Dependence of the solar cell performance on nanocarbon/Si heterojunctions
Project supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFA0208402), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2012CB932302), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11634014, 51172271, and 51372269), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA09040202).
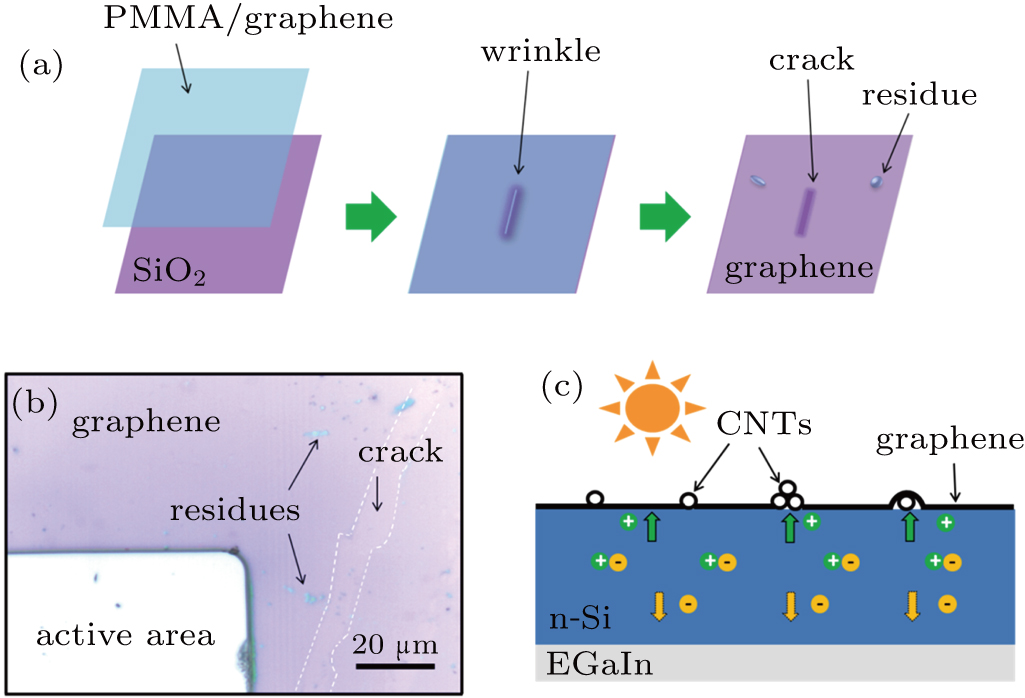
(color online) (a) Schematic diagram of the formation of cracks and residues in the transfer process. (b) Optical microscope image of as-fabricated G/Si solar cell. A dash-line crack of graphene can be observed by the different contrast of graphene and SiO2. (c) Mechanism graph of the photovoltaic process. The separated holes are collected by both CNTs and graphene individuals.