|
Ke Zhi-Jin1, 2, Wang Yi-Tao1, 2, Yu Shang1, 2, Liu Wei1, 2, Meng Yu1, 2, Li Zhi-Peng1, 2, Wang Hang1, 2, Li Qiang1, 2, Xu Jin-Shi1, 2, Xiao Ya3, Tang Jian-Shun1, 2, †, Li Chuan-Feng1, 2, ‡, Guo Guang-Can1, 2
|
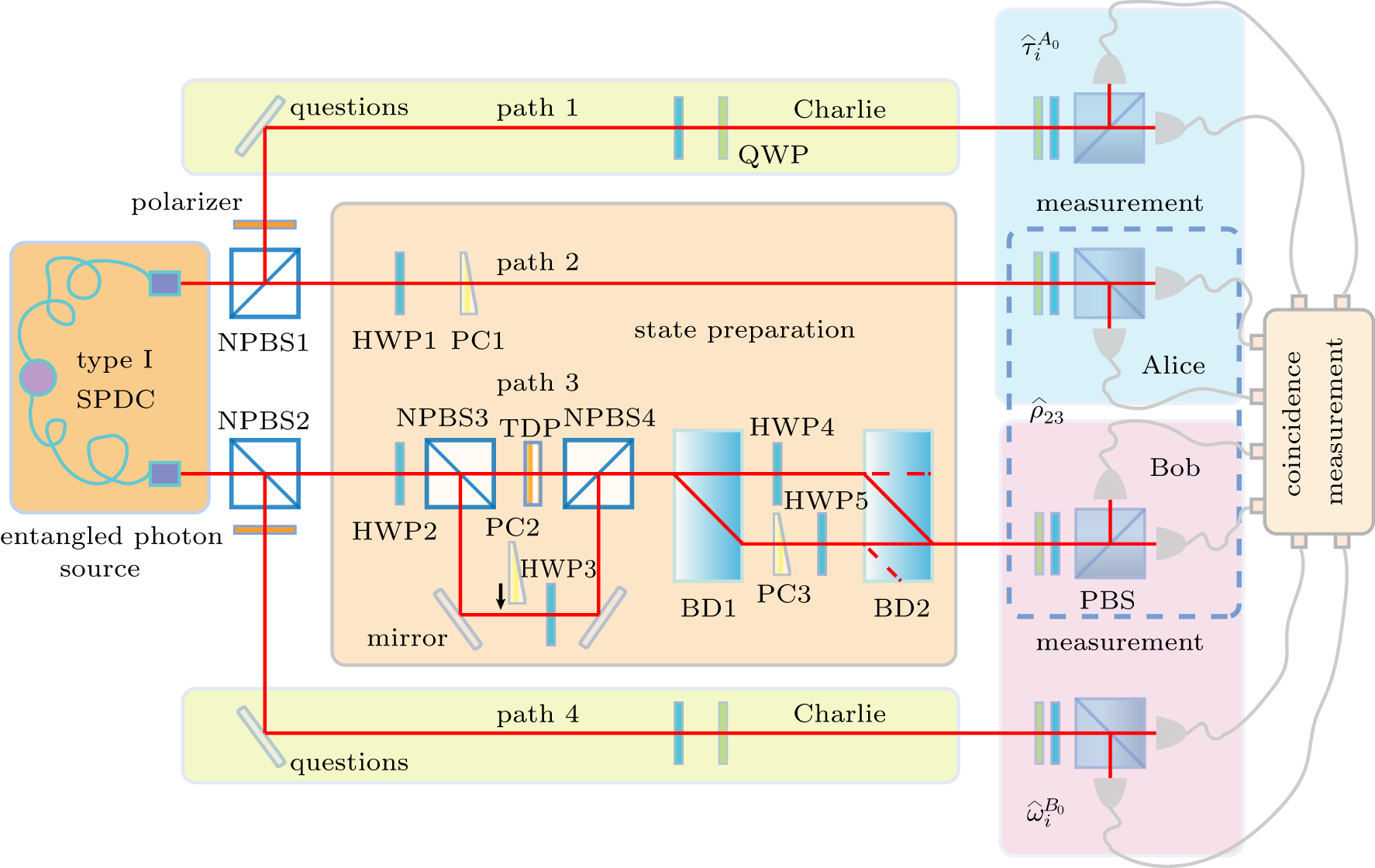
Experimental setup for MDI-UEW. The original entangled photon pairs are generated by type-I SPDC in two 2-mm BBO crystals with the form of
12(|HV〉+eiϕ|VV〉)
. The reflected parts of non-polarizing beam splitters NPBS1 and NPBS2 are used as question states. The transmitted parts of NPBS1 and NPBS2 are used to prepare
ρ^AB
. By selecting a suitable phase compensator PC1, |Φ+〉 or |Φ−〉 can be prepared. When half wave-plate HWP2 is set at an angle of 45°, and HWP1 is set at an angle of 0°, |Ψ+〉, |Ψ−〉 can be prepared. The bypath of NPBS3 is used to prepare the second Bell state component in the Bell diagonal state. HWP4 and HWP5 are used to change the ratio between H-polarization and V-polarization in |Φ+〉, then a redundant amount of H- or V-polarization will be discarded when passing through beam displacer BD2. Then states cos θ|HH〉 + sin θ|VV 〉 are prepared. Wave-plate combinations in path 1 and path 4 are used to rotate the polarizations to encode photons 1 and 4 to the desired question states,
τ^iA0
and
ω^iB0
. The measurement part consists of four QWP-HWP-PBS combinations, where QWP and PBS denoting quarter wave-plate and polarizing beam splitter, respectively. All the four photons are separately detected by single-photon avalanche diodes, but the four-photon events are coincidently counted together and analyzed by a picosecond time analyzer with well-tuned delays. |