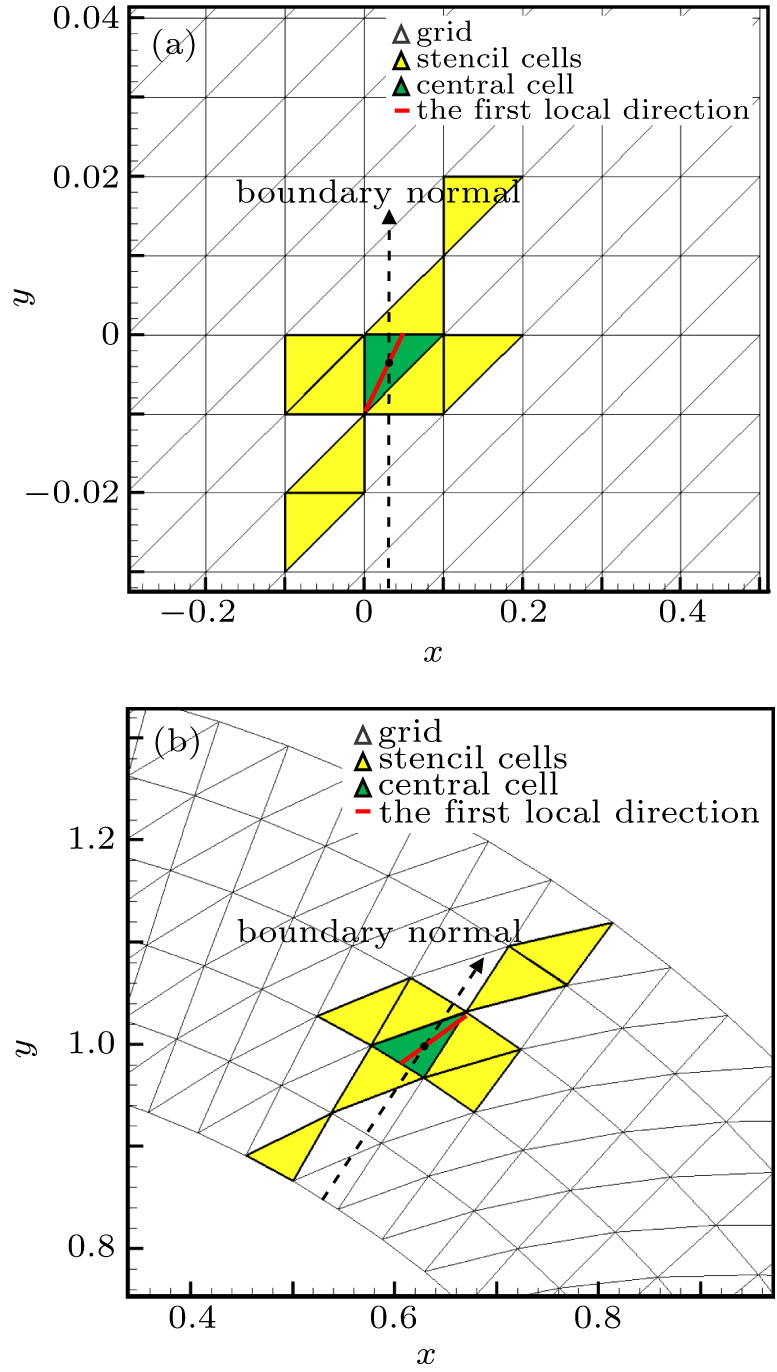
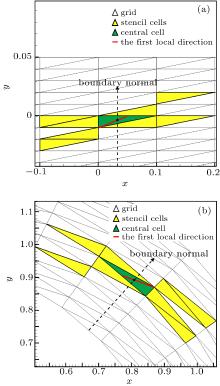
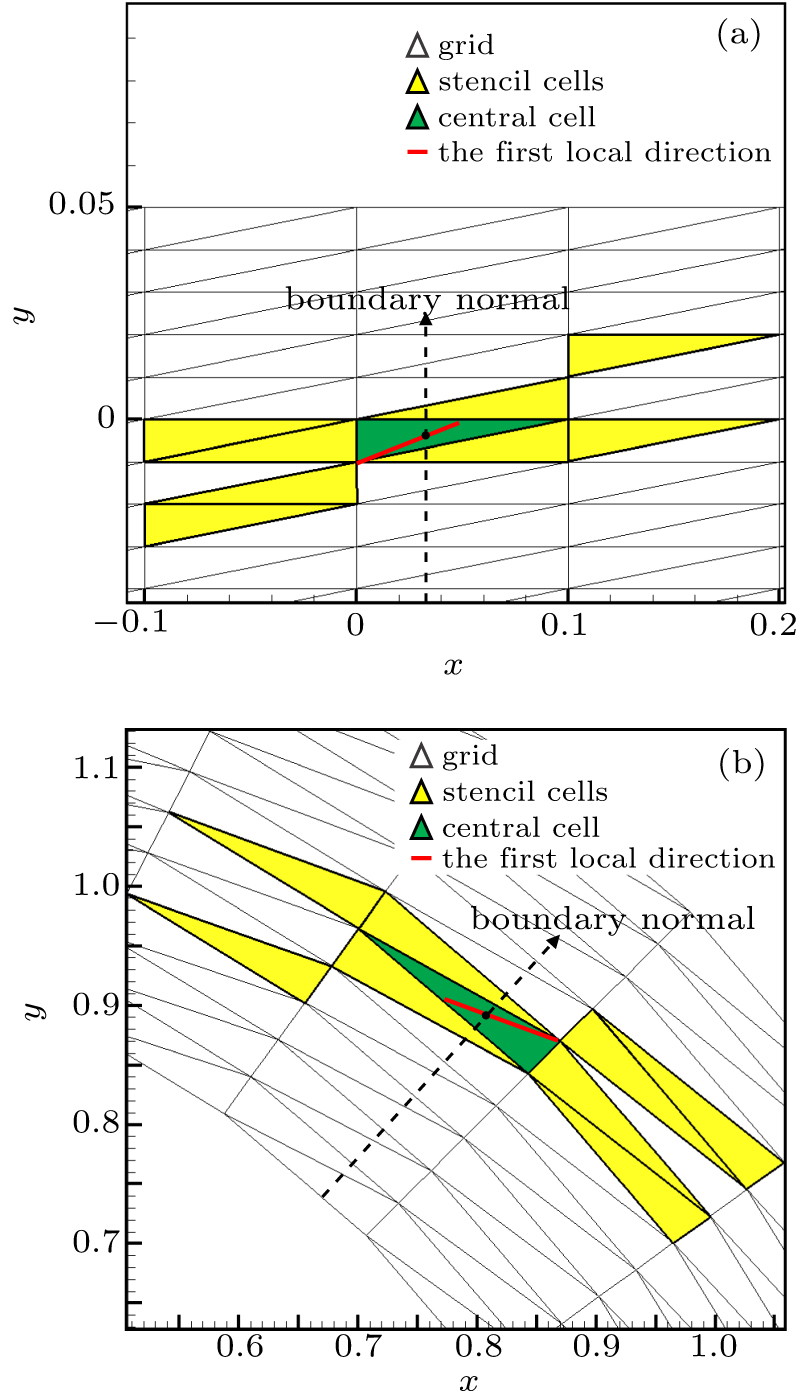
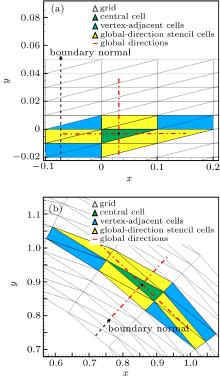
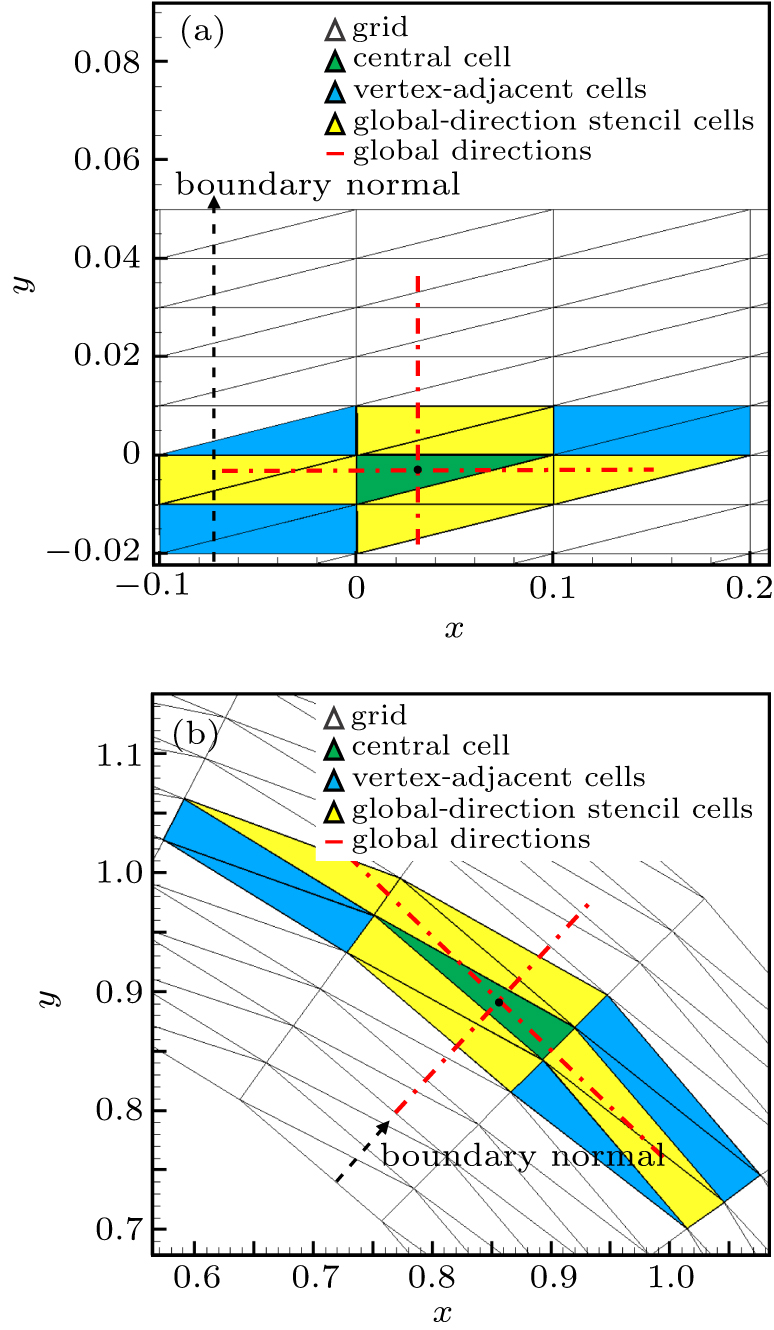
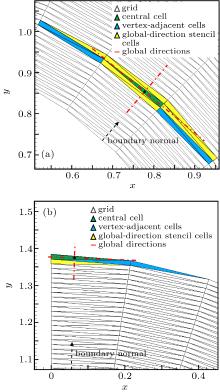
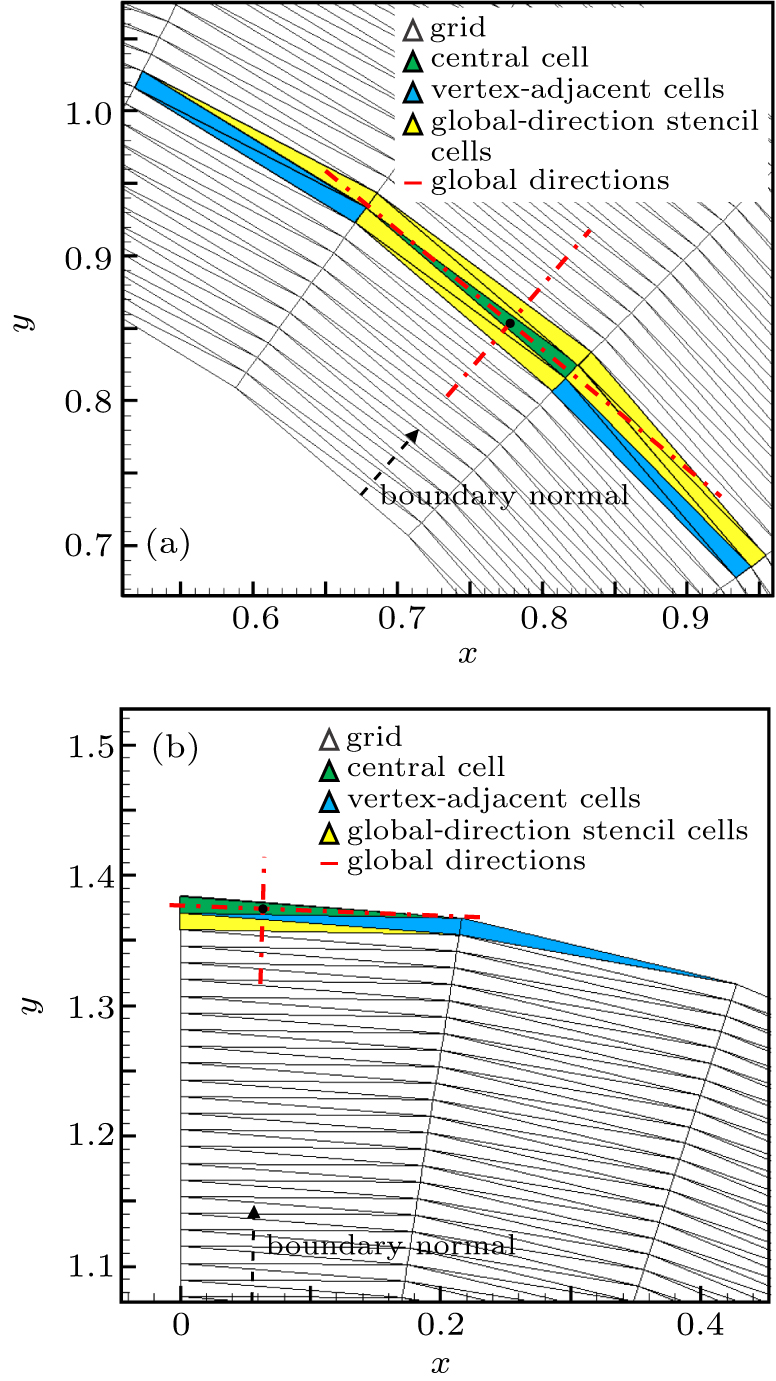
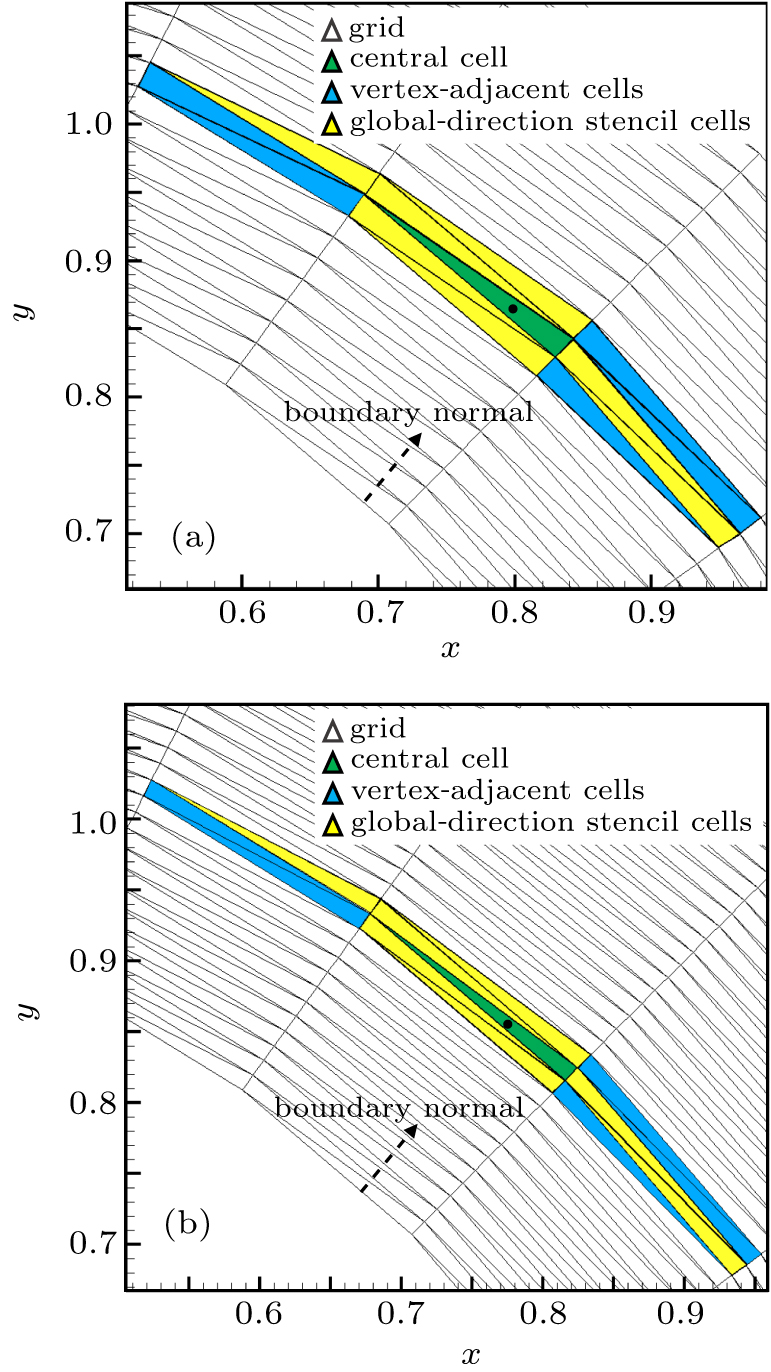
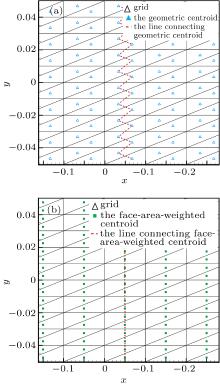
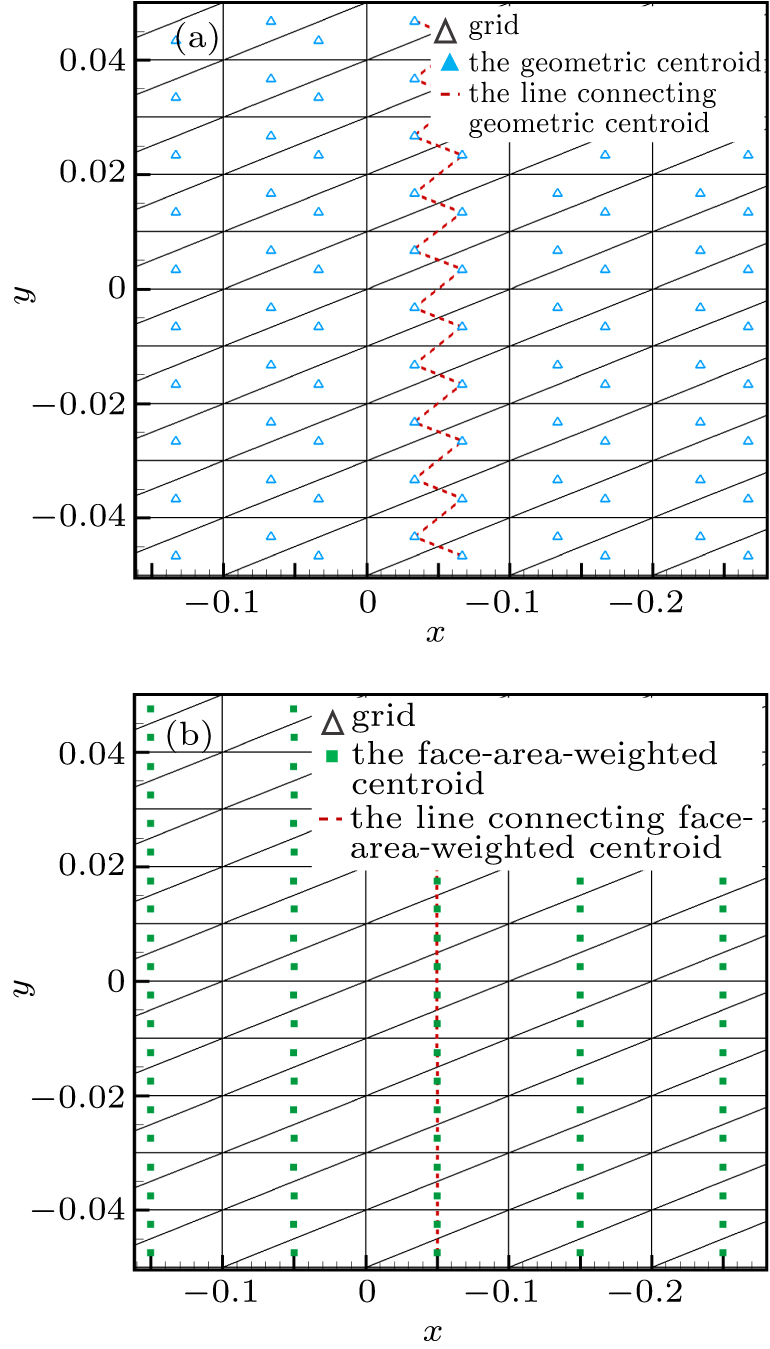
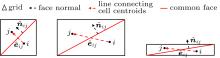
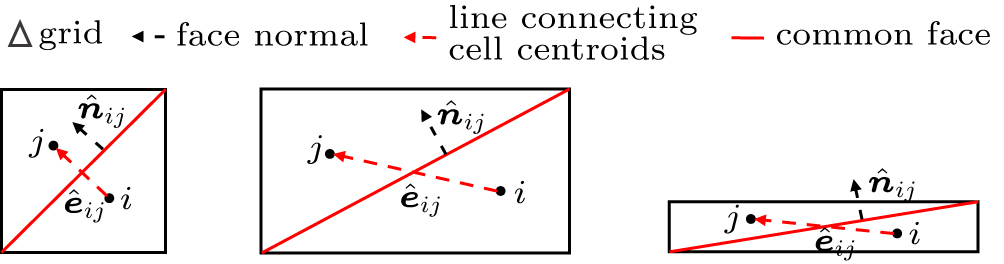
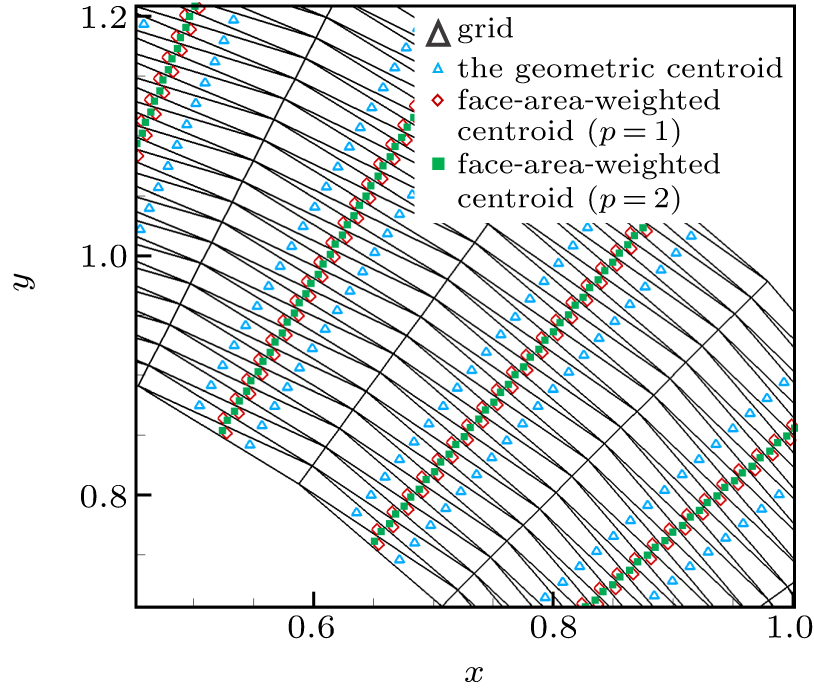
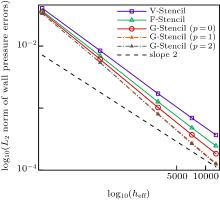
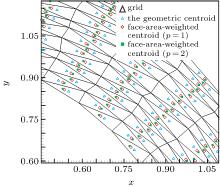
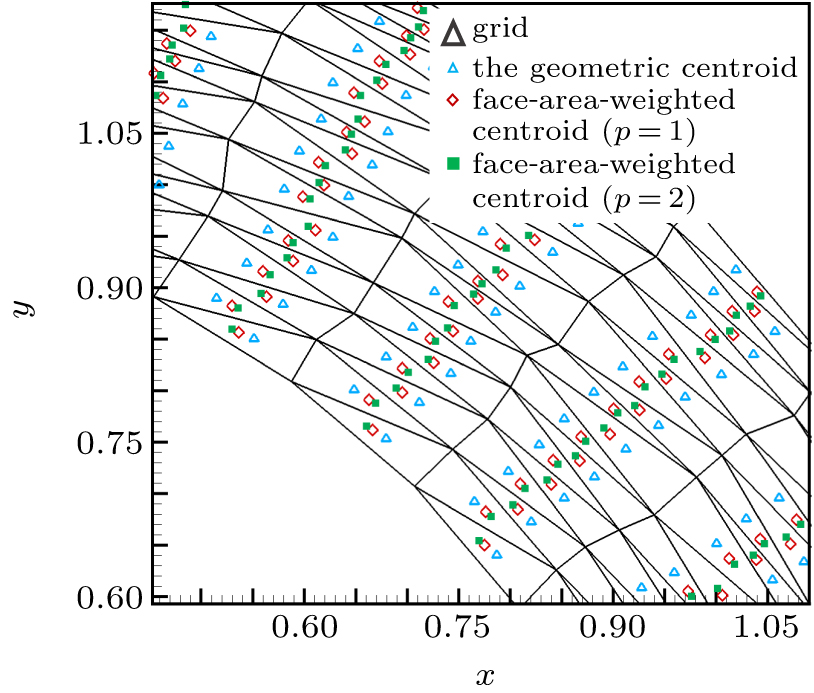
中国物理B ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 100203-.doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/aba2da
Ling-Fa Kong(孔令发)1, Yi-Dao Dong(董义道)1,†( ), Wei Liu(刘伟)1, Huai-Bao Zhang(张怀宝)2
), Wei Liu(刘伟)1, Huai-Bao Zhang(张怀宝)2
-
收稿日期:2020-03-04修回日期:2020-06-22接受日期:2020-07-06出版日期:2020-10-05发布日期:2020-10-05 -
通讯作者:Yi-Dao Dong(董义道)
An improved global-direction stencil based on the face-area-weighted centroid for the gradient reconstruction of unstructured finite volume methods
Ling-Fa Kong(孔令发)1, Yi-Dao Dong(董义道)1,†, Wei Liu(刘伟)1, and Huai-Bao Zhang(张怀宝)2
- 1
College of Aerospace Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology , Changsha 410073,China
2School of Physics, Sun Yat-sen University , Guangzhou 510275,China
-
Received:2020-03-04Revised:2020-06-22Accepted:2020-07-06Online:2020-10-05Published:2020-10-05 -
Contact:†Corresponding author. E-mail:tianyatingxiao@163.com -
About author:†Corresponding author. E-mail: tianyatingxiao@163.com* Project supported by the National Key Project, China (Grant No. GJXM92579).
