Tuning hybrid liquid/solid electrolytes by lowering Li salt concentration for lithium batteries
Project supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2014CB932400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51772167), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M591169), and the Shenzhen Municipal Basic Research Project, China (Grant No. JCYJ20170412171311288).
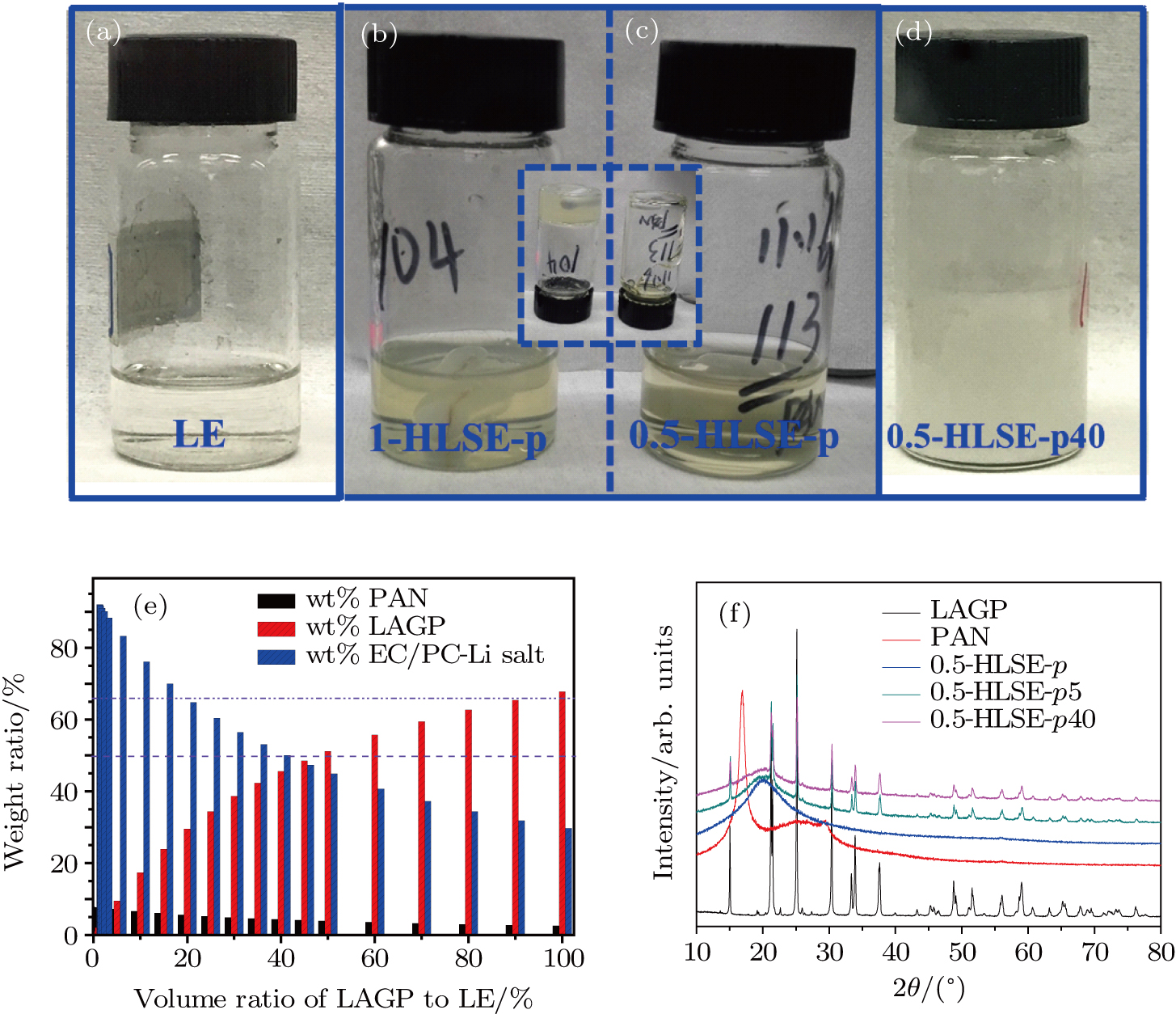
(color online) Optical photos of electrolytes: (a) liquid electrolyte; (b) and (c) hybrid liquid/solid electrolyte after polymer addition [(b) 1.0-HLSE-p and (c) 0.5-HLSE-p], the inserts are the photos after putting them upside down, and (d) 0.5-HLSE-p40, (e) weight percent variation of liquid electrolyte, PAN and LAGP in HLSE with different amounts of LAGP addition; (f) x-ray diffraction patterns of HLSEs and components used here.