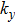|
Hong Guang-Hao1, 2, 4, Wang Cheng-Wei3, 4, Jiang Juan2, 5, 6, Chen Cheng7, Cui Sheng-Tao2, Yang Hai-Feng2, Liang Ai-Ji2, Liu Shuai2, Lv Yang-Yang8, Zhou Jian8, Chen Yan-Bin8, Yao Shu-Hua8, Lu Ming-Hui8, Chen Yan-Feng8, Wang Mei-Xiao2, Yang Le-Xian9, Liu Zhong-Kai2, †, Chen Yu-Lin2, 7, 9, ‡
|
|
(color online) Kz measurements and Dirac line node in ZrSiS. (a) Plot of the constant energy contour at
 in
in
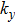 –kz space. The bulk and surface state bands are indicated by the red and green arrows, respectively. Magenta dotted lines indicate the kz positions of four representing cuts shown in (b) and (d). (b) Detailed analysis of the four representing cuts, the surface bands and linear dispersions are marked. (c) The 3D BZ shows the constant energy contours (ky–kz plane and kx–ky plane) around the DP and illustrates the location of the Dirac line node (green solid line) in ZrSiS (X–R direction). (d) (i) Schematic of the Dirac line node along the kz direction (labelled by the green curve) with the grey planes which are corresponding to each cut in (b) and (d) (ii). The bright curves sketch the Dirac dispersions we observe in each cut as in (ii). (ii) Stack plot of the four cuts as in (b). Green curve indicates the dispersion of the Dirac line node. (e) The fitted DP positions (red dots) at various kz values, the green curve indicates the calculated dispersion along the X–R direction.
–kz space. The bulk and surface state bands are indicated by the red and green arrows, respectively. Magenta dotted lines indicate the kz positions of four representing cuts shown in (b) and (d). (b) Detailed analysis of the four representing cuts, the surface bands and linear dispersions are marked. (c) The 3D BZ shows the constant energy contours (ky–kz plane and kx–ky plane) around the DP and illustrates the location of the Dirac line node (green solid line) in ZrSiS (X–R direction). (d) (i) Schematic of the Dirac line node along the kz direction (labelled by the green curve) with the grey planes which are corresponding to each cut in (b) and (d) (ii). The bright curves sketch the Dirac dispersions we observe in each cut as in (ii). (ii) Stack plot of the four cuts as in (b). Green curve indicates the dispersion of the Dirac line node. (e) The fitted DP positions (red dots) at various kz values, the green curve indicates the calculated dispersion along the X–R direction.
|