A high-performance rechargeable Li–O2 battery with quasi-solid-state electrolyte
Project supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2016YFB0100300 and 2016YFB0100100), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2014CB932300), the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission, China (Grant No. D171100005517001), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA09010000), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51502334).
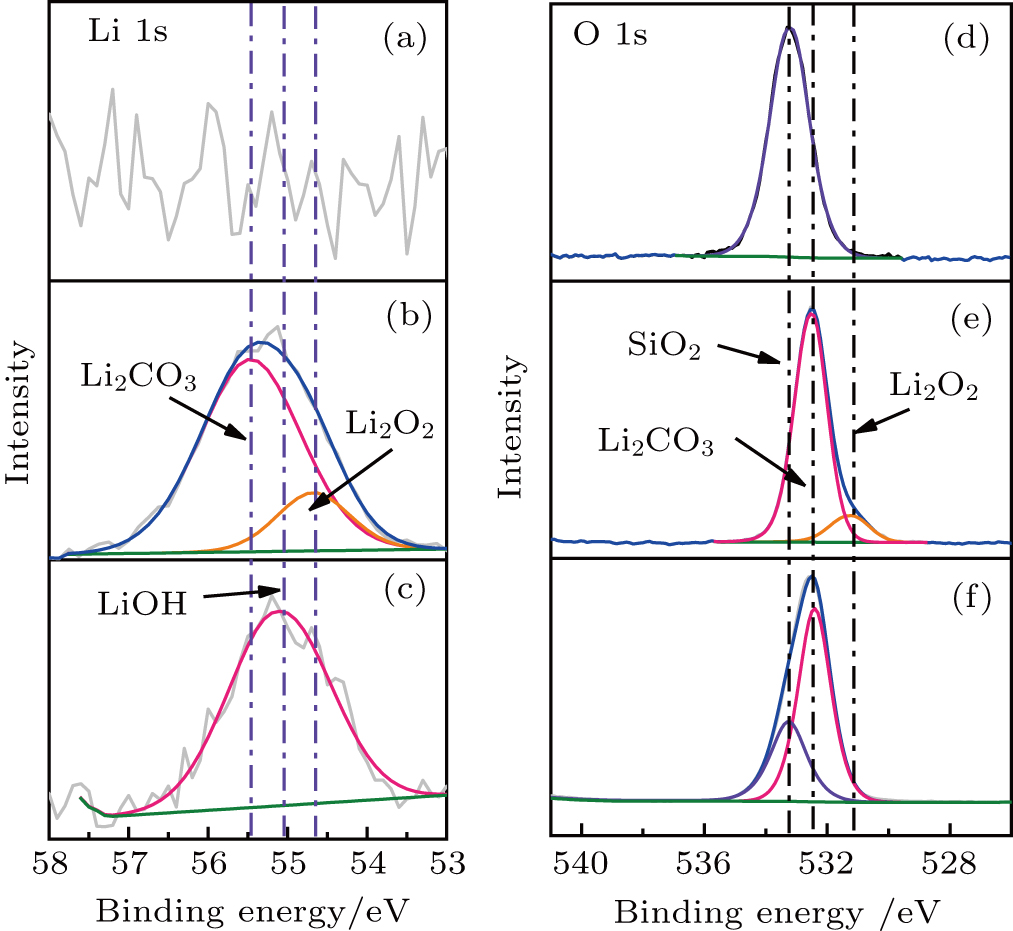
(color online) The (a, b, c) Li 1s and (d, e, f) O 1s XPS spectra collected on cathode electrodes at pristine, first discharge and first charge states, respectively. The Li–O2 battery was tested at a current density of 100 mA/g with a fixed capacity of 1000 mAh/g at 80 °C.