High-throughput research on superconductivity
Project supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant Nos. 2015CB921000, 2016YFA0300301, 2017YFA0303003, and 2017YFA0302902), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11674374, 11804378, and 11574372), the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Grant No. Z161100002116011), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos. QYZDBSSW-SLH008 and QYZDY-SSW-SLH001), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB07020100), and the Opening Project of Wuhan National High Magnetic Field Center (Grant No. PHMFF2015008).
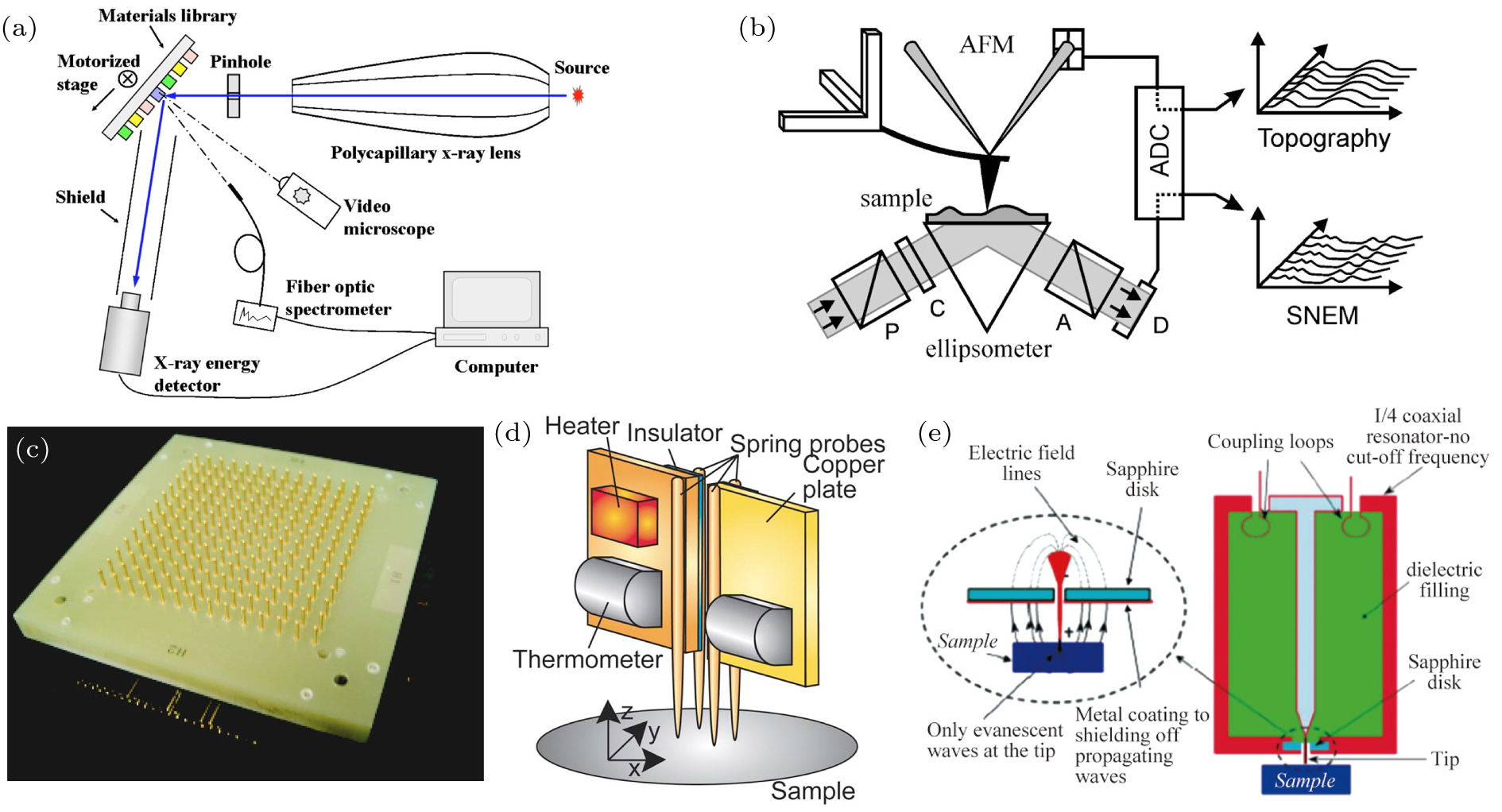
(color online) Typical high-throughput characterization techniques. (a) Schematic diagram of the x-ray characterization system for combinatorial material studies.[