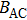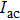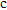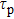|
(color online) Experimental demonstration of spin qubits. (a) SEM image of the silicon CMOS quantum dot for single- and two-qubit operations. The spin states of two qubits are controlled by the magnetic field
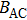 produced by the ESR transmission line with ac current
produced by the ESR transmission line with ac current
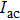 . A single or double quantum dot can be formed by adjusting the voltages of gates G1–G4. G
. A single or double quantum dot can be formed by adjusting the voltages of gates G1–G4. G
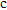 denotes the confinement gate while R denotes the reservoir.[5] (b) Fidelity of a single qubit formed in the device of panel (a) through randomized benchmarking of Clifford gates. From the decay an average fidelity of 99.6% can be inferred.[37] (c) Rabi oscillations of individual spin qubit in each quantum dot of panel (a).[5] (d) Two-spin probabilities as functions of the microwave pulse length
denotes the confinement gate while R denotes the reservoir.[5] (b) Fidelity of a single qubit formed in the device of panel (a) through randomized benchmarking of Clifford gates. From the decay an average fidelity of 99.6% can be inferred.[37] (c) Rabi oscillations of individual spin qubit in each quantum dot of panel (a).[5] (d) Two-spin probabilities as functions of the microwave pulse length
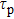 on the control qubit (Q1) after applying a CNOT gate (the inset shows the corresponding Bloch sphere). Black solid lines are the fits based on a CNOT gate considering read-out errors while green dotted lines show the intended maximally entangled states.[5]
on the control qubit (Q1) after applying a CNOT gate (the inset shows the corresponding Bloch sphere). Black solid lines are the fits based on a CNOT gate considering read-out errors while green dotted lines show the intended maximally entangled states.[5]
|