Tuning hybrid liquid/solid electrolytes by lowering Li salt concentration for lithium batteries
Project supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2014CB932400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51772167), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M591169), and the Shenzhen Municipal Basic Research Project, China (Grant No. JCYJ20170412171311288).
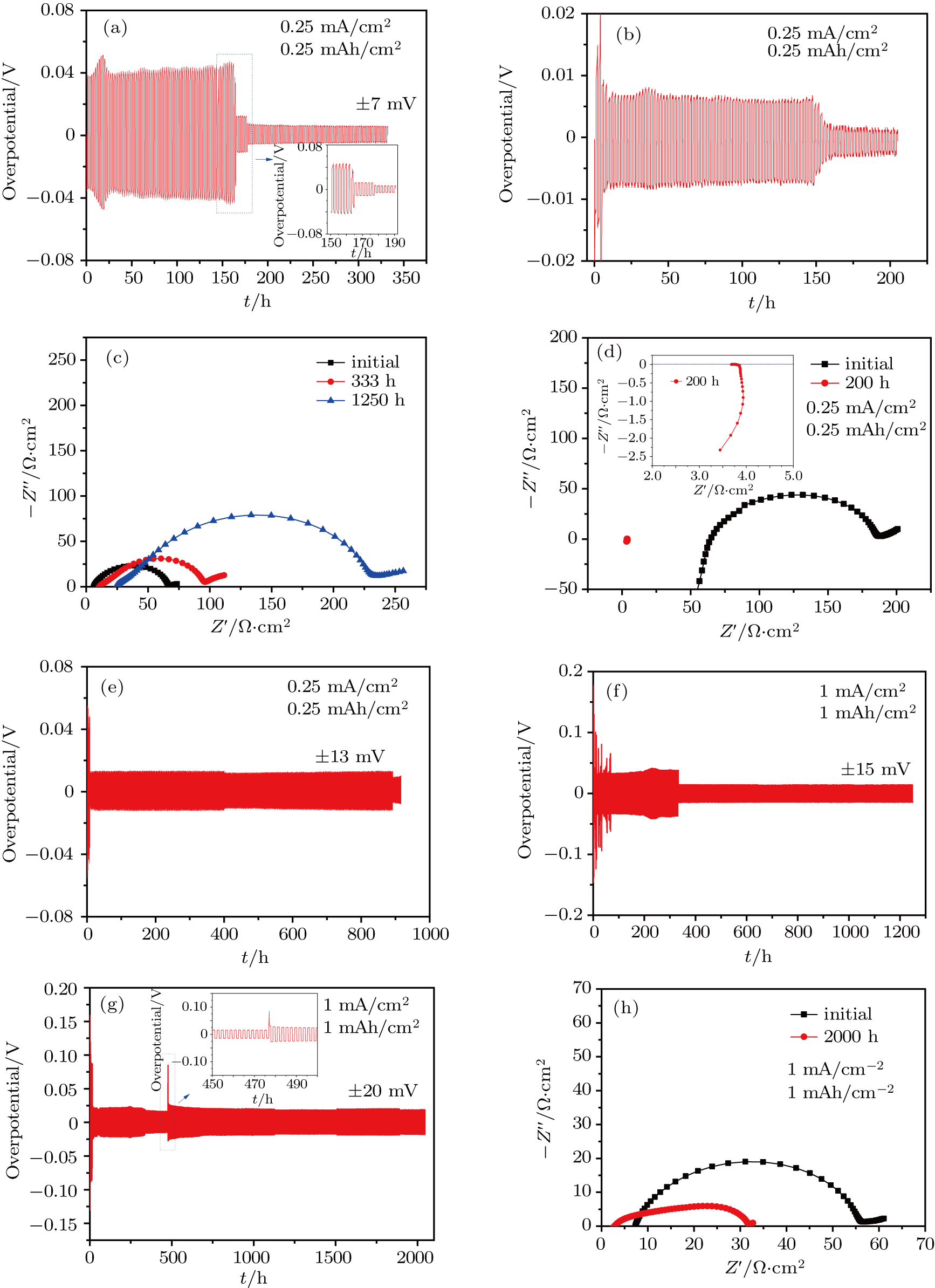
(color online) Polarizations of Li|electrolyte|Li symmetric cells with different current densities and capacities. [(a) and (e)] Li|0.5-HLSE-p|Li with 0.25 mA/cm2 and 0.25 mAh/cm2; (f) 1 mA/cm2 and 1 mAh/cm2; (b) Li|LE|Li with 0.25 mA/cm2 and 0.25mAh/cm2; (g) Li|0.5-HLSE-px|Li with 1 mA/cm2 and 1 mAh/cm2; the Nyquist plots of (c) Li|0.5-HLSE-p|Li before cycling (black solid square), after 333 h (red solid cycle) and 1250 h (blue solid triangle) cycling, with 0.25 mA/cm2, 0.25 mAh/cm2; (d) Li|LE|Li before cycling (black solid square), after 200 h (red solid cycle), with 0.25 mA/cm2, 0.25 mAh/cm2; of (g) Li|0.5-HLSE-px|Li before (black solid square) and after 2000 h (red solid cycle) cycling, with 1 mA/cm2, 1 mAh/cm2.