中图分类号: (Numerical simulation; solution of equations)
- 02.60.Cb
引用本文
Ling-Fa Kong(孔令发), Yi-Dao Dong(董义道), Wei Liu(刘伟), Huai-Bao Zhang(张怀宝). [J]. 中国物理B, 2020, 29(10): 100203-.
Ling-Fa Kong(孔令发), Yi-Dao Dong(董义道)†, Wei Liu(刘伟), and Huai-Bao Zhang(张怀宝). An improved global-direction stencil based on the face-area-weighted centroid for the gradient reconstruction of unstructured finite volume methods[J]. Chin. Phys. B, 2020, 29(10): 100203-.
"
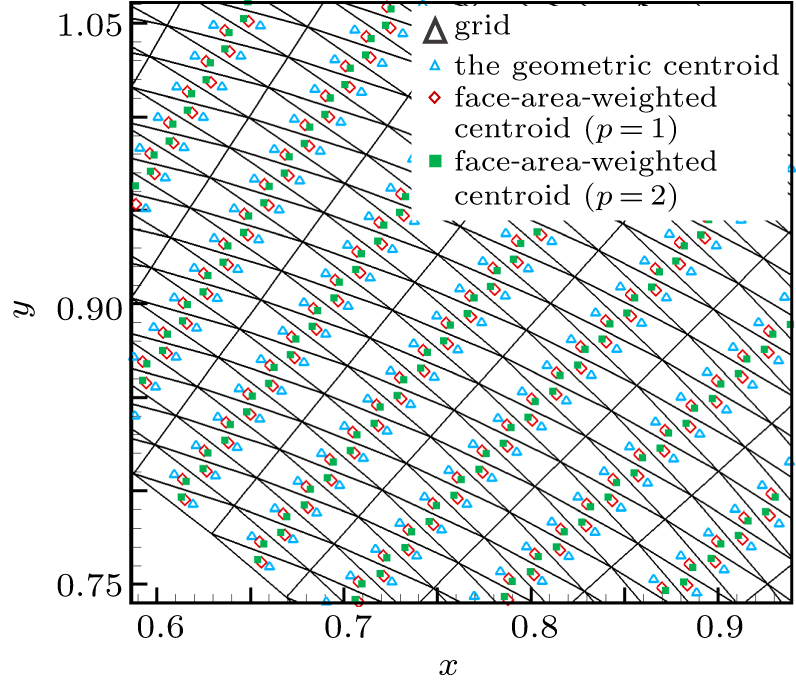
| Full name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
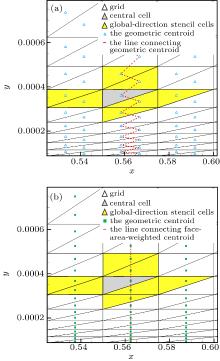
| Vertex-neighbor stencil | V-stencil |
| Face-neighbor stencil | F-stencil |
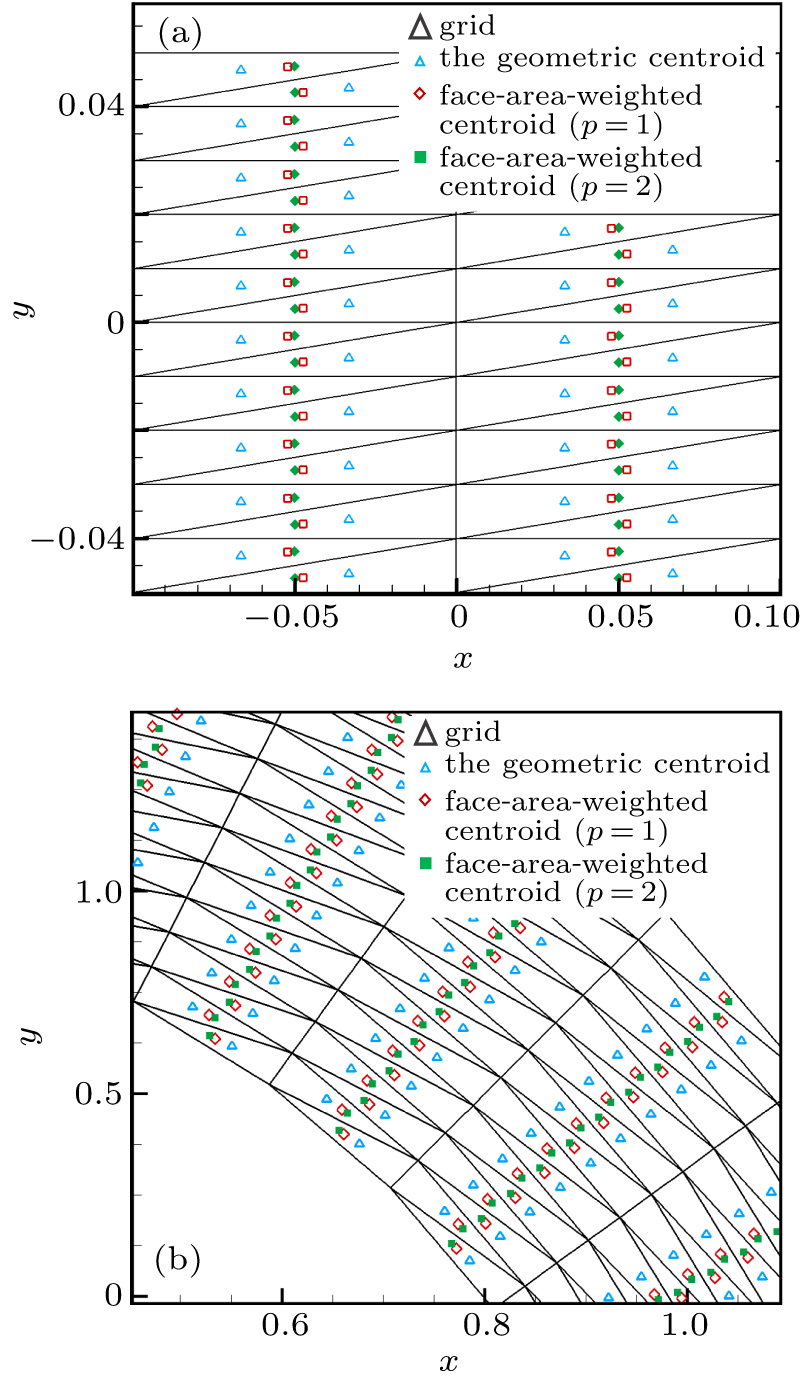
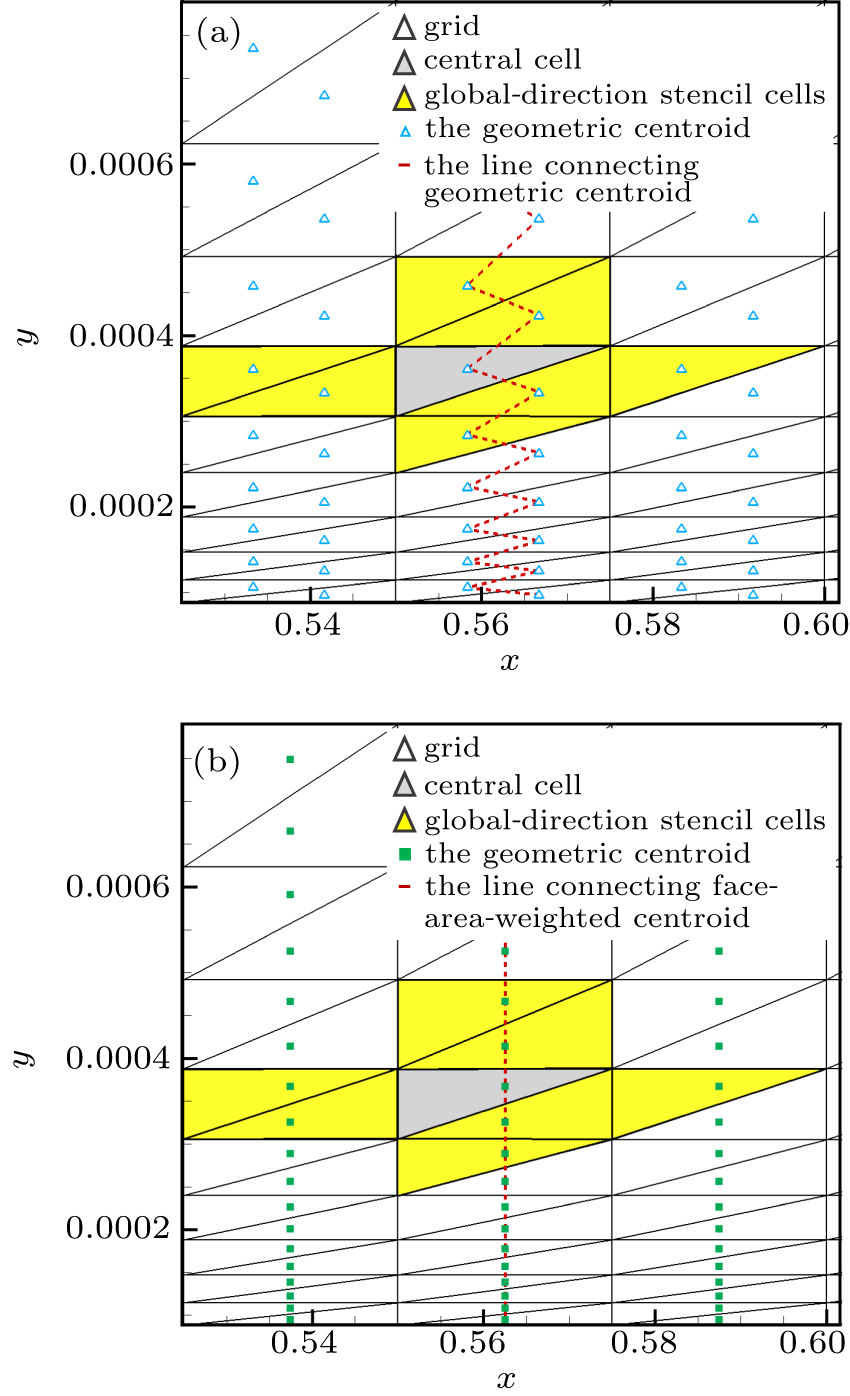
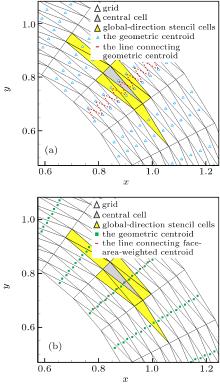
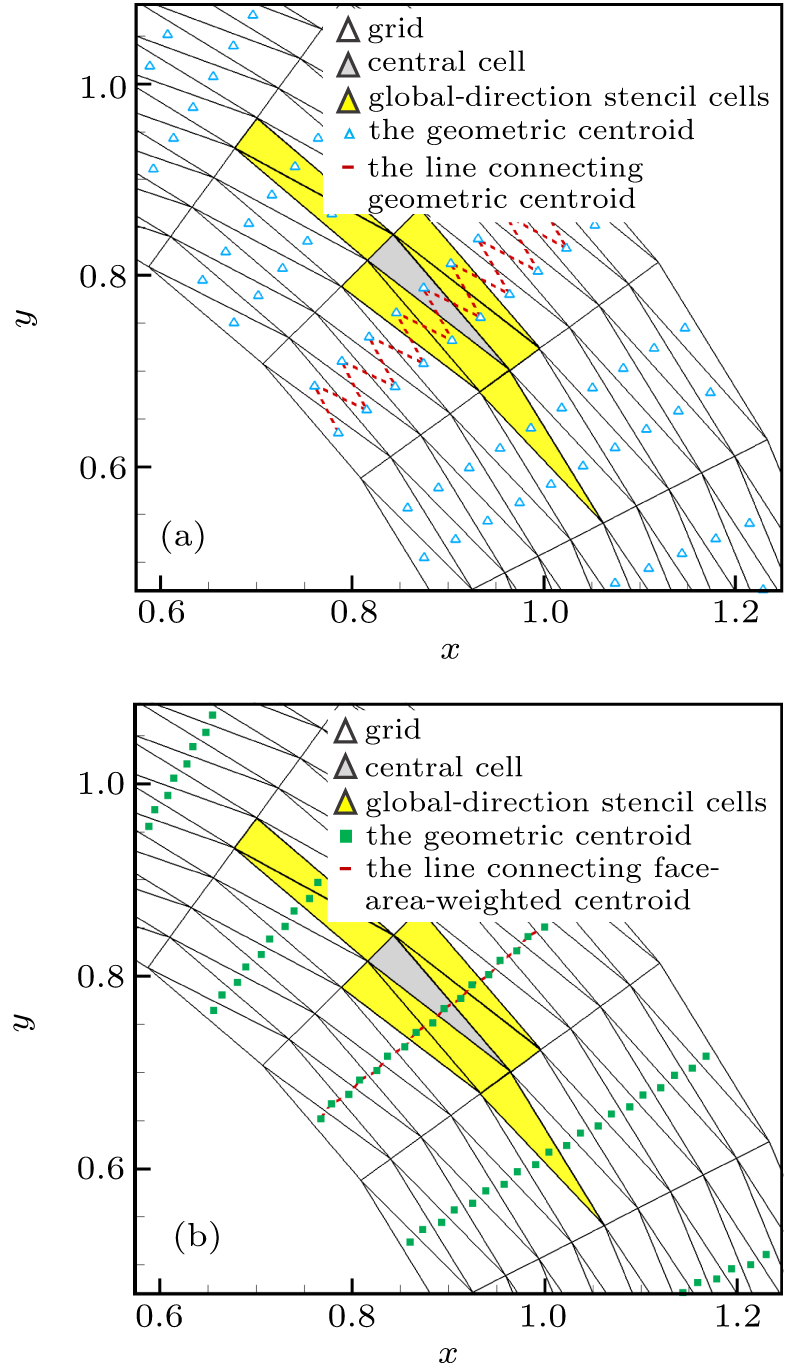
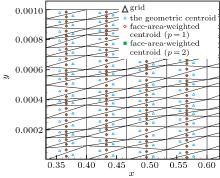
| Global-direction stencil with geometric centroid (i.e., p = 0) | G-stencil (p = 0) |
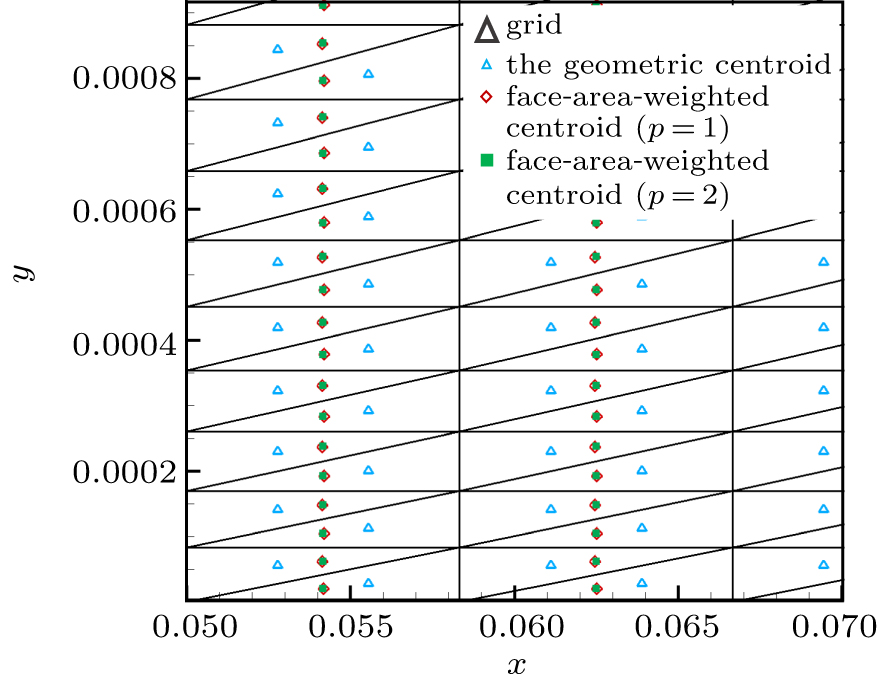
| Global-direction stencil with the face-area-weighted centroid and p = 1 | G-stencil (p = 1) |
| Global-direction stencil with the face-area-weighted centroid and p = 2 | G-stencil (p = 2) |
"
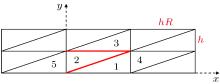
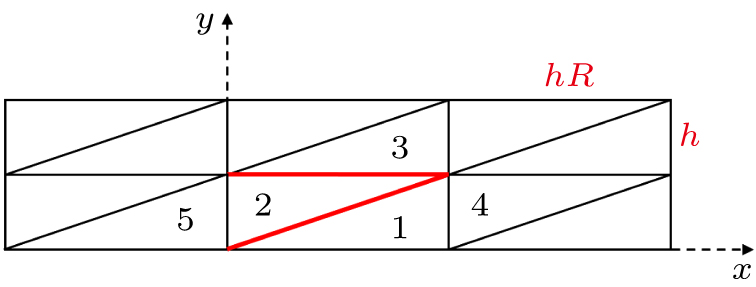
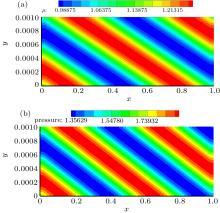
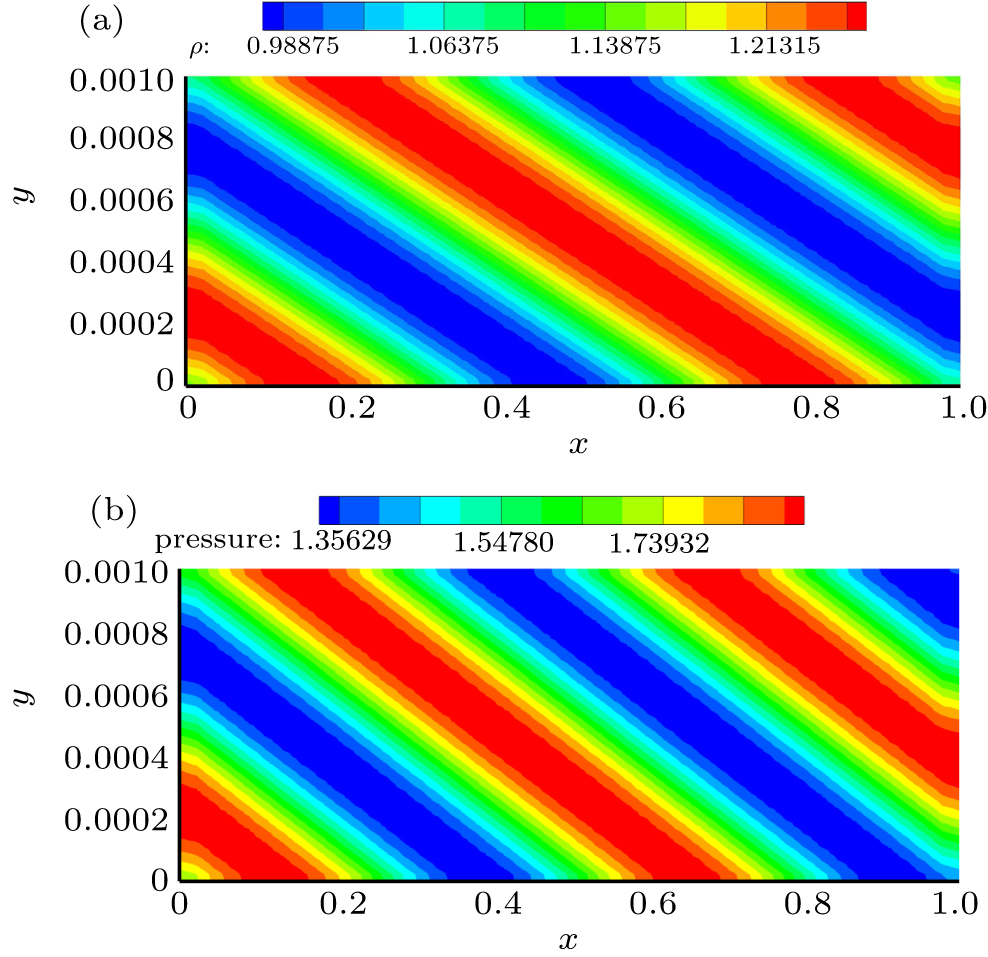
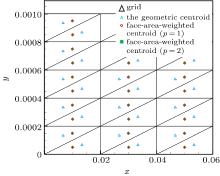
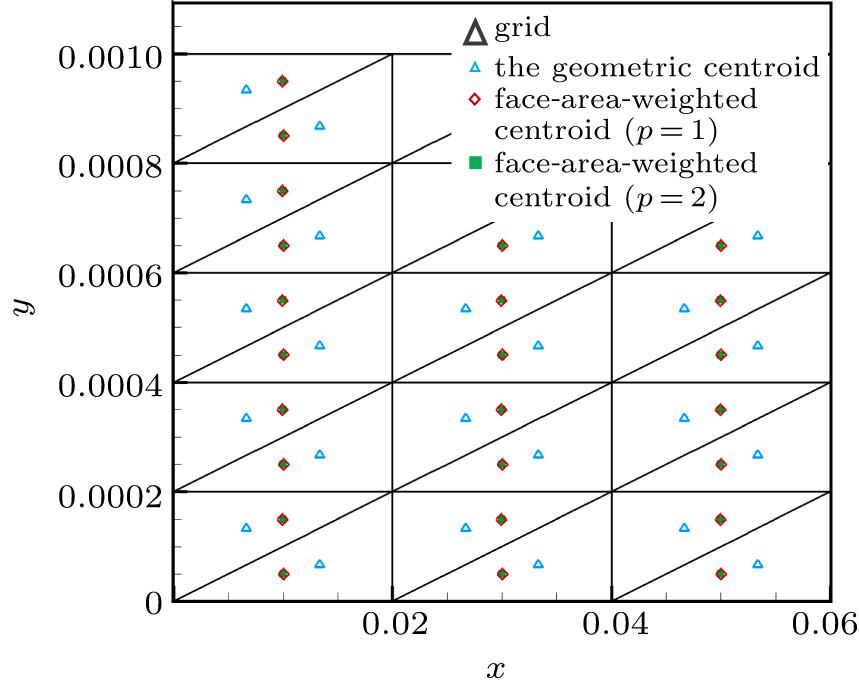
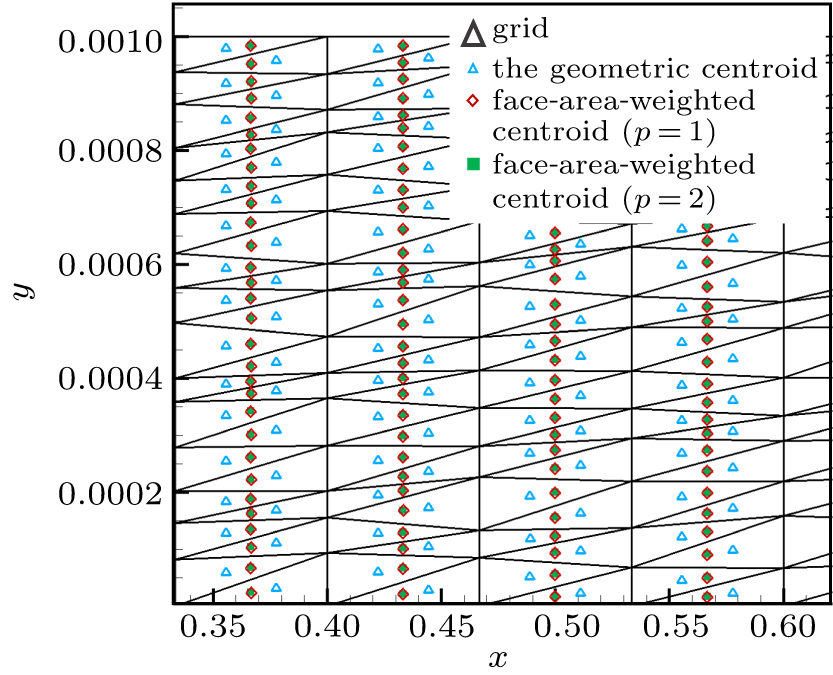
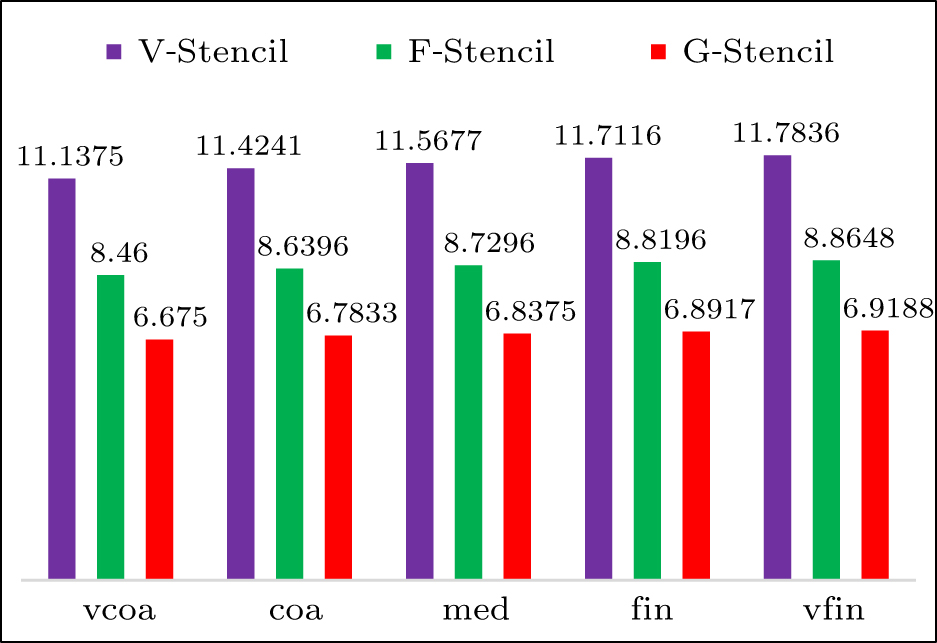
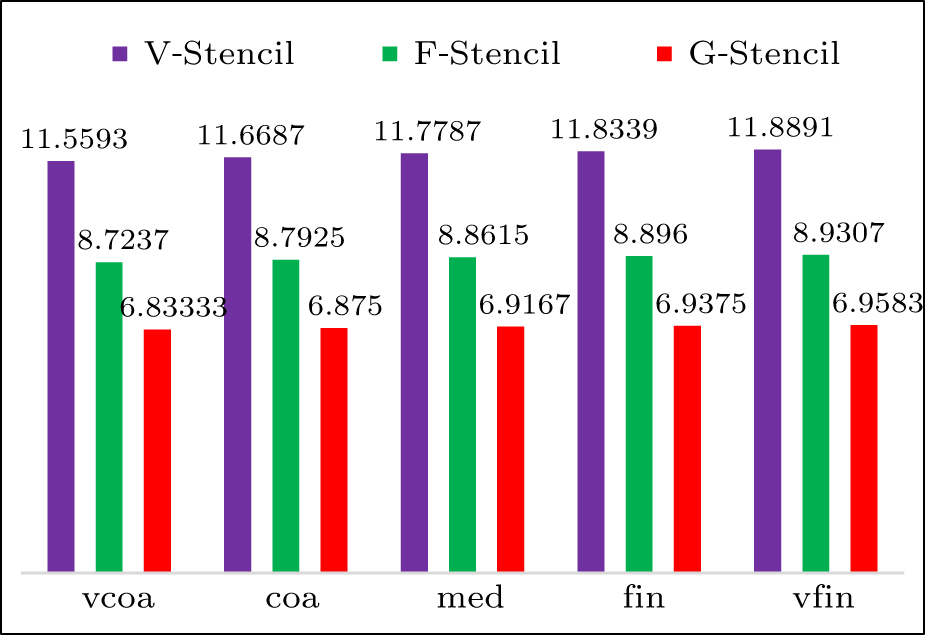
| Grid name | Distribution in x and x directions (x,y ∈ [0, 1] × [0, 0.001] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR = 102 | AR = 103 | AR = 104 | AR = 105 | |
