Influence of fluoroethylene carbonate on the solid electrolyte interphase of silicon anode for Li-ion batteries: A scanning force spectroscopy study
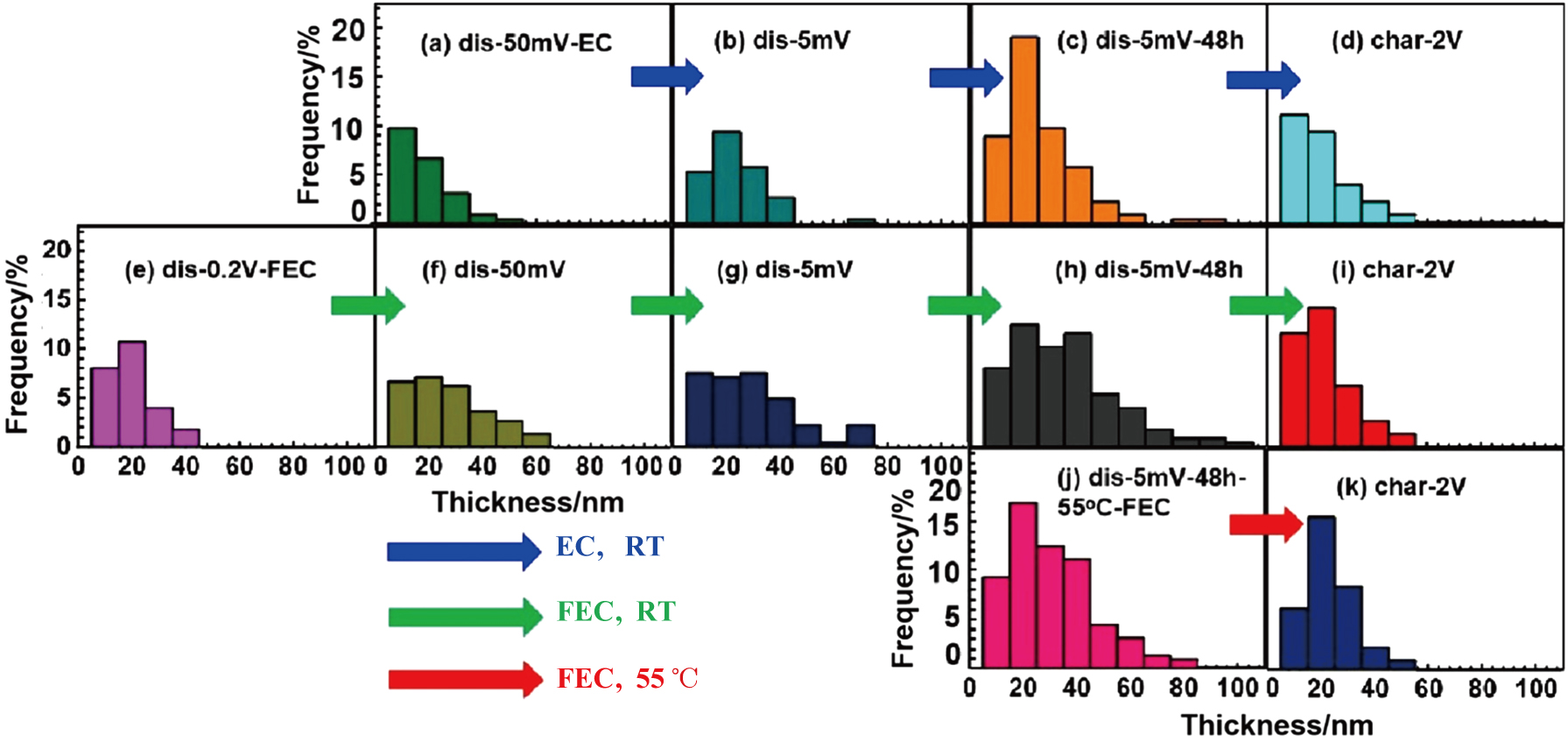
Thickness distribution of SEI: (a)–(d) for samples 2–5 (blue arrow: discharged to 0.05 V, 0.005 V, 0.005 V and kept at 0.005 V for 48 h, charged to 2 V; EC-based electrolyte, RT), (e)–(i) for samples 6–10 (olive arrow: discharged to 0.2 V 0.05 V, 0.005 V, 0.005 V and kept at 0.005 V for 48 h, charged to 2 V; FEC-based electrolyte, RT), (j)–(k) for samples 11–12 (red arrow: discharged to 0.005 V and kept at 0.005 V for 48 h, charged to 2 V; FEC-based electrolyte, 55 °C).