|
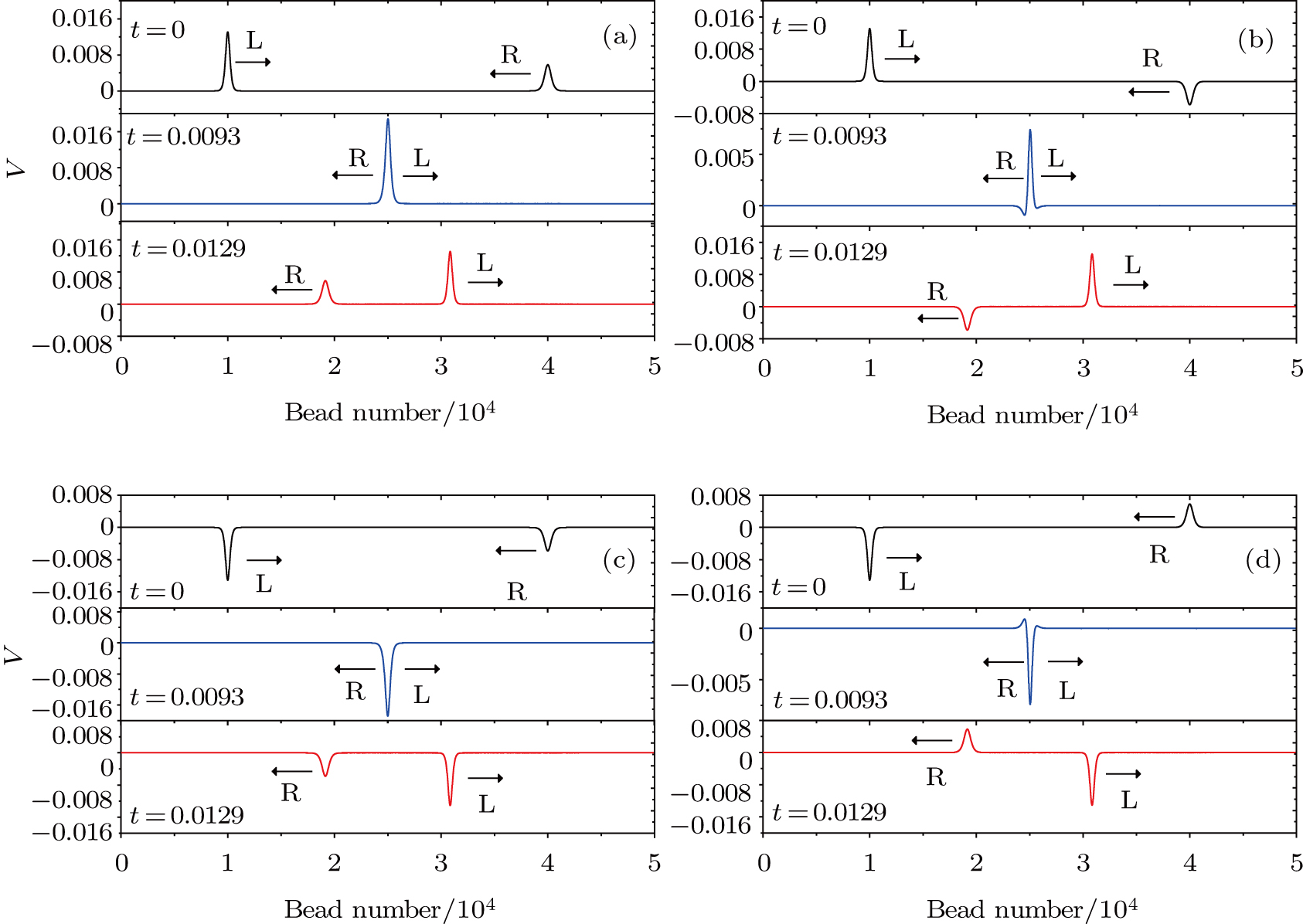
(color online) The interaction process of the head on collision between two solitary waves L and R. There are four cases. Initial amplitudes of colliding solitary waves L and R are about AL = 0.01309 and AR = 0.00582, respectively. In the figure, the arrows stand for the propagation directions of waves. The black solid line represents the initial state of the solitary waves L and R, the blue solid line represents the collision of solitary waves L and R and the red solid line represents the evolution of solitary wave L and R at the different times after collision. Four different cases are shown in panels (a), (b), (c), and (d). Case (a) is for
A
+
L
&
A
+
R
, case (b) for
A
−
L
&
A
−
R
, case (c) for
A
+
L
&
A
−
R
, and case (d) for
A
−
L
&
A
+
R
. Here A
L and A
R represent amplitudes of solitary waves L and R, respectively, while “+” and “−” represent the propagation directions of solitary waves, respectively.
|