| vcoa | 120 × 10 | 60 × 20 | 20 × 30 | 30 × 30 |
| coa | 180 × 15 | 90 × 30 | 30 × 45 | 45 × 45 |
| med | 240 × 20 | 120 × 40 | 40 × 60 | 60 × 60 |
| fin | 360 × 30 | 180 × 60 | 60 × 90 | 90 × 90 |
| vfin | 480 × 40 | 240 × 80 | 80 × 120 | 120 × 120 |
"
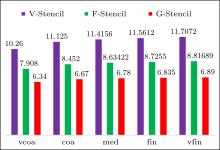
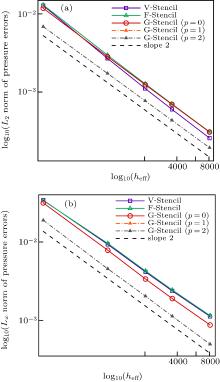
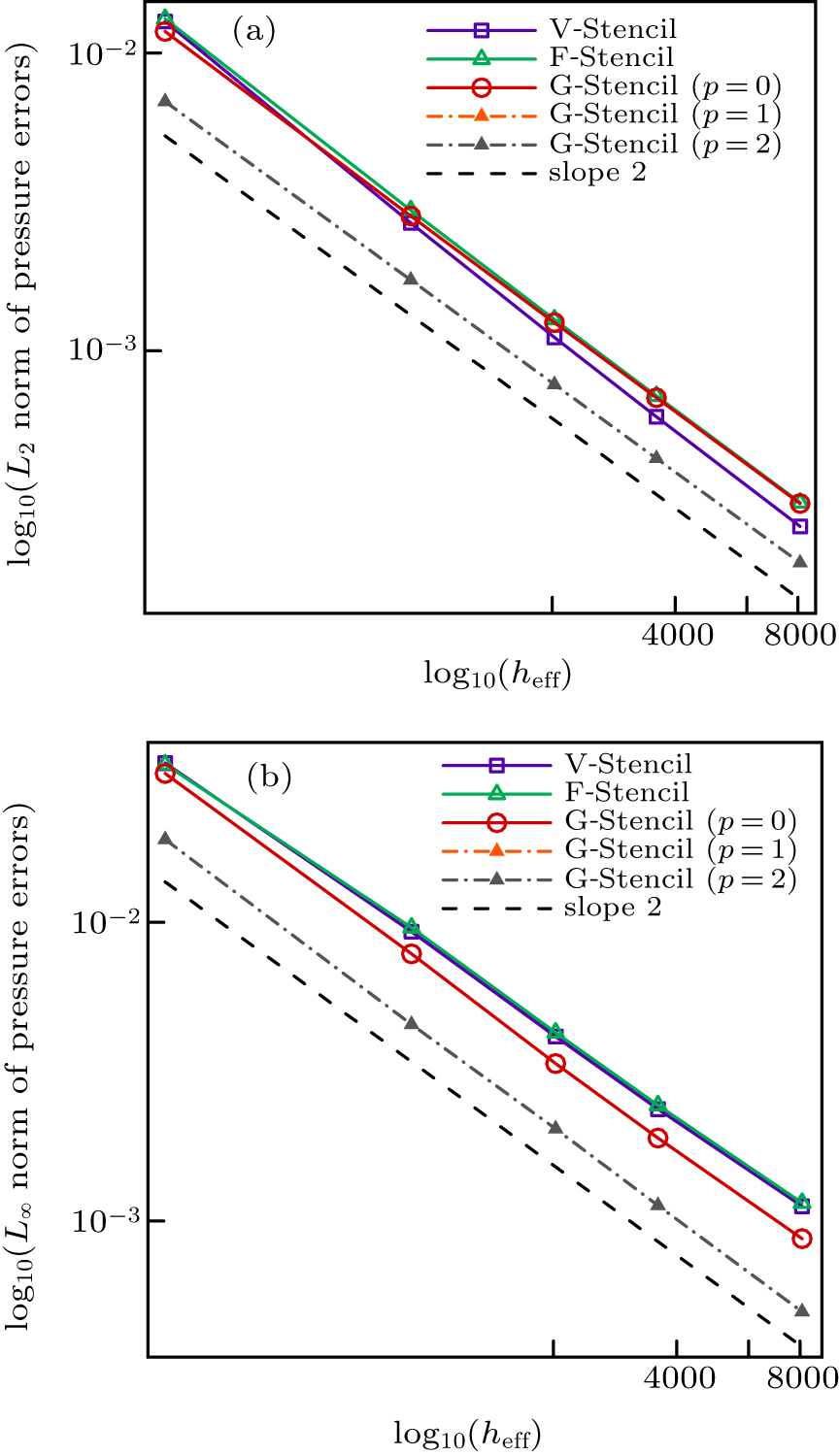
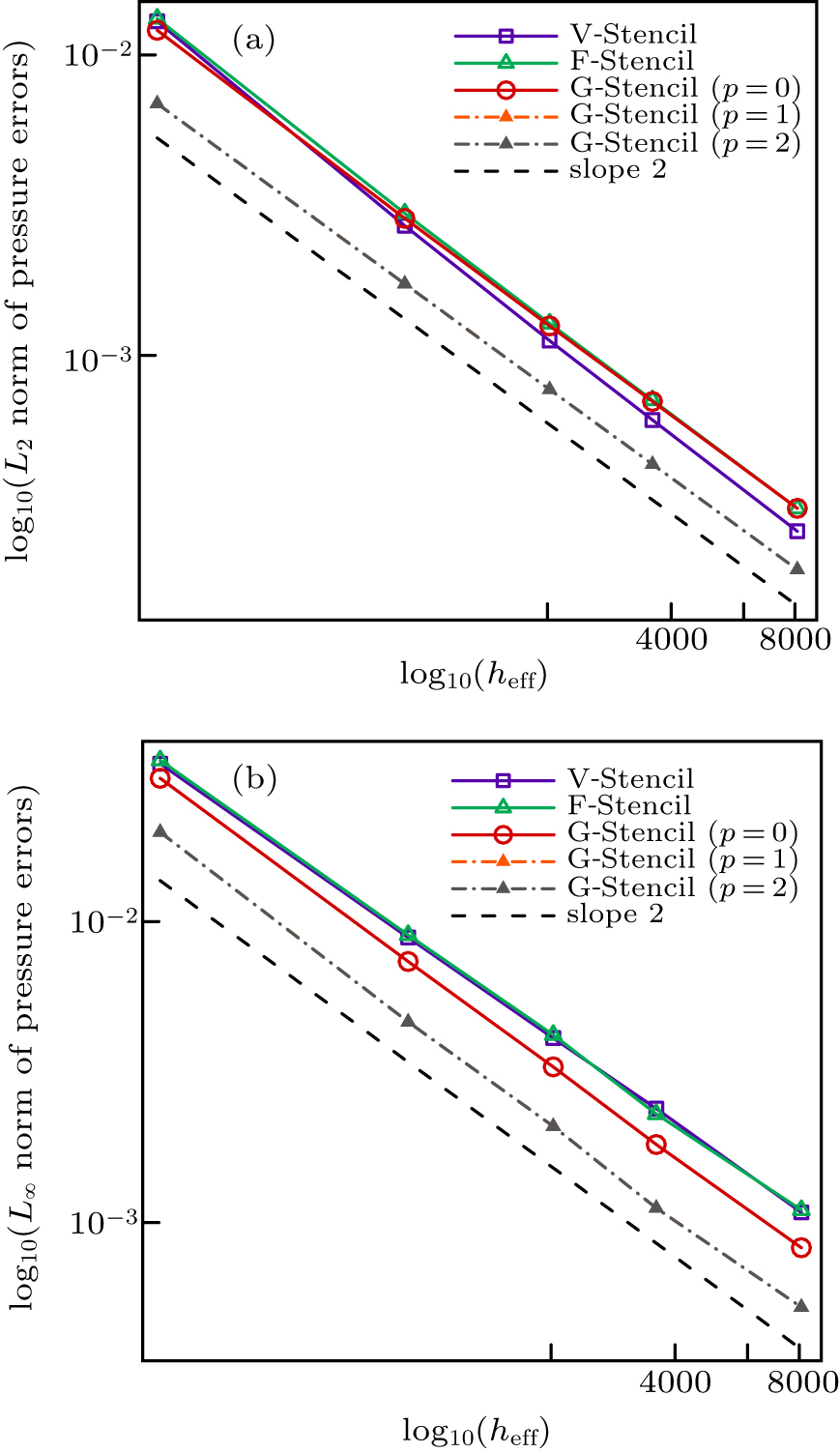
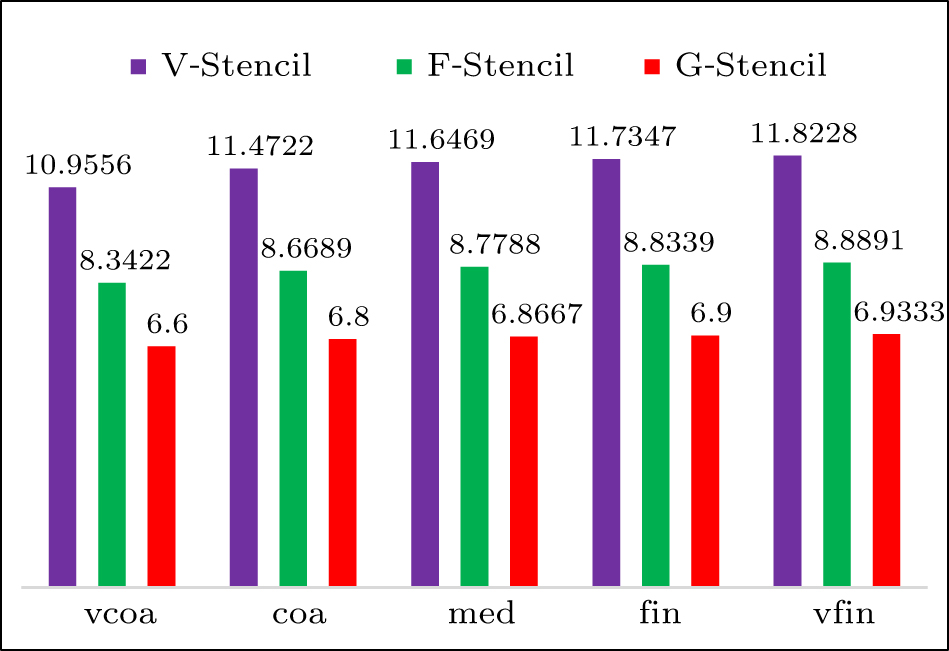
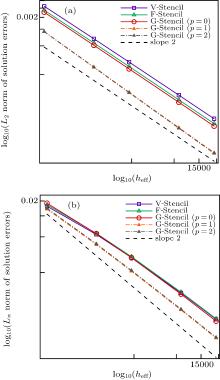
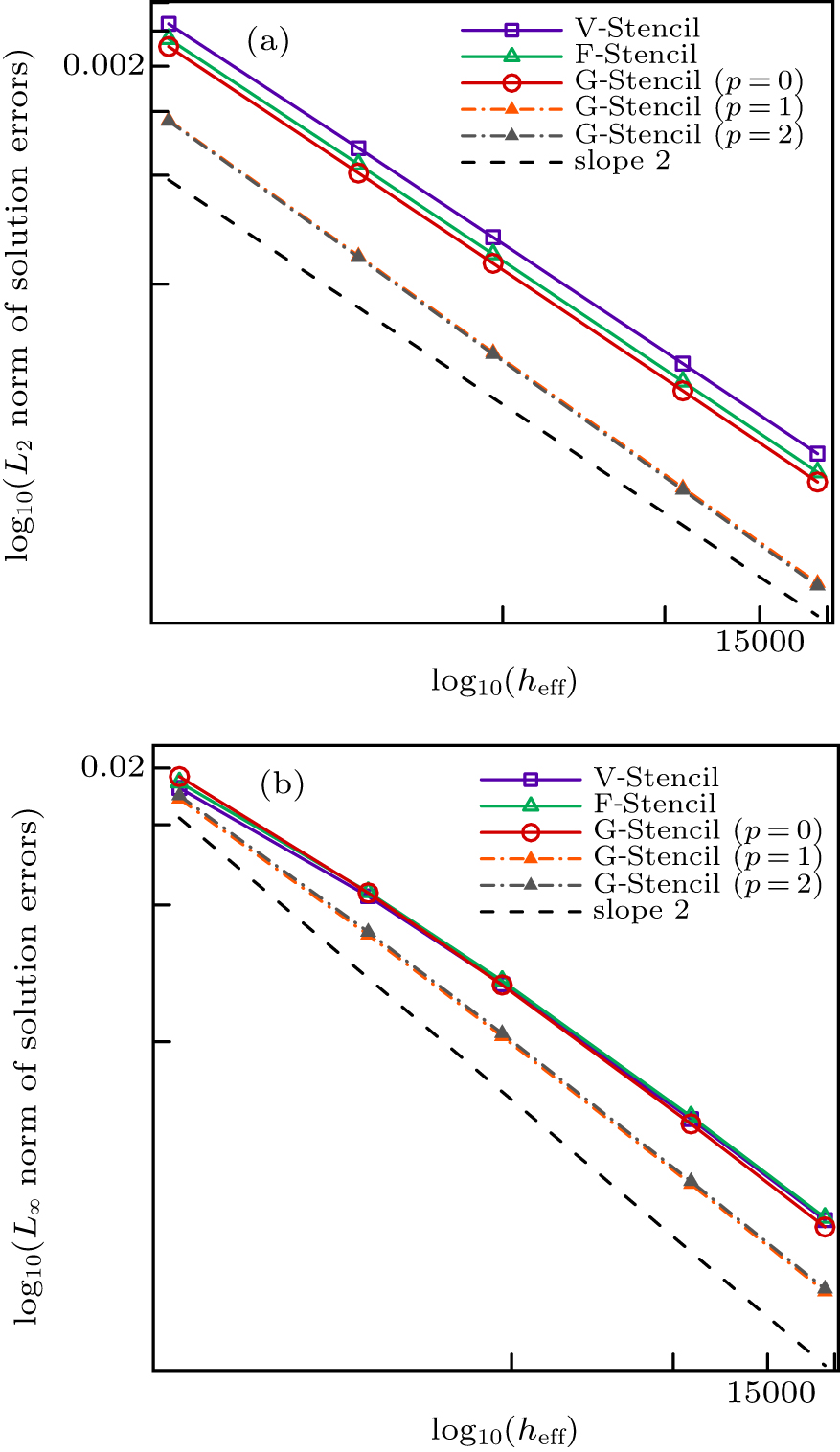
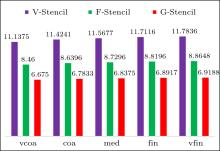
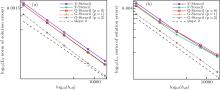
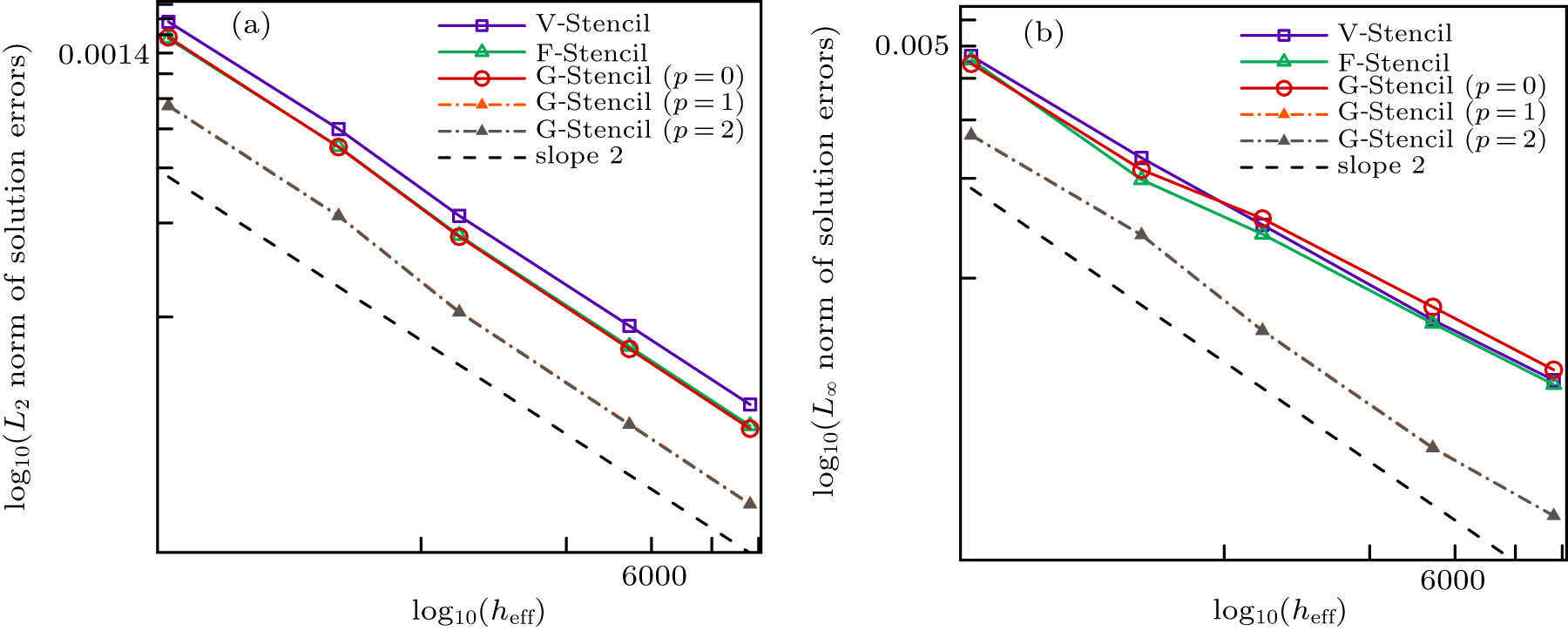
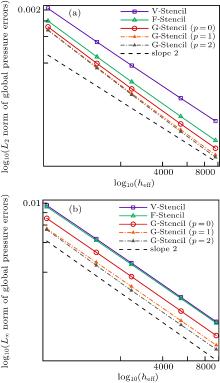
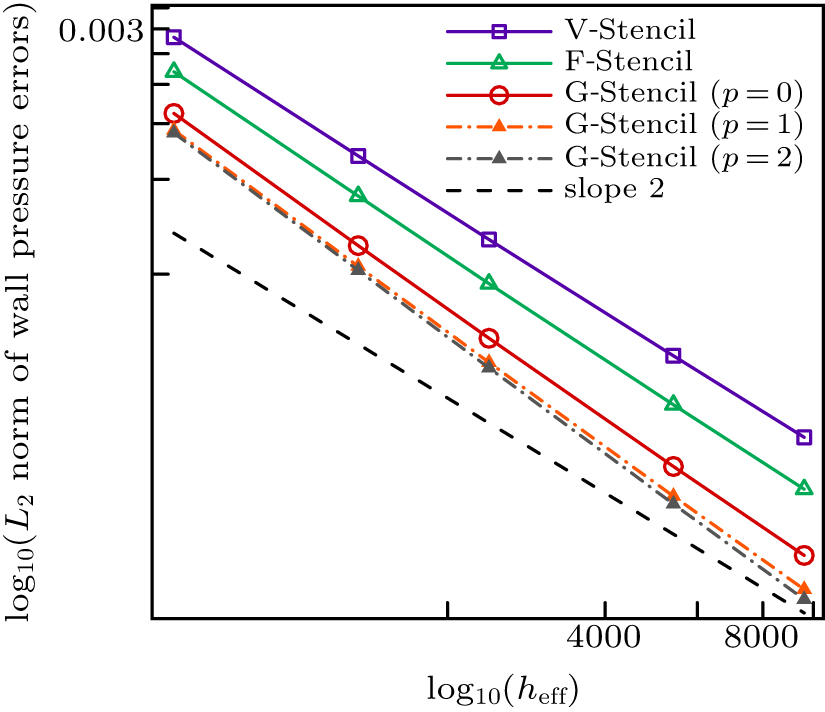
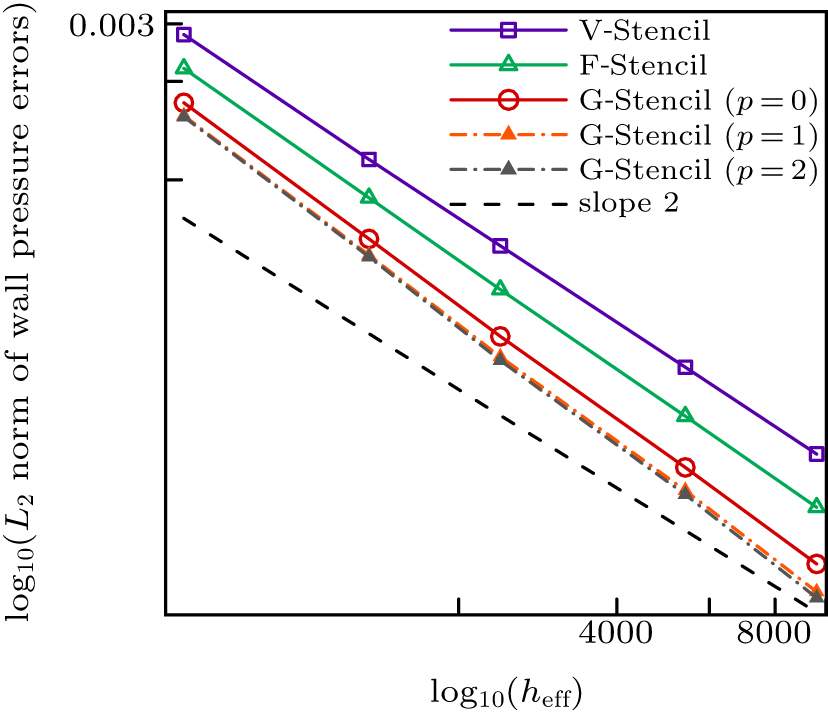
| Different stencils | L2 norm of global pressure errors | L∞ norm of global pressure errors | Average stencil size |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-stencil | 0.000109909 | 0.000631396 | 11.8339 |
| F-stencil | 0.000066257 | 0.000612726 | 8.896 |
| G-stencil (p = 0) | 0.0000541208 | 0.000457848 | 6.9375 |
| G-stencil (p = 1) | 0.0000454133 | 0.000366076 | 6.9375 |
| G-stencil (p = 2) | 0.0000427758 | 0.000331916 | 6.9375 |
"
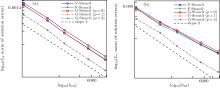
| Different stencils | L2 norm of global pressure errors | L∞ norm of global pressure errors | Average stencil size |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-stencil | 0.000261469 | 0.00144312 | 11.8008 |
| F-stencil | 0.00017859 | 0.00141231 | 8.87531 |
| G-stencil (p = 0) | 0.000151624 | 0.00112674 | 6.925 |
| G-stencil (p = 1) | 0.000128455 | 0.00085544 | 6.925 |
| G-stencil (p = 2) | 0.00012346 | 0.000787497 | 6.925 |
| [1] |
