gavagnin M, Longo V, Heikkilä M, Puukilainen E, Pallem V R, Dussarrat C, Ritala M, Leskelä M 2013 RSC Adv. 3 1179 DOI: 10.1039/C2RA22820C |
| [19] |
Rampelberg G, Deduytsche D, Schutter B D, Premkumar P A, Toeller M, Schaekers M, Martens K, Radu I, Detavernier C 2014 Thin Solid Films 550 59 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.039 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
Monnier D, Nuta I, Chatillon C, Gros-Jean M, Volpi F, Blanquet E 2009 J. Electrochem. Soc. 156 H71 DOI: 10.1149/1.3009595 |
| [22] |
Mattelaer F, Geryl K, Rampelberg G, Dobbelaere T, Dendooven J, Detavernier C 2016 RSC Adv. 6 114658 DOI: 10.1039/C6RA25742A |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
Li W, Wang D K, Zhang Z Z, Chu X Y, Fang X, Wang X W, Fang D, Lin F Y, Wang X H, Wei Z P 2018 Opt. Mater. Express 8 3561 DOI: 10.1364/OME.8.003561 |
| [26] |
|
 ), Deshuang Guo(郭德双)1, Juncheng Liu(刘俊成)1, Xuan Fang(方铉)1, Jilong Tang(唐吉龙)1, Fengyuan Lin(林逢源)1, Xinwei Wang(王新伟)1, Dan Fang(房丹)1, Zhipeng Wei(魏志鹏)1,‡(
), Deshuang Guo(郭德双)1, Juncheng Liu(刘俊成)1, Xuan Fang(方铉)1, Jilong Tang(唐吉龙)1, Fengyuan Lin(林逢源)1, Xinwei Wang(王新伟)1, Dan Fang(房丹)1, Zhipeng Wei(魏志鹏)1,‡( )
)