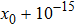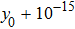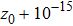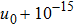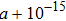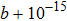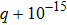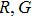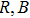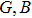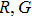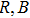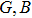† Corresponding author. E-mail:
In this paper, Adomian decomposition method (ADM) with high accuracy and fast convergence is introduced to solve the fractional-order piecewise-linear (PWL) hyperchaotic system. Based on the obtained hyperchaotic sequences, a novel color image encryption algorithm is proposed by employing a hybrid model of bidirectional circular permutation and DNA masking. In this scheme, the pixel positions of image are scrambled by circular permutation, and the pixel values are substituted by DNA sequence operations. In the DNA sequence operations, addition and substraction operations are performed according to traditional addition and subtraction in the binary, and two rounds of addition rules are used to encrypt the pixel values. The simulation results and security analysis show that the hyperchaotic map is suitable for image encryption, and the proposed encryption algorithm has good encryption effect and strong key sensitivity. It can resist brute-force attack, statistical attack, differential attack, known-plaintext, and chosen-plaintext attacks.
Based on network and cloud computing, the development of the information technology brings lots of challenges to protection of confidential and sensitive transmitted information, and the information security of digital information has become a hot topic.[1–7] The encryption is very important for the image transmission, such as military image and private image.[8,9] However, most conventional ciphers such as Data Encryption Standard (DES) and International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) are not suitable for digital images, because of the inherent features of image data including the bulk data capacity and strong correlation among adjacent pixels. Due to the advantages in extreme sensitivity to initial conditions and parameters, ergodicity, high randomness and mixing, the chaotic signals possess great value in the field of cryptography, and a lot of chaos-based cryptosystems have been developed up to now.[4–9]
