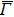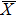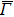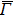|
Hong Guang-Hao1, 2, 4, Wang Cheng-Wei3, 4, Jiang Juan2, 5, 6, Chen Cheng7, Cui Sheng-Tao2, Yang Hai-Feng2, Liang Ai-Ji2, Liu Shuai2, Lv Yang-Yang8, Zhou Jian8, Chen Yan-Bin8, Yao Shu-Hua8, Lu Ming-Hui8, Chen Yan-Feng8, Wang Mei-Xiao2, Yang Le-Xian9, Liu Zhong-Kai2, †, Chen Yu-Lin2, 7, 9, ‡
|
|
(color online) General electronic structure of ZrSiS. (a) Stacking plots of constant-energy contours in broader binding energy range show the band structure evolution. (b) Top row: photoemission spectral intensity map showing the constant energy contours of bands at
 (i), 0.25 eV (ii), 0.5 eV (iii) and 0.75 eV (iv), respectively. Bulk states (BS) and surface states (SS) are labelled. Bottom row: corresponding calculated constant energy contours at the same binding energies as in the experiments above. (c) 3D intensity plot of the photoemission spectra centred around
(i), 0.25 eV (ii), 0.5 eV (iii) and 0.75 eV (iv), respectively. Bulk states (BS) and surface states (SS) are labelled. Bottom row: corresponding calculated constant energy contours at the same binding energies as in the experiments above. (c) 3D intensity plot of the photoemission spectra centred around
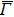 point. High symmetry cuts are exposed. (d) Broad range high symmetry cut along the
point. High symmetry cuts are exposed. (d) Broad range high symmetry cut along the
 –
–
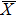 –
–
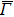 direction (i), with their corresponding calculated bulk band structure (ii). BSs and SSs are labelled on the data and zoomed in surface states near the Fermi level (iii). (e) High symmetry cuts along the
direction (i), with their corresponding calculated bulk band structure (ii). BSs and SSs are labelled on the data and zoomed in surface states near the Fermi level (iii). (e) High symmetry cuts along the
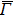 –
–
 (i) and
(i) and
 –
–
 –
–
 (iii) directions and corresponding calculated bulk band structures ((ii), (iv)). SS is labelled in the data.
(iii) directions and corresponding calculated bulk band structures ((ii), (iv)). SS is labelled in the data.
|