|
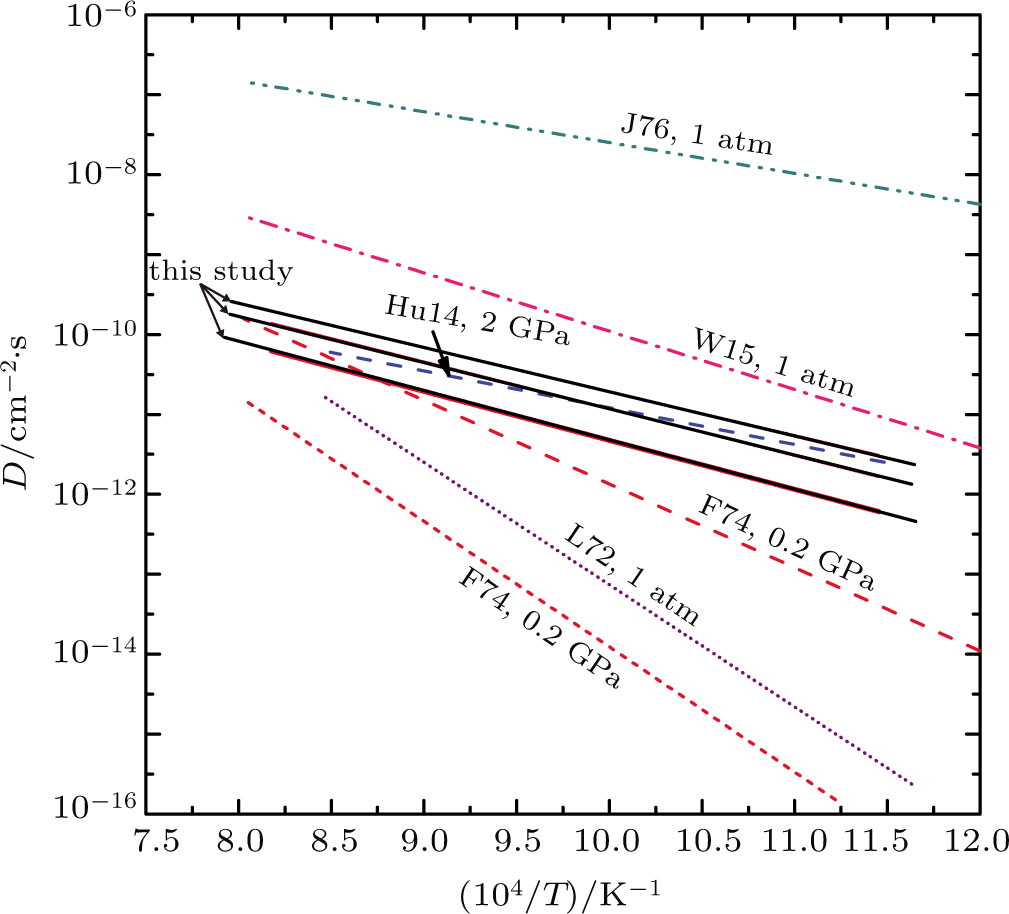
(color online) Calculated diffusion coefficients of dry K-feldspar single crystal by using the Nernst–Einstein equation at 2.0 GPa, and their comparison with previous studies. Black solid lines represent the results of this work; pink dotted line represents the self-diffusion coefficient of sodium in natural single-crystal alkali sanidine with a chemical composition of
 at room pressure from Wilangowski et al.;[66] blue dashed line represents the calculated average diffusion coefficient of potassium ions in polycrystalline K-feldspar aggregate along different orientations at 2.0 GPa from Hu et al.;[30] green dashed line represents the potassium diffusion coefficient of orthoclase glass at room pressure from Jambon and Carron;[73] red dotteded and dash lines represent the self-diffusion coefficients of potassium and sodium ions for the natural orthoclase (
at room pressure from Wilangowski et al.;[66] blue dashed line represents the calculated average diffusion coefficient of potassium ions in polycrystalline K-feldspar aggregate along different orientations at 2.0 GPa from Hu et al.;[30] green dashed line represents the potassium diffusion coefficient of orthoclase glass at room pressure from Jambon and Carron;[73] red dotteded and dash lines represent the self-diffusion coefficients of potassium and sodium ions for the natural orthoclase (
 ) at 0.2 GPa from Foland,[72] respectively; purple dotted line represents the K self-diffusion coefficient for pure microcline perthite (
) at 0.2 GPa from Foland,[72] respectively; purple dotted line represents the K self-diffusion coefficient for pure microcline perthite (
 ) at room pressure from Lin and Yund.[71]
) at room pressure from Lin and Yund.[71]
|