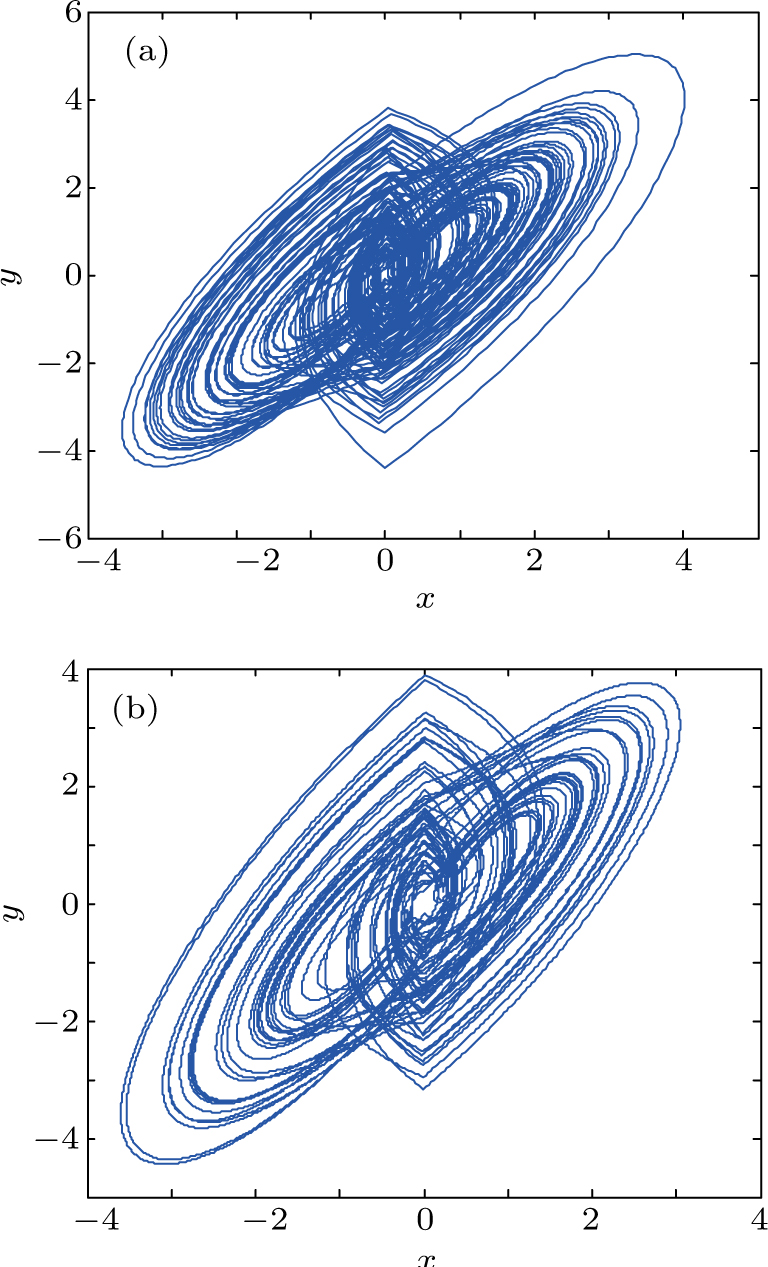
Compared with integer-order chaotic system, the encryption scheme based on fractional-order system has higher security because of its nonlocal character and high nonlinearity.[10,11] In addition, the key space is greatly improved by introducing fractional-order system, although its computing cost maybe increase. For the sake of security improvement, on one hand, the novel piecewise-linear (PWL) hyperchaotic system[12] is solved by ADM algorithm,[13–15] which owns less time and more space complexity. The system possesses seven terms without any quadratic or higher-order polynomials, and contains the piecewise continuous functions, such as absolute value function. Thus, it is meaningful to study the system dynamics and its applications in the image encryption. On the other hand, we reduce the iteration cost of hyperchaotic system in the encryption algorithm as far as possible.
Many hybird algorithms have been proposed[16–29] to improve the security. Among them, DNA-based algorithm arises most of concerned,[18–22,24,28] because DNA computing has some good characteristics such as massive parallelism, huge storage and ultra-low power consumption. The core of these schemes are DNA encoding and DNA computing, which includes some biological and algebra operations on DNA sequence, such as the DNA complementary rule,[20] DNA addition[21,22,28] and XOR operations.[24] However, most of these algorithms cannot resist differencial attack, because their ciphered image only relys on the secret key. Attackers may use some special plaintext image to crack these schemes. To address this problem, we proposed a scheme that the ciphered image not only depends on the secret key, but also relys on the plaintext. It improves the ability to resist these attacks greatly.
In this paper, based on the fractional-order PWL hyperchaotic map, we proposed a new image encryption scheme. In this scheme, permutation and substitution are combined to smash the correlations between R, G, B components, and design a rule of twin DNA addition for DNA operation. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section
There are several different definitions of fractional-order integration and differential so far,[10,11] such as Riemann-Liouville definition and Caputo definition.
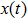
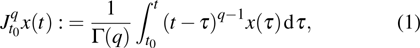 |
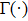
