|
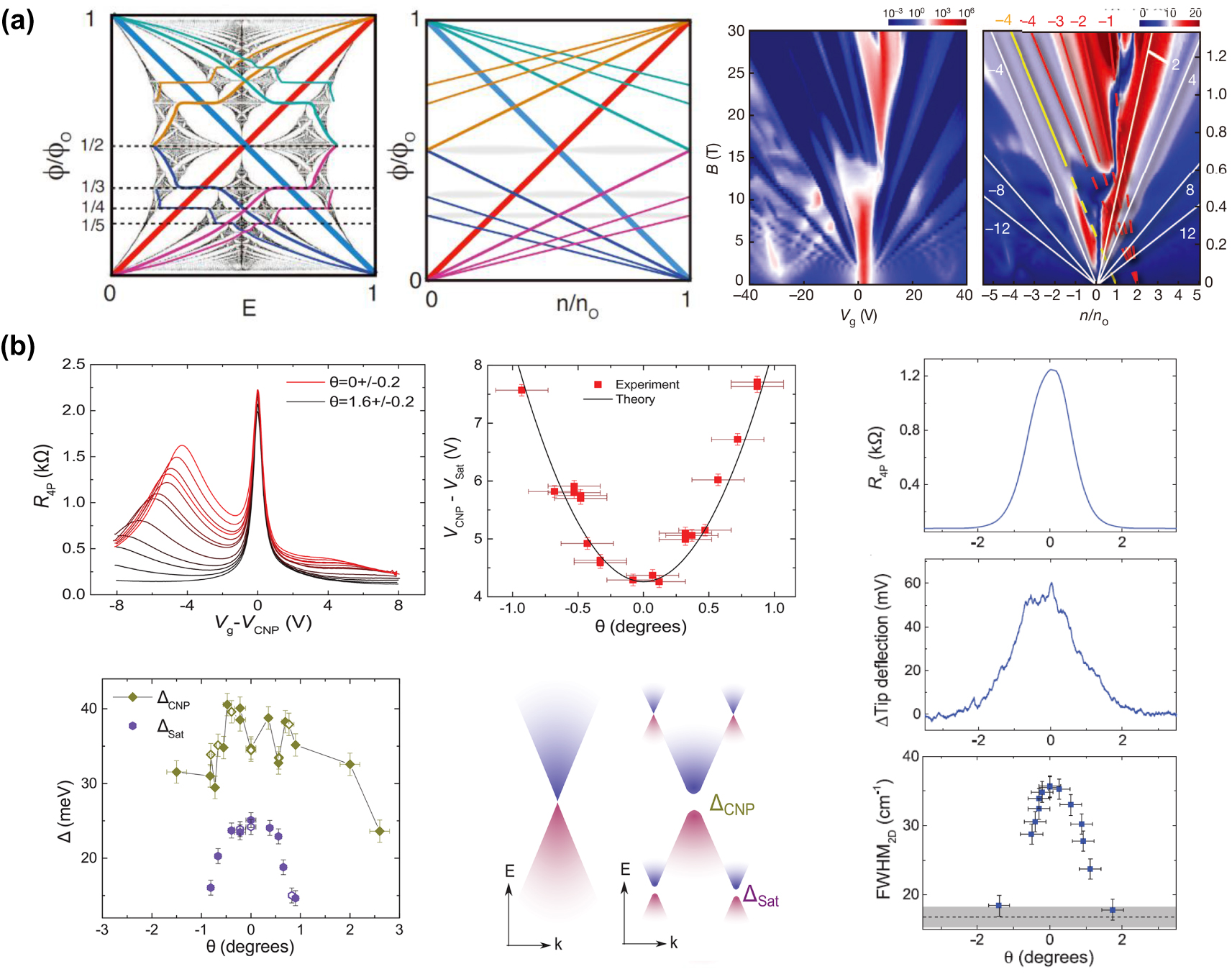
Physical properties of graphene/hBN heterostructures. (a) Left, normalized Hofstadter butterfly spectrum for square lattice in a magnetic field. Middle, density-field diagrams of such system. Colored lines stand for constant chemical potential for both two above. Right, transport measurement results of graphene/hBN heterostructures. The slope of each line has been marked in the figure. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [68]. Copyright 2013, Nature Publishing Group. (b) Top left, four-probe resistance as a function of gate voltage (Vg) results. A satellite peak locates away from charge neutrality point and indicates an extra energy gap. Bottom left, energy gap as a function of twist angle. Top middle, satellite peak position as a function of twist angle. Bottom middle, illustration of energy gap. Right, four-probe resistance (R4P), tip deflection (reflection of friction force), and full width at half maximum of the 2D peak (FWHM2D) in Raman spectroscopy as a function of twist angle at a carrier density of
−
1.9
×
10
12
cm
−
2
. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [22]. Copyright 2018, Nature Publishing Group.
|