|
Zhong Hai1, Sun Qin-Chao1, Li Guo1, Du Jian-Yu1, 2, Huang He-Yi1, 2, Guo Er-Jia1, 3, He Meng1, Wang Can1, 2, 4, Yang Guo-Zhen1, Ge Chen1, 2, †, Jin Kui-Juan1, 2, 4, ‡
|
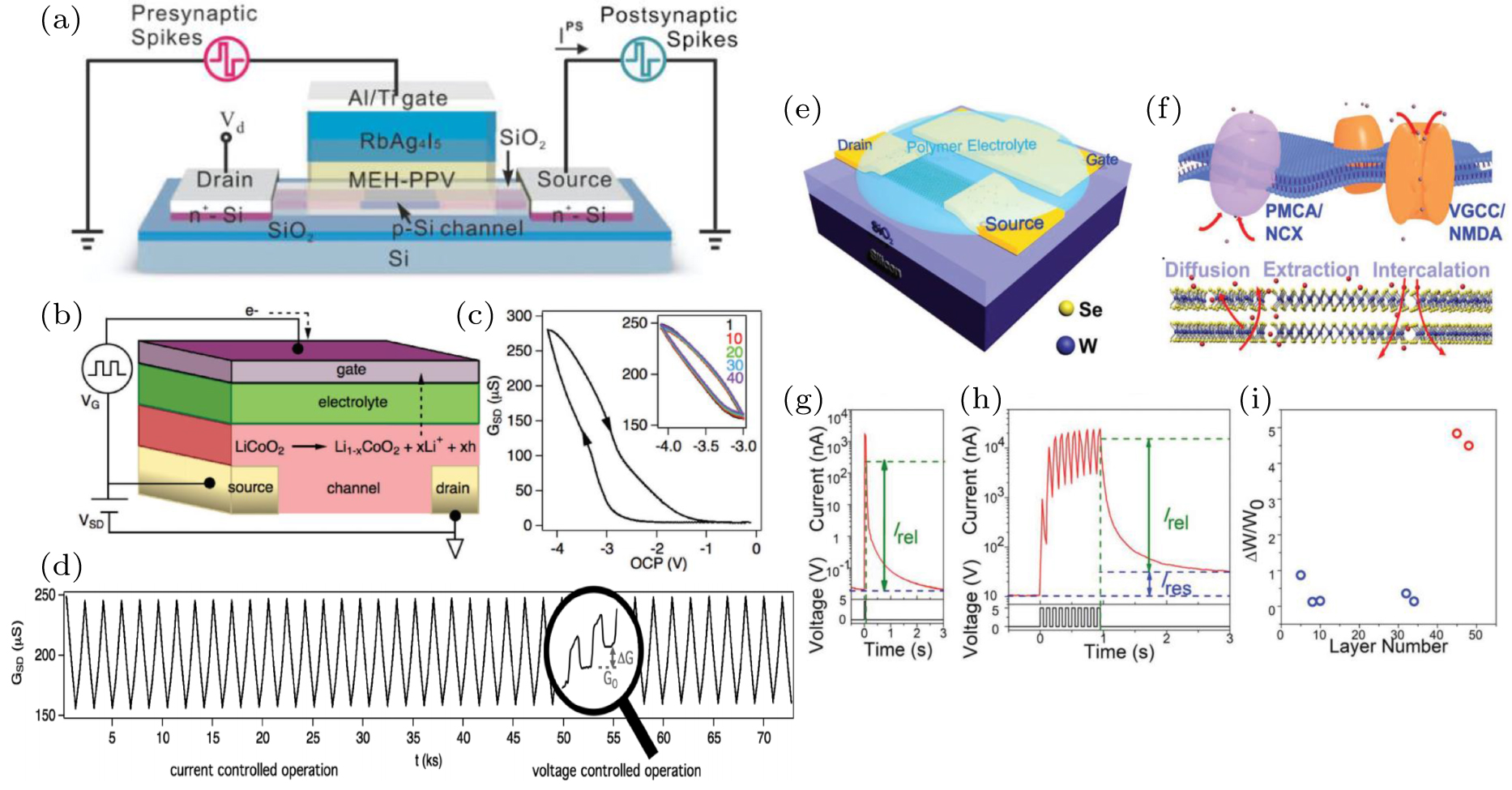
(a) Schematic of a synaptic transistor with RbAg4I5 electrolyte. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [84]. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons. (b) Schematic of device with Li1–xCoO2 channel material. (c) GSD as a function of gate voltage. (d) Conductance responseGSD(t) during current-controlled cycling. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [73]. Copyright 2017, John Wiley & Sons. (e) Schematic of the ion gated synaptic transistor, with 2D materials as the channel. (f) Similarity of the migration and dynamic balance of ion concentrations between biological systems and present synaptic transistors. (g) EPSC characteristic. (h) Transition from STP to LTP. (i) Dependence of long-term weight changes on the layer number of WSe2. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [71]. Copyright 2018, John Wiley & Sons. |