Computing methods for icosahedral and symmetry-mismatch reconstruction of viruses by cryo-electron microscopy
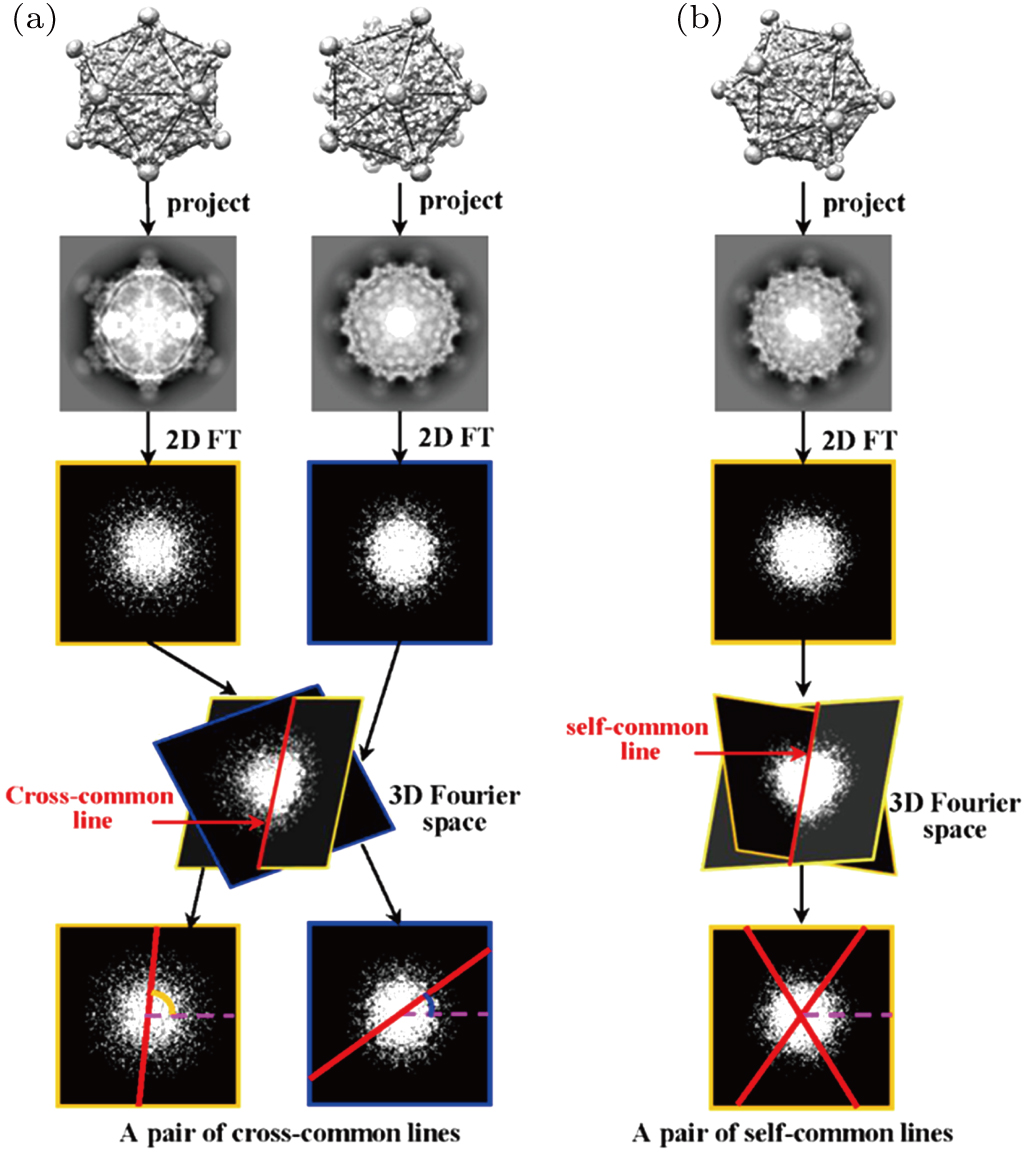
(color online) Illustration of (a) cross-common line and (b) self-common line. (a) Fourier transformations of two projections (images) intersecting a line in 3D Fourier space, and mapping of the intersecting line to the two Fourier transformations (bottom of (a)) to produce a pair of cross-common lines. (b) Two central sections form one Fourier transformation with two symmetry operations intersecting a line in 3D Fourier space to produce a pair of self-common lines. According to the symmetry operation of an icosahedron, 60 pairs of cross-common lines exist for any two different Fourier transformation, and 37 pairs of self-common lines exist for one Fourier transformation.