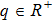
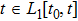
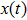
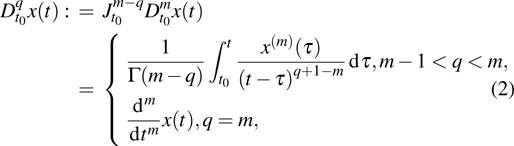 |
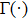
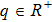
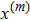
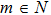
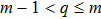
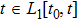
Although the Riemann–Liouville derivative and Caputo derivative are equivalent in the same homogenous initial conditions, the Caputo derivative (
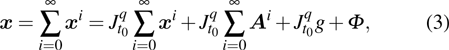 |
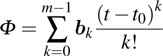 |
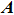
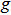
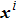
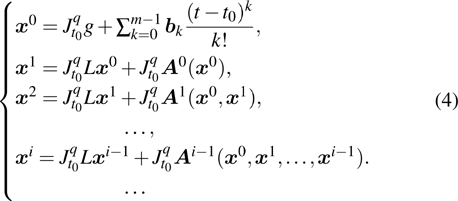 |
The equation of integer-order PWL hyperchaotic system proposed by Li et al.,[12] and its fractional-order form is expressed as
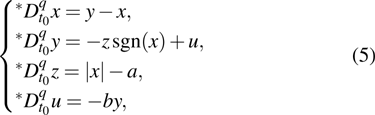 |
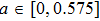
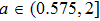
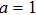
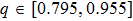
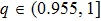
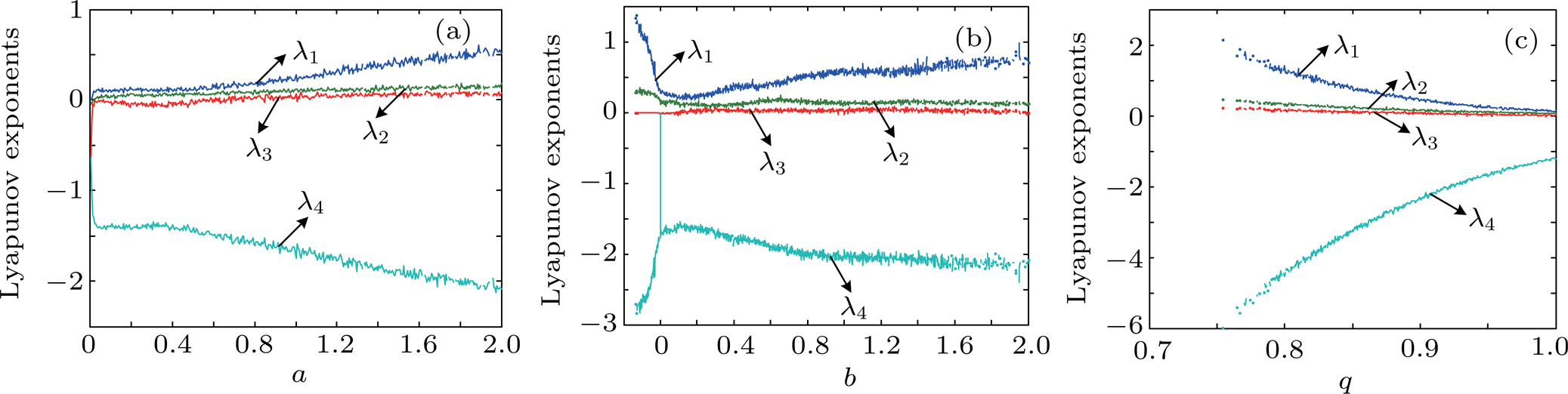 | Fig. 1. (color online) The Lyapunov exponents of the PWL fractional-order system (a) q = 0.95, b = 0.25, 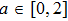 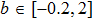 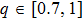 |
A DNA sequence consists of four nucleic acid bases A (adenine), G (guanine), T (thymine), C (cytosine), where T and A are complementary, and C and G are complementary. For a binary signal, 0 and 1 are complementary, so it is obtained that 00 and 11 are complementary, and 01 and 10 are also complementary. By using the four bases A, C, G, and T to encode 00, 01, 10, and 11, the number of coding combination kinds is 4! = 24. Because of the complementary relationamong DNA bases, there are only eight kinds of coding combinations which satisfy the Watson–Crick complement rule[25] as listed in Table
| Table 1.
DNA encoding rules. . |
For DNA sequences, addition and subtraction operations are performed according to traditional addition and subtraction in the binary. Thus, there are 8 kinds of DNA addition and subtraction rules corresponding to 8 kinds of DNA encoding schemes. For instance, we adopt one type of addition operation as shown in Table
| Table 2.
Addition operation for DNA sequences. . |
| Table 3.
