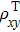Heavy fermions in high magnetic fields
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1632275), the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2017YFA0303100 and 2016YFA0300202), and the Science Challenge Project of China (Grant No. TZ2016004).
Schematic diagram to illustrate the evolution of Weyl fermions in YbPtBi, as the temperature is reduced and the Kondo interaction becomes stronger. The dramatic decrease of the Fermi velocity v* at low temperatures leads to the disappearance of the chiral anomaly contribution ca, but the large entropy associated with the renormalized bands leads to a sizeable cubic term in the temperature dependence of the specific heat Ce. Meanwhile a sizeable topological Hall effect contribution