|
Li Yuqi1, 2, Lu Yaxiang1, 3, †, Chen Liquan1, 2, 3, Hu Yong-Sheng1, 2, 3, ‡
|
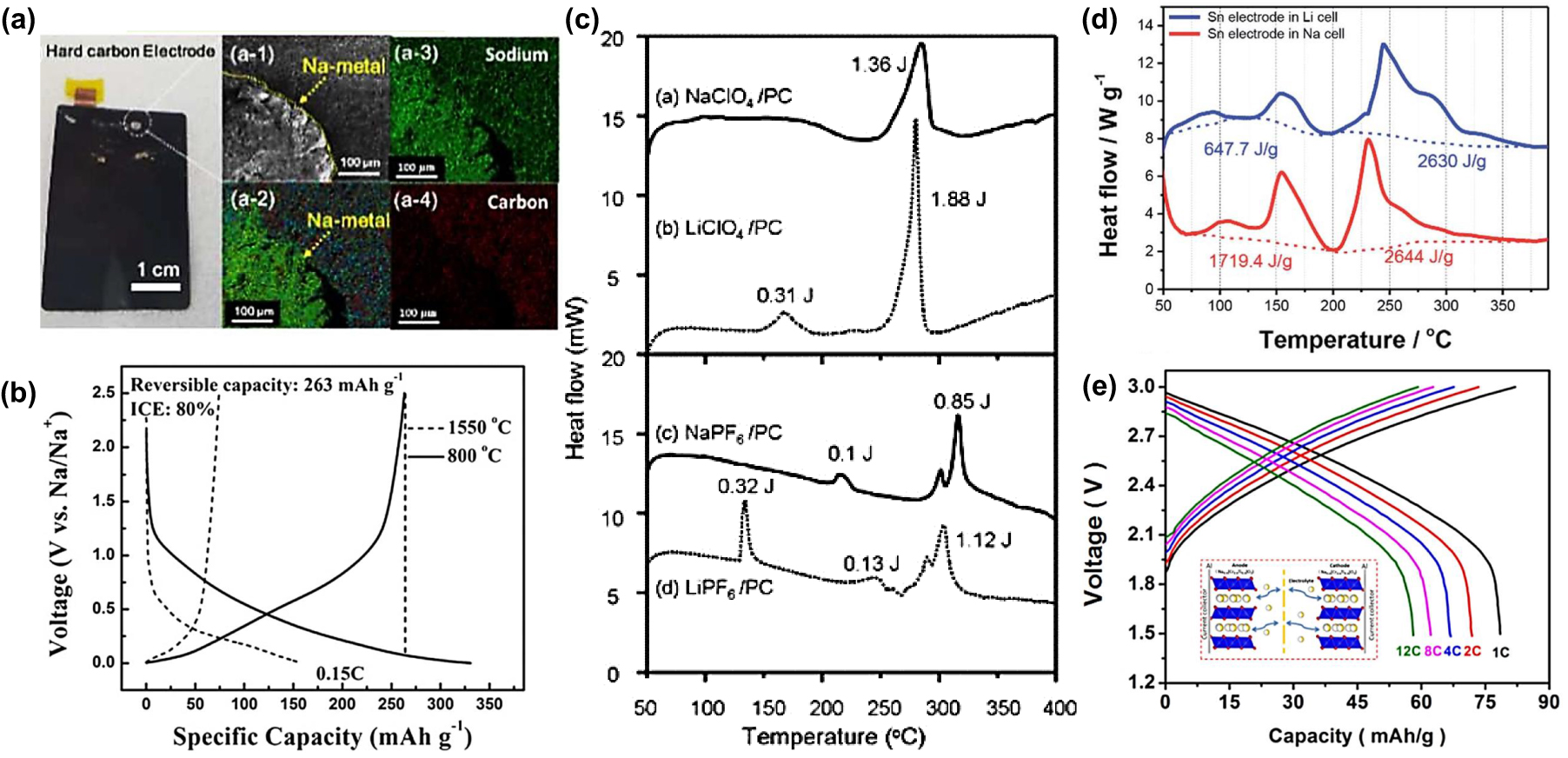
(a) Digital photograph of hard carbon electrode collected from bare coated Na[Ni0.6Co0.2Mn0.2]O2/hard carbon full cell. (a-1) Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image and (a-2)–(a-4) corresponding energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy mappings of the white circle region in (a).[18] (b) Comparison of the first discharge/charge curves of pitch-carbon-800 and pitch-carbon-1550 in half cells.[21] (c) DSC curves of 1 mg charged hard carbon electrode mixed with 2 ml EC/DMC (1 : 1 vol.%) solution containing 1 mol/dm3 NaClO4, LiClO4, NaPF6, or LiPF6.[23] (d) DSC profiles of the lithiated (using LiPF6 salt) and sodiated (using NaPF6 salt) tin electrodes after three cycles.[26] (e) Discharge profiles of Na0.6Cr0.6Ti0.4O2/Na0.6Cr0.6Ti0.4O2 sodium-ion full cell at various rates.[27] |