Mavriplis D J 1997 Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 29 473 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.29.1.473
|
| [2] |
Qin J X, Chen Y M, Deng X G 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 104701 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab3f26
|
| [3] |
Venkatakrishnan V 1996 AIAA J. 34 533 DOI: 10.2514/3.13101
|
| [4] |
Diskin B, Thomas J L 2011 AIAA J. 49 836 DOI: 10.2514/1.J050897
|
| [5] |
Diskin B, Thomas J L, Nielsen E J, Nishikawa H, White J A 2010 AIAA J. 48 1326 DOI: 10.2514/1.44940
|
| [6] |
Fu Z, Liu K X 2012 Chin. Phys. B 21 040202 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/4/040202
|
| [7] |
Sozer E, Brehm C, Kiris C C 2014 Proceedings of the 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting January 13–17, 2014 Convention Center Washington DC
|
| [8] |
Jameson A, Mavriplis D J 1986 AIAA J. 24 611 DOI: 10.2514/3.9315
|
| [9] |
Mavriplis D J 1988 AIAA J. 26 824 DOI: 10.2514/3.9975
|
| [10] |
Zhou Y F, Feng X S 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 094703 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/29/9/094703
|
| [11] |
Xiong M, Deng X G, Gao X, Dong Y D, Xu C F, Wang Z H 2018 Comput. Fluids 172 426 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2018.03.072
|
| [12] |
Veluri S P, Roy C J, Luke E A 2012 Comput. Fluids 70 59 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2012.04.028
|
| [13] |
Ghoreyshi M, Seidel J, Bergeron K, Jirasek A, Lofthouse A J, Cummings R M 2015 Proceedings of the 53rd Aerospace Sciences Meeting January 5–9, 2015 Kissimmee Florida
|
| [14] |
Kallinderis Y, Fotia S 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 280 465 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.09.036
