Infrared light-emitting diodes based on colloidal PbSe/PbS core/shell nanocrystals
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0401702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61674074 and 61405089), Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Project, China (Grant No. [2017]1395), Shenzhen Peacock Team Project, China (Grant No. KQTD2016030111203005), Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Advanced Quantum Dot Displays and Lighting, China (Grant No. ZDSYS201707281632549), Guangdong Province’s Key R&D Program: Micro-LED Display and Ultra-high Brightness Micro-display Technology, China (Grant No. 2019B010925001), Guangdong University Key Laboratory for Advanced Quantum Dot Displays and Lighting, China (Grant No. 2017KSYS007), and Distinguished Young Scholar of National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong, China (Grant No. 2017B030306010). We thank the start-up fund from Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China.
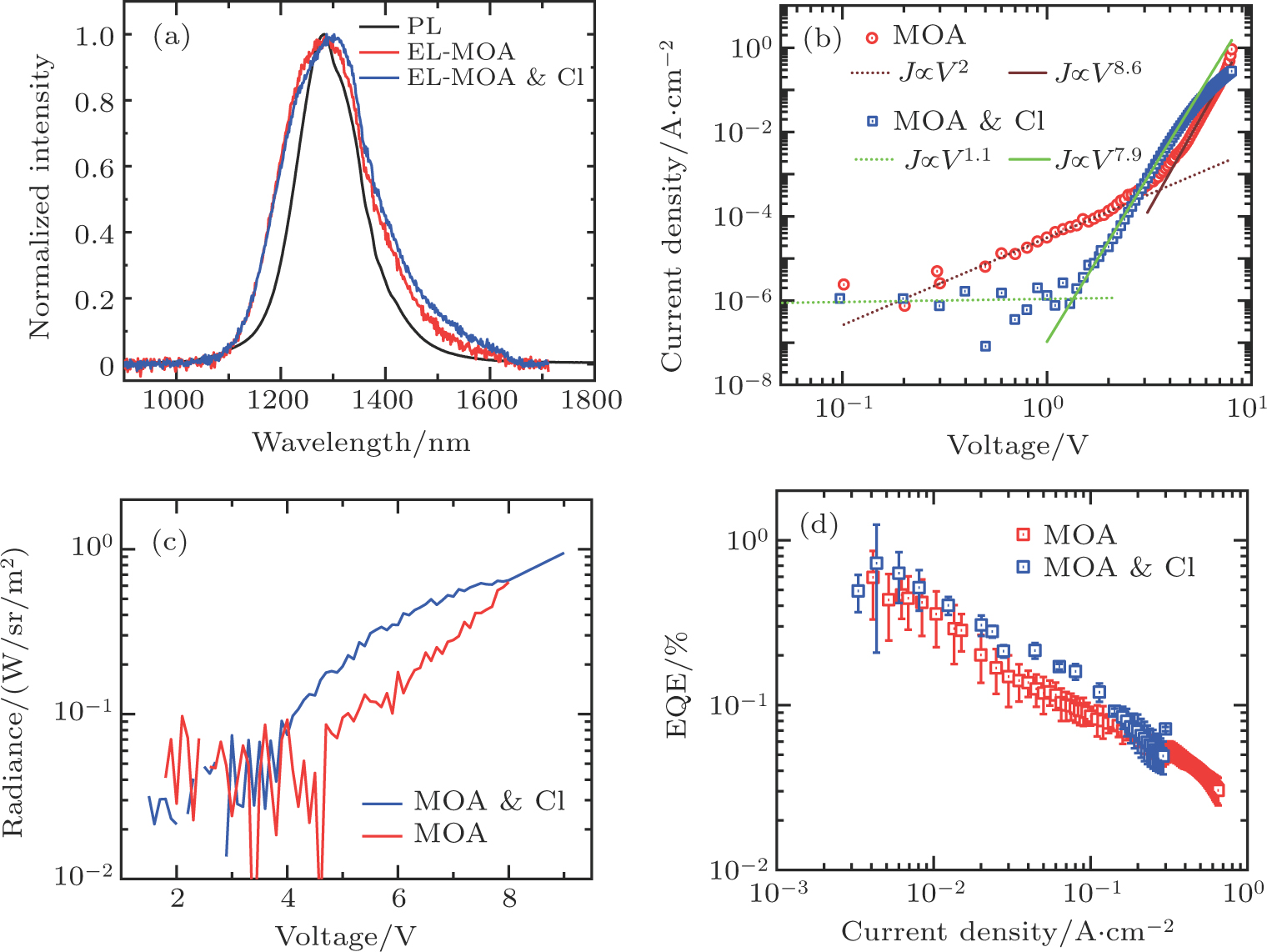
(a) PL (black line) spectrum of PbSe/PbS NCs in TCE and EL spectra of MOA-capped (red line) and MOA/Cl-treated (blue line) devices. (b) Electrical characteristics of MOA-capped (red circles) and MOA/Cl-treated (blue circles) devices. Fitted results are displayed by the wine lines for MOA-capped devices and by green lines for MOA/Cl-treated devices. (c) Radiance–voltage characteristics of these devices. (d) External quantum efficiency–current density performance of these devices. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of device-to-device variations.