An artificial synapse by superlattice-like phase-change material for low-power brain-inspired computing
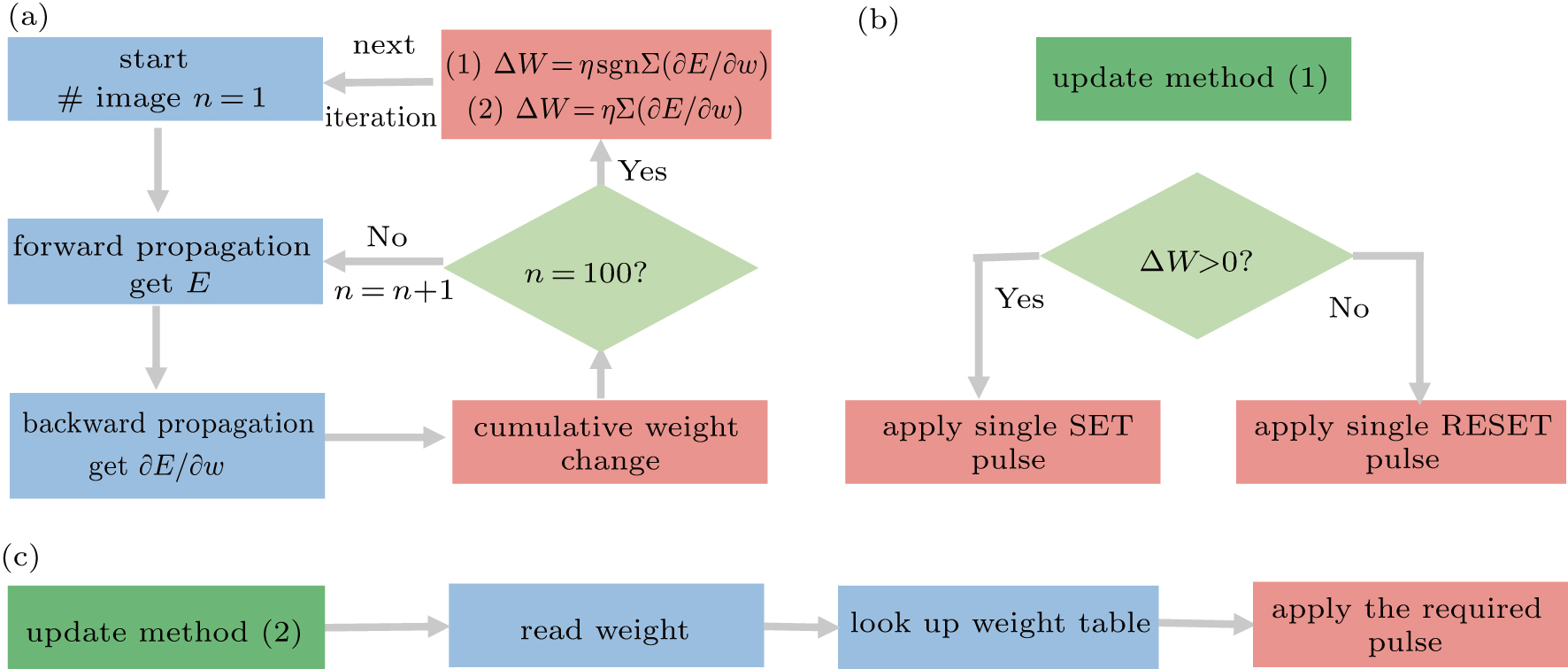
Part of the training process flow chart and schematic diagram of two types of weight update methods. (a) The steps in the blue box mainly use the resistance characteristics of the device to reflect synaptic efficacy. Weight updates in the red box take advantage of the device’s resistive state transition to reflect synaptic plasticity, where E is the loss function in the back-propagation algorithm. (b) The update method 1 corresponds to the weight data of Figs.