|
| [15] |
Dannenhoffer J 2012 Proceedings of the 50th Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference January 9–12, 2012 Nashville Tennessee
|
| [16] |
Braaten M, Shyy W 1986 Numer. Heat Transfer B: Fundamentals 9 559 DOI: 10.1080/10407788608913493
|
| [17] |
Denner F, Wachem V, Berend G M 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 298 466 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.06.008
|
| [18] |
Zangeneh R, Ollivier-Gooch C F 2017 Comput. Fluids. 156 590 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2017.04.020
|
| [19] |
Veluri S P 2010 Code verification and numerical accuracy assessment for finite volume CFD codes Ph.D. Dissertation Blacksburg Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
|
| [20] |
Nishikawa H 2020 J. Comput. Phys. 401 109001 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.109001
|
| [21] |
Diskin B, Thomas J L 2007 NIA Report: Accuracy analysis for mixed-element finite-volume discretization schemes https://fun3d.larc.nasa.gov/papers/nia_2007_08.pdf
|
| [22] |
Barth T 1993 Proceedings of the 31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting January 11–14, 1993 Reno, Nevada
|
| [23] |
Ollivier-Gooch C F, Altena M V 2002 J. Comput. Phys. 181 729 DOI: 10.1006/jcph.2002.7159
|
| [24] |
Sejekan C B, Ollivier-Gooch C F 2016 Comput. Fluids 139 216 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.08.002
|
| [25] |
Loseille A, Dervieux A, Alauzet F 2010 J. Comput. Phys. 229 2866 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2009.12.021
|
| [26] |
Toro E 1999 Riemann Solvers and Numerical Method for Fluid Dynamics - A Practical Introduction Berlin Springer 2
|
| [27] |
