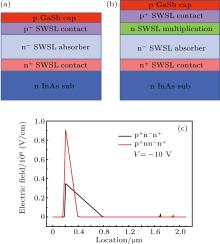
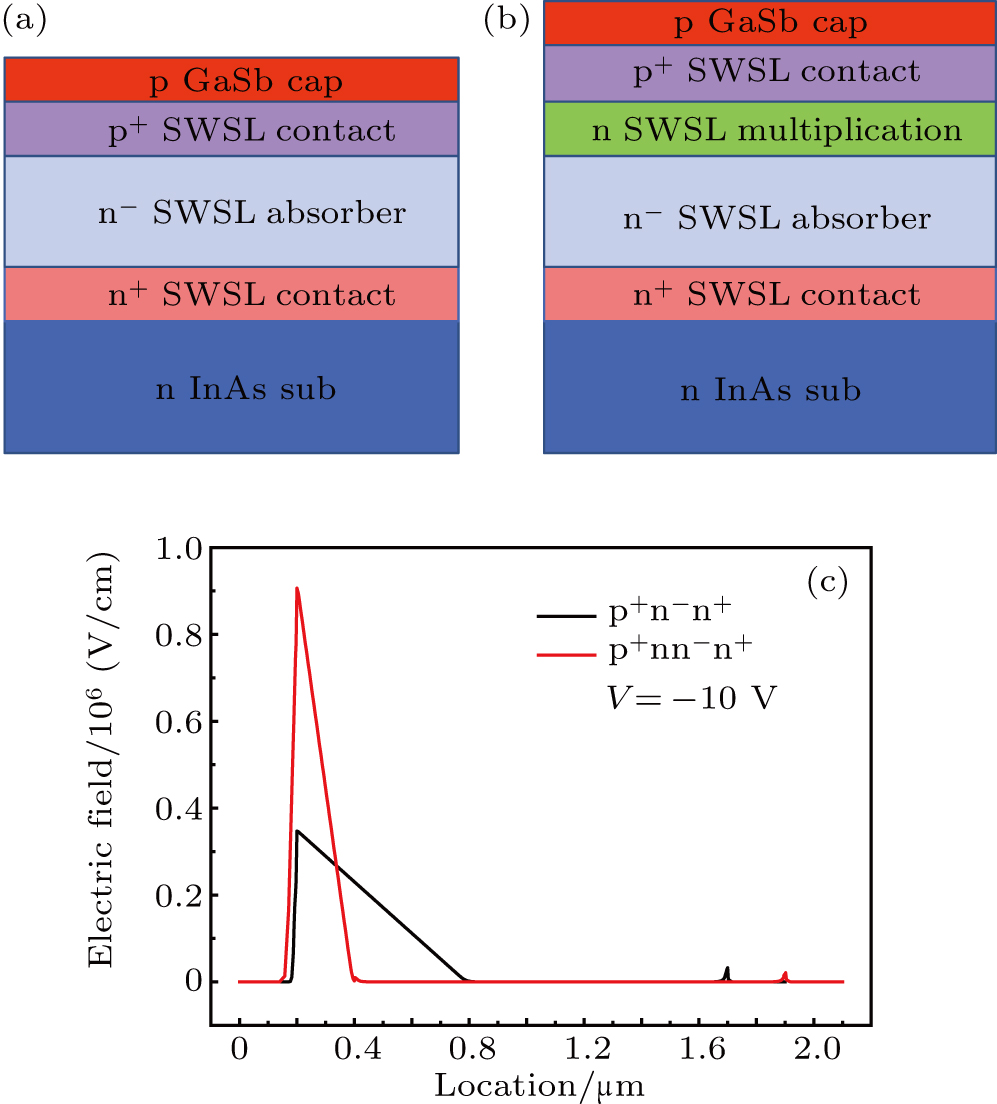
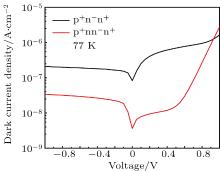
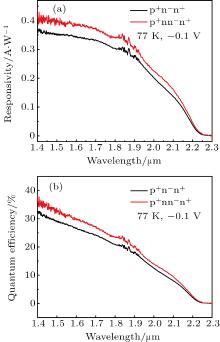
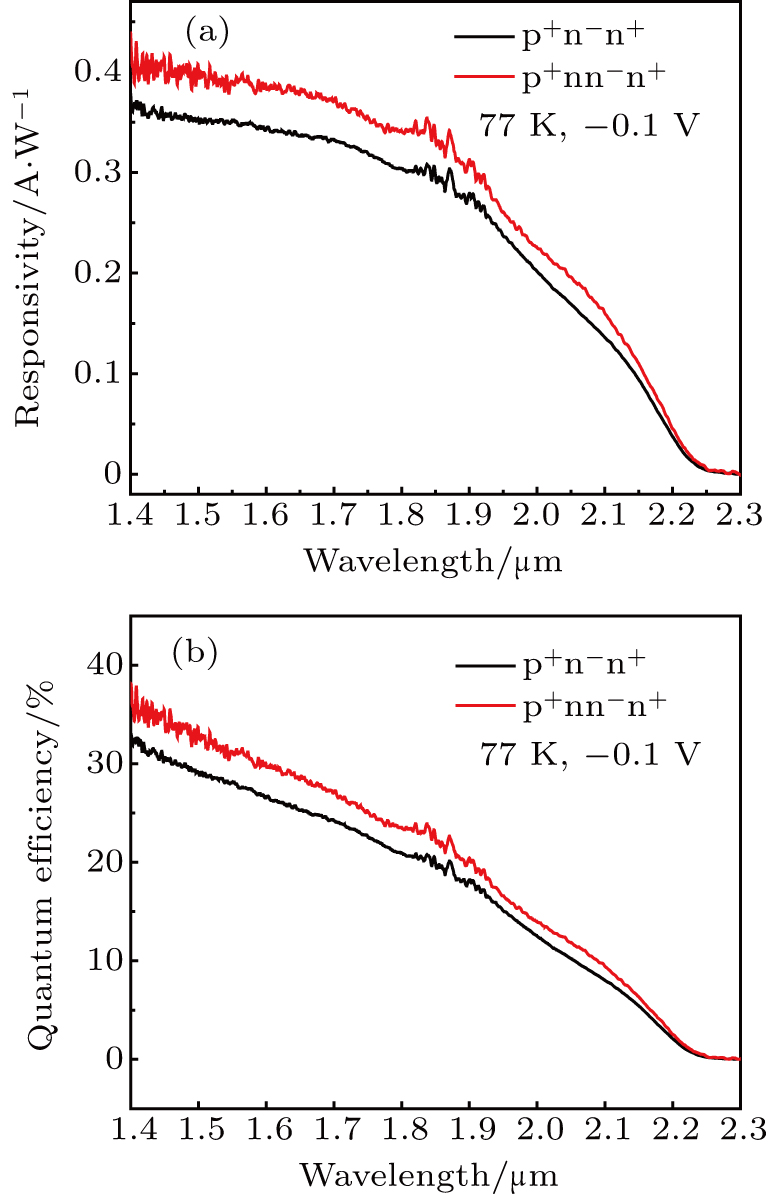
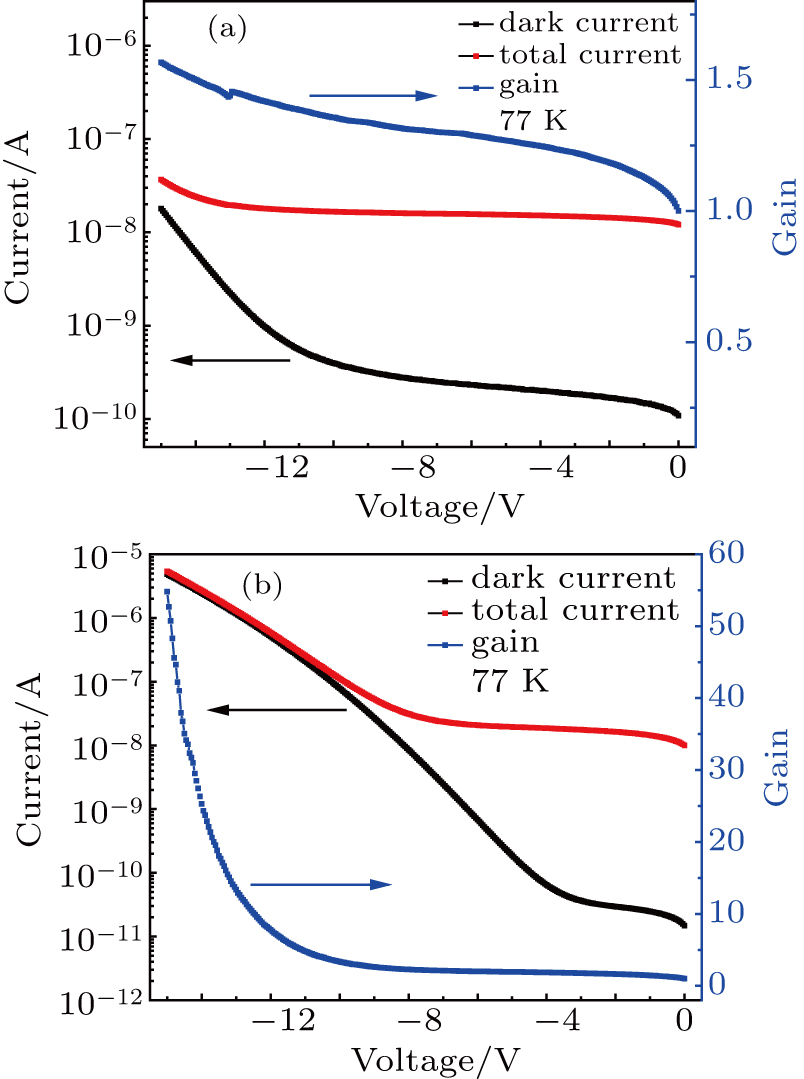
中国物理B ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 117301-.doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/aba2e0
Jia-Feng Liu(刘家丰)1,2, Ning-Tao Zhang(张宁涛)4, Yan Teng(滕)1,2, Xiu-Jun Hao(郝修军)2,3, Yu Zhao(赵宇)2, Ying Chen(陈影)1,2, He Zhu(朱赫)1,2, Hong Zhu(朱虹)1,2, Qi-Hua Wu(吴启花)2, Xin Li(李欣)2, Bai-Le Chen(陈佰乐)4,§, Yong Huang(黄勇)1,2,‡( )
)
Short-wavelength infrared InAs/GaSb superlattice hole avalanche photodiode
Jia-Feng Liu(刘家丰)1,2, †, Ning-Tao Zhang(张宁涛)4, †, Yan Teng(滕)1,2, Xiu-Jun Hao(郝修军)2,3, Yu Zhao(赵宇)2, Ying Chen(陈影)1,2, He Zhu(朱赫)1,2, Hong Zhu(朱虹)1,2, Qi-Hua Wu(吴启花)2, Xin Li(李欣)2, Bai-Le Chen(陈佰乐)4,§, and Yong Huang(黄勇)1,2,, ‡
- 1 School of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Key Laboratory of Nanodevices and Applications, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215123, China
3 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
4 School of Information Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China