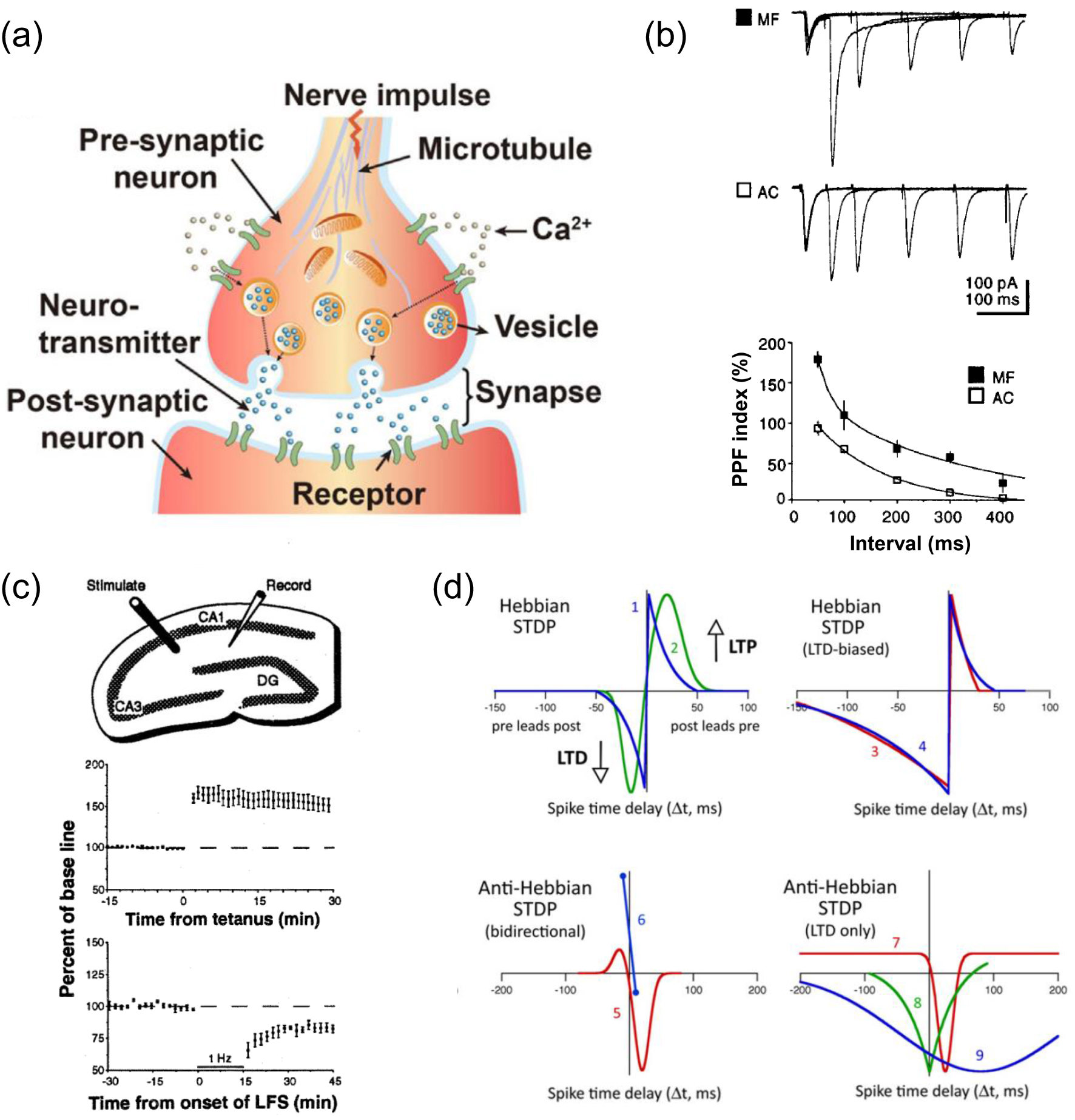
(a) A Schematic illustration of biological synaptic transmission. Signals are transmitted from the pre-synaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron via the neurotransmitter. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [61]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier Ltd. (b) PPF of a mossy fiber (MF) synapse and a assoc/com (AC) synapse. Current traces: superimposed sweeps with five different interstimulus intervals. The graph shows the average PPF index plotted against interstimulus intervals. The points for the AC synapse were fitted with a single exponential (t = 133 ms), while the points for the MF synapses were fitted with a double exponential (t1 = 27 ms, t2 = 301 ms). Adapted with permission from Ref. [59]. Copyright 1996, National Academy of Sciences. (c) Experiments illustrating NMDAR-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression of hippocampal CA1 synapses. Top: configuration of stimulation and recording. Middle: average change of the response magnitude after high-frequecny (e.g., 100 Hz) stimulations. Bottom: average change of the response magnitude after low-frequency (e.g., 1 Hz) stimulations. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [62]. Copyright 1993, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (d) Typical forms of STDP indicated by nine different curves. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [63]. Copyright 2012, Elsevier Ltd. |