Barth T, Jespersen D 1989 Proceedings of the 27th Aerospace Sciences Meeting January 8–12, 1989 Reno, Nevada
|
| [28] |
Roe P L 1986 Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 18 337 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.fl.18.010186.002005
|
| [29] |
Jalali A, Ollivier-Gooch C F 2017 Comput. Fluids 143 32 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.11.004
|
| [30] |
Roy C J 2005 J. Comput. Phys. 205 131 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2004.10.036
|
| [31] |
Katz A, Sankaran V 2011 J. Comput. Phys. 230 7670 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.06.023
|
| [32] |
Roache P J 2002 J. Fluids. Eng. 124 4 DOI: 10.1115/1.1436090
|
| [33] |
Park M A, Barral N, Ibanez D, Kamenetskiy D S, Krakos J A, Michal T R, Loseille A 2018 Proceedings of the 56th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting January 8–10, 2018 Kissimmee, Florida
|
| [34] |
Dong Y D, Deng X G, Gao X, Xiong M, Wang G X 2018 Comput. Fluids 172 284 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2018.04.031
|
| [35] |
Krivodonova L, Berger M 2006 J. Comput. Phys. 211 492 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.05.029
|
| [36] |
Gerolymos L, Senechal M, Vallet I 2009 J. Comput. Phys. 228 8481 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2009.07.039
|
| [1] | Qi Wang(王琦), Fei-Fan Zhu(朱非凡), Rui Li(李瑞), Shi-Jie Zhang(张世杰), and Da-Wei Zhang(张大伟). Bidirectional visible light absorber based on nanodisk arrays[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(3): 30205-030205. |
| [2] | Ming-Jing Du(杜明婧), Bao-Jun Sun(孙宝军), and Ge Kai(凯歌). Adaptive multi-step piecewise interpolation reproducing kernel method for solving the nonlinear time-fractional partial differential equation arising from financial economics[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(3): 30202-030202. |