Subtraction operation for DNA sequences. . |
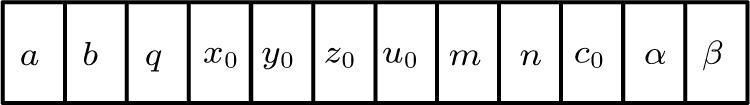
The key format used in this encryption scheme is shown in Fig. 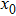
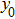
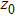
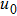
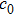
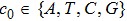
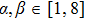
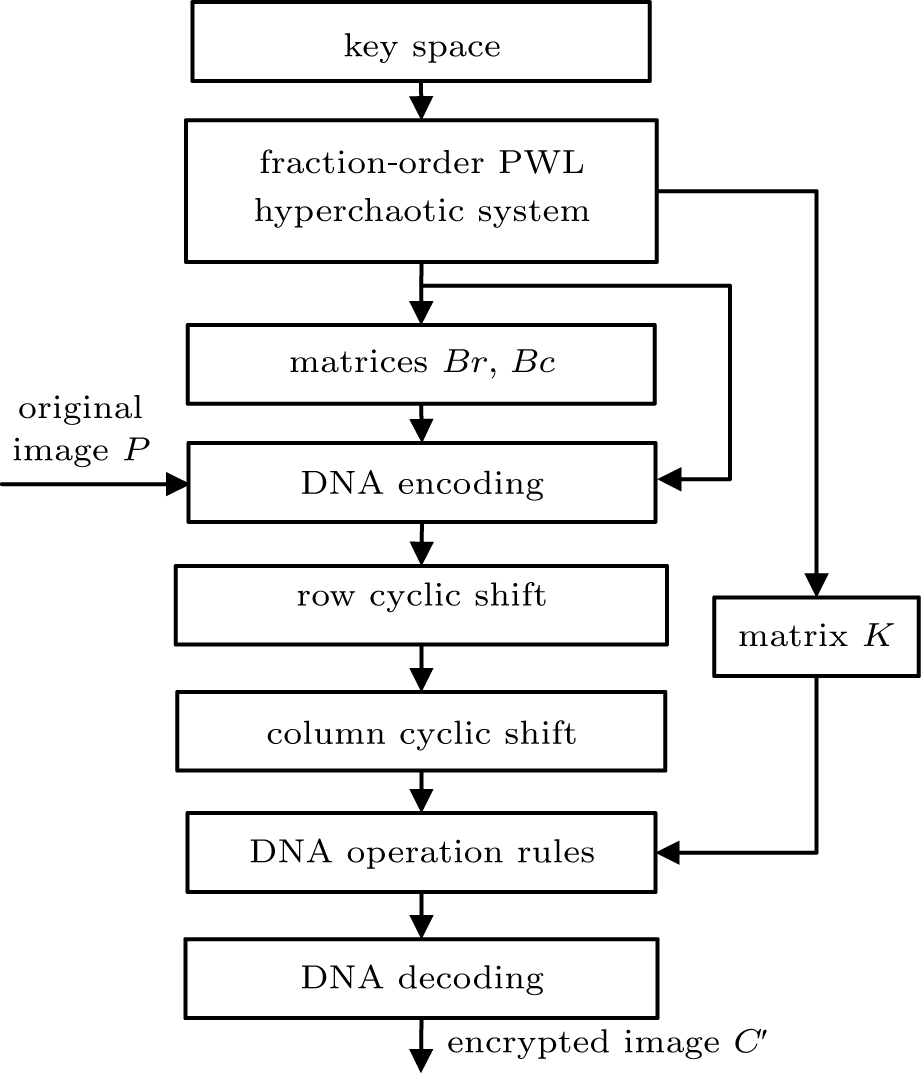
The flowchart of encryption scheme is shown in Fig.
