Lorentz transmission electron microscopy studies on topological magnetic domains
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0700902), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51590880, 11674379, 51431009, 11674373, and 51625101), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 2015004).
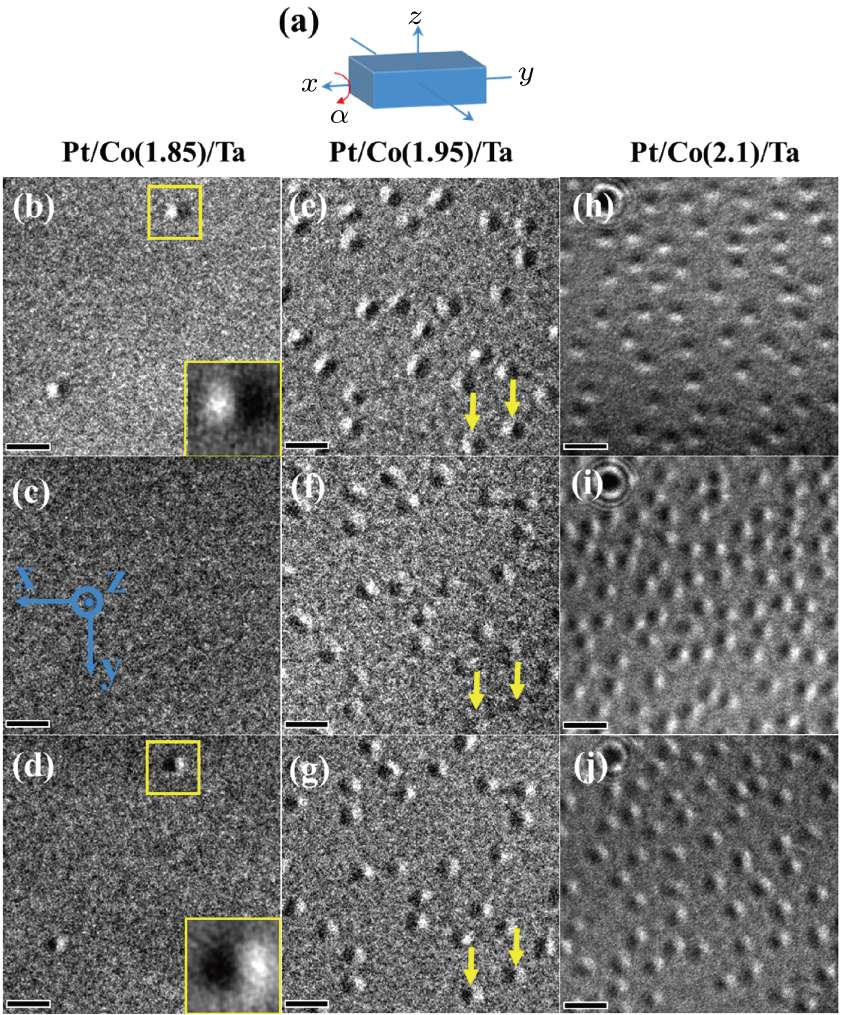
(color online) Identification of skyrmion spin configuration by tilting samples in real-space Lorentz TEM at 300 K. (a) Schematic diagram of titling process, α is the tilt angle around x-axis. The angle α for Pt/Co(1.85)/Ta is (b) −18°, (c) 0°, and (d) 18°, respectively. The enlarged views of a single skyrmion in the insets (b) and (d) with bright and dark reversed magnetic contrast for the opposite tilting angle are identified as Néel-type skyrmion. The tilting angle α are (e) −18°, (f) 0°, and (g) 18° for Pt/Co(1.95)/Ta, respectively. The tilting angle α are (h) −20°, (i) 0°, and (j) 20° for Pt/Co(2.1)/Ta, respectively. Scale bars in panels (b)–(j) correspond to 50 nm.[