Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement station in SECUF using hybrid superconducting magnets
Project supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB07020200), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2016YFA0300502 and 2015CB921304), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11634015).
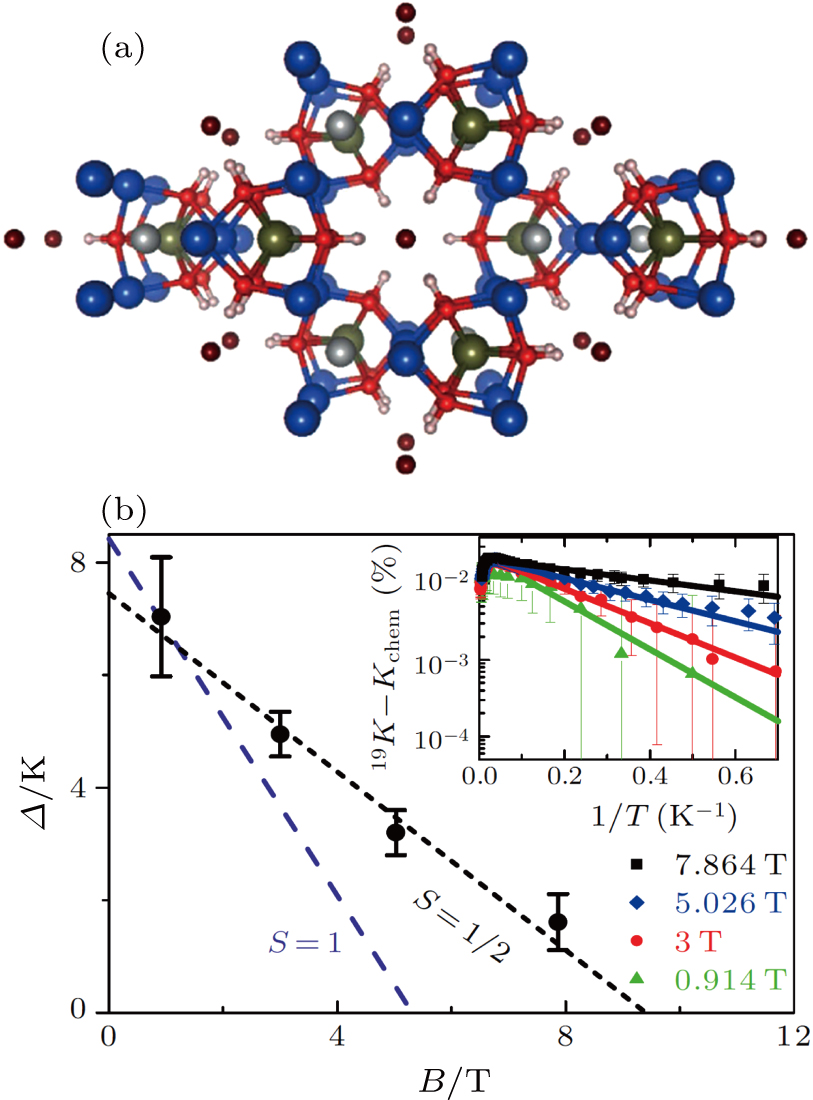
(color online) (a) Top view of the Cu3Zn(OH)6FBr crystal structure, where F (brown) is in the center between two hexagons of two kagome Cu planes. (b) Magnetic field dependence of the spin gap. The black short-dash line is fitted by