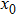
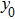
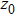
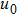
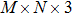
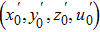
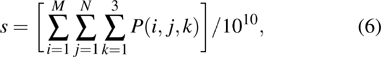 |
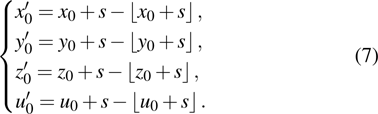 |
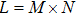
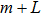
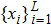
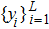
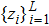
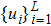
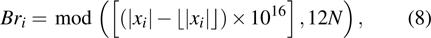 |
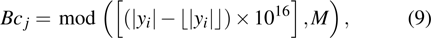 |
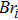
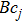
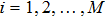
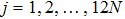
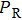
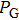
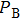
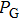
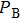
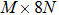
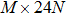
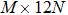
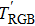
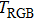
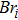
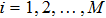
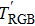
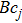
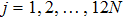
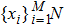
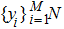
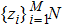
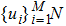
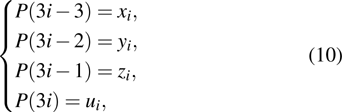 |
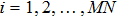
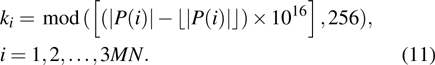 |
The sequence k is transformed to binary matrix, and the matrix is encoded by using the same DNA rule α to obtain the matrix K with 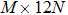
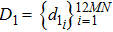
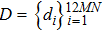
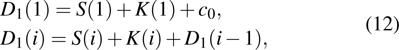 |
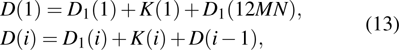 |
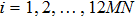
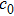
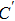
The decryption algorithm is the inverse of encryption algorithm. First of all, the encrypted image 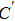
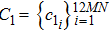
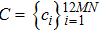
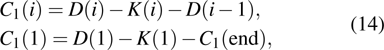 |
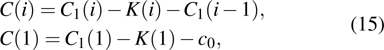 |
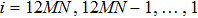
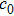
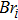
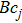
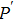
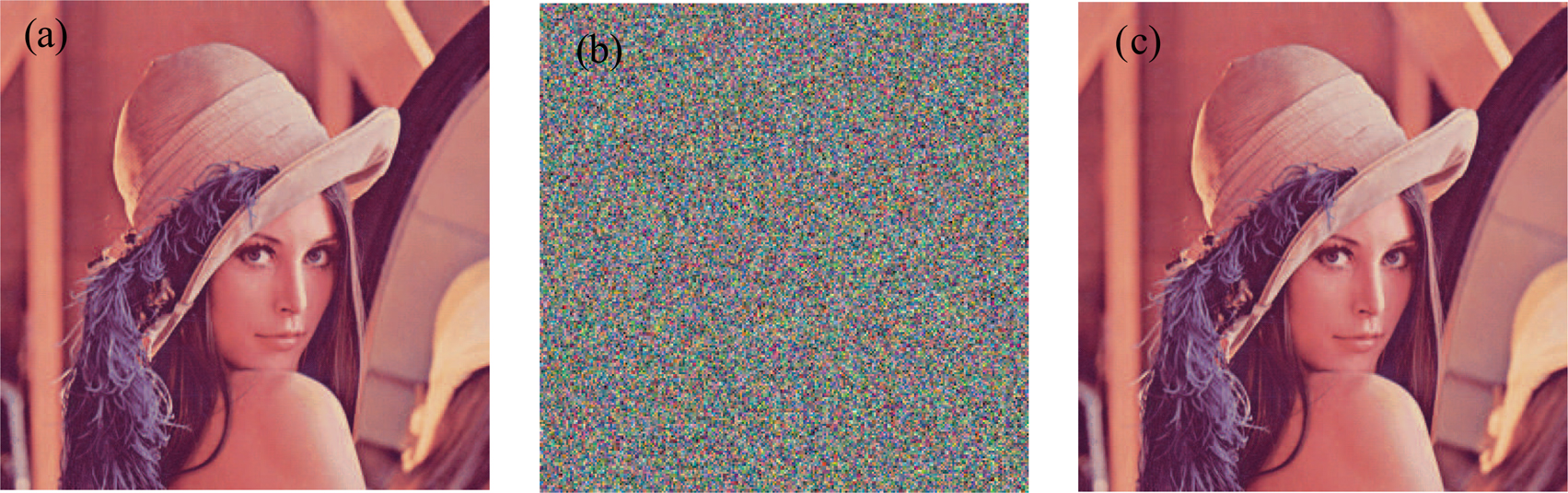
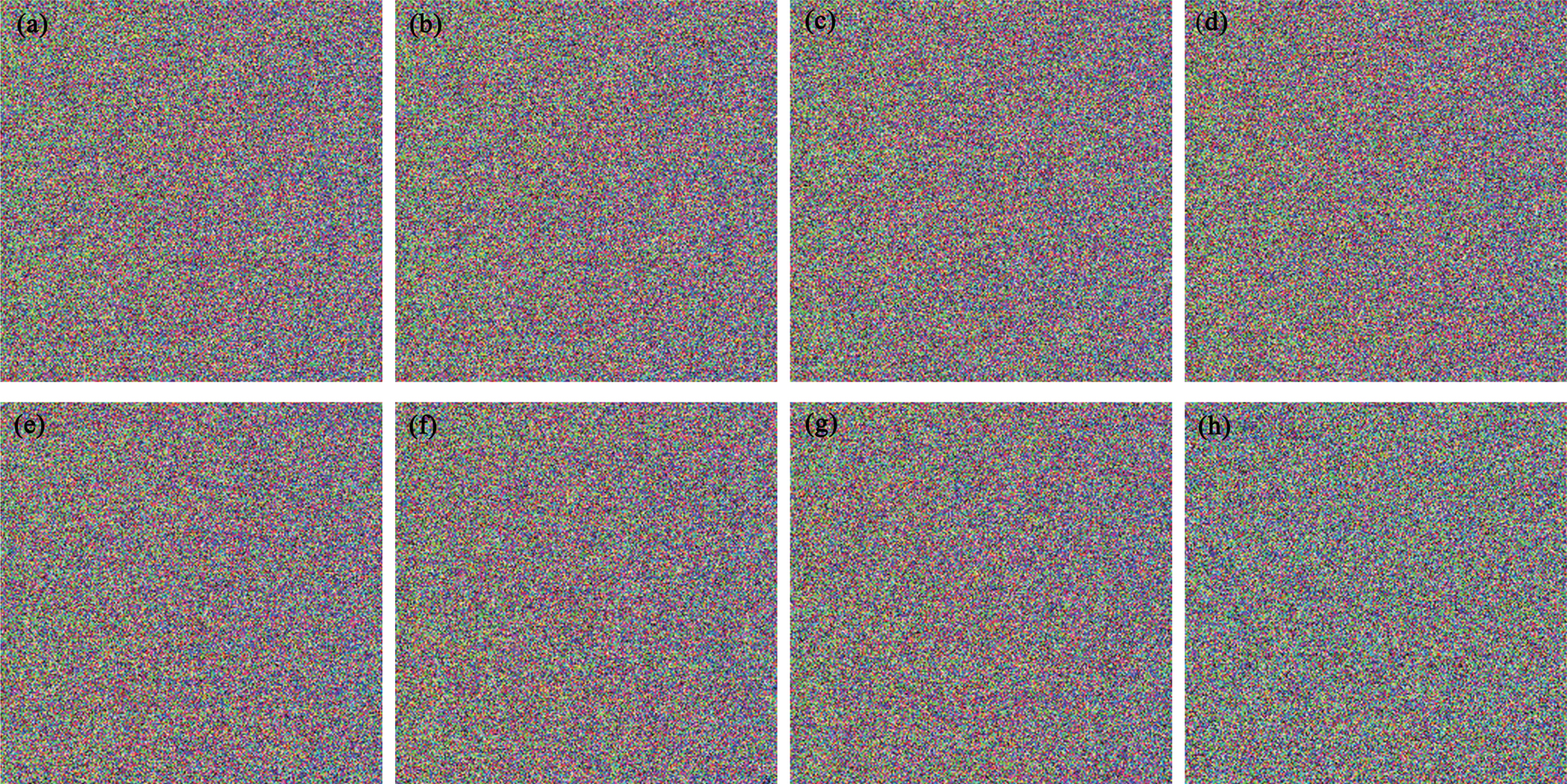
The simulation experiments are carried out on MATLAB 8.1, and the results are shown in Fig. 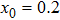