| [3] | Xin Cheng(程鑫), Xiu-Juan Lu(鲁秀娟), Ya-Nan Liu(刘亚楠), and Sen Kuang(匡森). Comparison of differential evolution, particle swarm optimization, quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization, and quantum evolutionary algorithm for preparation of quantum states[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(2): 20202-020202. |
| [4] | Beibei Zhu(朱贝贝), Lun Ji(纪伦), Aiqing Zhu(祝爱卿), and Yifa Tang(唐贻发). Explicit K-symplectic methods for nonseparable non-canonical Hamiltonian systems[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(2): 20204-020204. |
| [5] | Gang Zhang(张刚), Yu-Jie Zeng(曾玉洁), and Zhong-Jun Jiang(蒋忠均). Characteristics of piecewise linear symmetric tri-stable stochastic resonance system and its application under different noises[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(8): 80502-080502. |
| [6] | Jia-Rong Ye(叶家容), Wei-Shen Huang(黄伟深), and Xiu-Jun Fu(傅秀军). Substitutions of vertex configuration of Ammann-Beenker tiling in framework of Ammann lines[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(8): 86101-086101. |
| [7] | Li-Fang He(贺利芳), Qiu-Ling Liu(刘秋玲), and Tian-Qi Zhang(张天骐). Research and application of stochastic resonance in quad-stable potential system[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(7): 70503-070503. |
| [8] | Jinlian Jiang(姜金连), Wei Xu(徐伟), Ping Han(韩平), and Lizhi Niu(牛立志). Most probable transition paths in eutrophicated lake ecosystem under Gaussian white noise and periodic force[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(6): 60203-060203. |
| [9] | Yun-Xian Pei(裴云仙), Xue-Lan Zhang(张雪岚), Lian-Cun Zheng(郑连存), and Xin-Zi Wang(王鑫子). Coupled flow and heat transfer of power-law nanofluids on non-isothermal rough rotary disk subjected to magnetic field[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(6): 64402-064402. |
| [10] | Li-Jun Chang(常莉君), Yi-Fan Mo(莫一凡), Li-Ming Ling(凌黎明), and De-Lu Zeng(曾德炉). Data-driven parity-time-symmetric vector rogue wave solutions of multi-component nonlinear Schrödinger equation[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(6): 60201-060201. |
| [11] | Xian-Li Sun(孙先莉), You-Guo Wang(王友国), and Lin-Qing Cang(仓林青). Correlation and trust mechanism-based rumor propagation model in complex social networks[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(5): 50202-050202. |
| [12] | Kun Zheng(郑坤), Yu Miao(缪宇), Tong Li(李通), Shuang-Long Yang(杨双龙), Li Xi(席力), Yang Yang(杨洋), Dun Zhao(赵敦), and De-Sheng Xue(薛德胜). Anti-function solution of uniaxial anisotropic Stoner-Wohlfarth model[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(4): 40202-040202. |
| [13] | Qi Wang(王琦), Rui Li(李瑞), Xu-Feng Gao(高旭峰), Shi-Jie Zhang(张世杰), Rui-Jin Hong(洪瑞金), Bang-Lian Xu(徐邦联), and Da-Wei Zhang(张大伟). Ultra-broadband absorber based on cascaded nanodisk arrays[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(4): 40203-040203. |
| [14] | Chao Yan(颜超), Jing Feng(冯径), Ping-Lv Yang(杨平吕), and Si-Xun Huang(黄思训). A new algorithm for reconstructing the three-dimensional flow field of the oceanic mesoscale eddy[J]. 中国物理B, 2021, 30(12): 120204-120204. |
| [15] | Jing-Wei Sun(孙竟巍), Xu Qian(钱旭), Hong Zhang(张弘), and Song-He Song(宋松和). Novel energy dissipative method on the adaptive spatial discretization for the Allen-Cahn equation[J]. 中国物理B, 2021, 30(7): 70201-070201. |
|
||