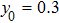
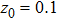
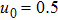
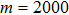
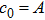
The size of the key space is the total number of different keys that should be large enough to withstand the brute-force attack. For the keys 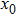
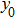
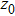
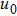
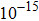
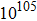
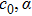
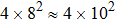
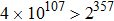
An efficient encryption scheme should also be sensitive to its secret key. It means that a very small change in the key will cause a significant change in the decrypted image. In this test, we employ a scheme to slightly change the keys to the following
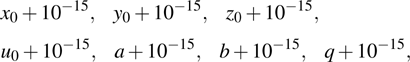 |
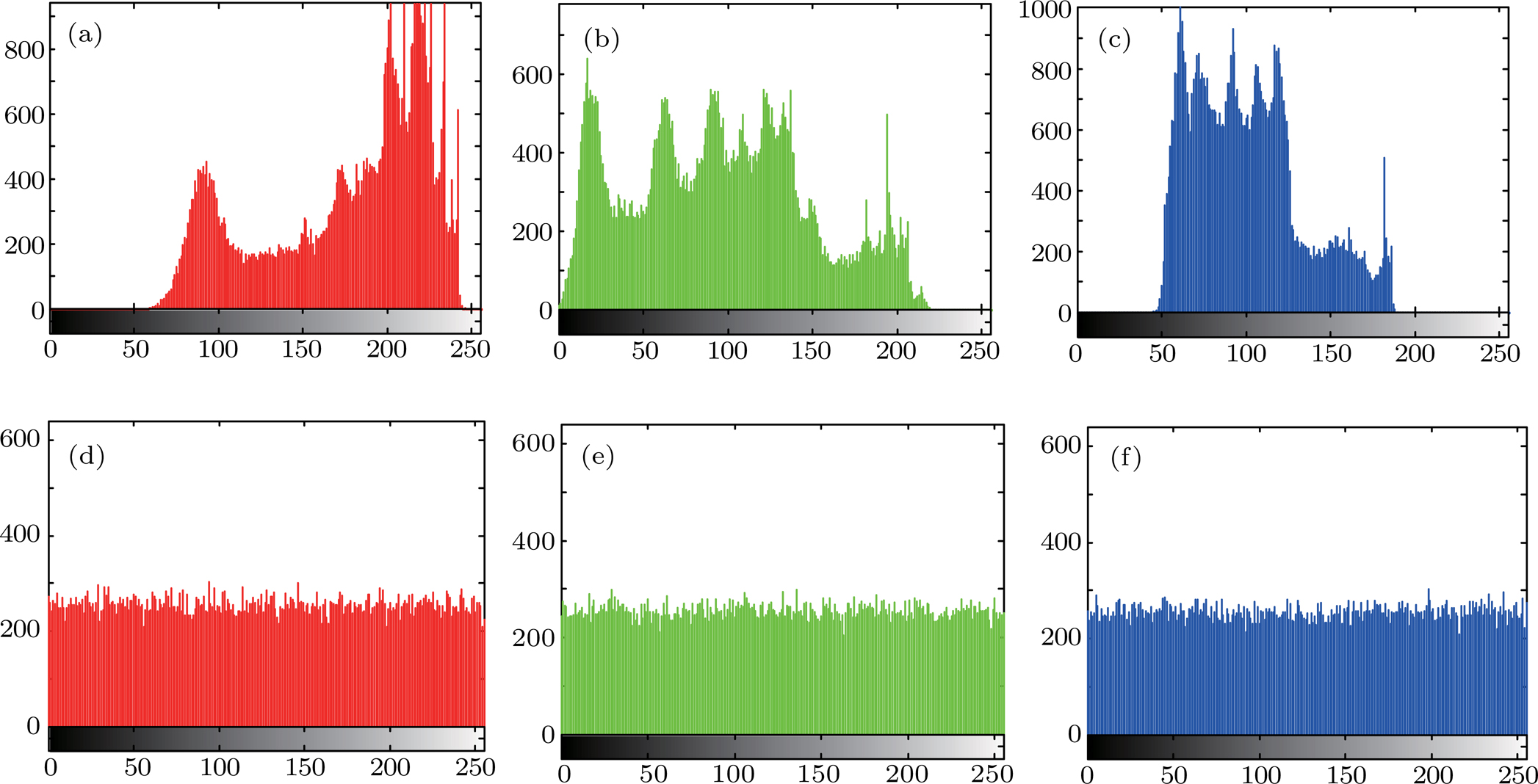
Shannon suggested that diffusion and confusion should be employed in a cryptosystem for frustrating a powerful statistical analysis.[26] Histogram and correlation coefficient of two adjacent pixels are employed to assess the ability of resisting statistical attack.
An ideal encryption algorithm should be robust against any statistical attack. Figure
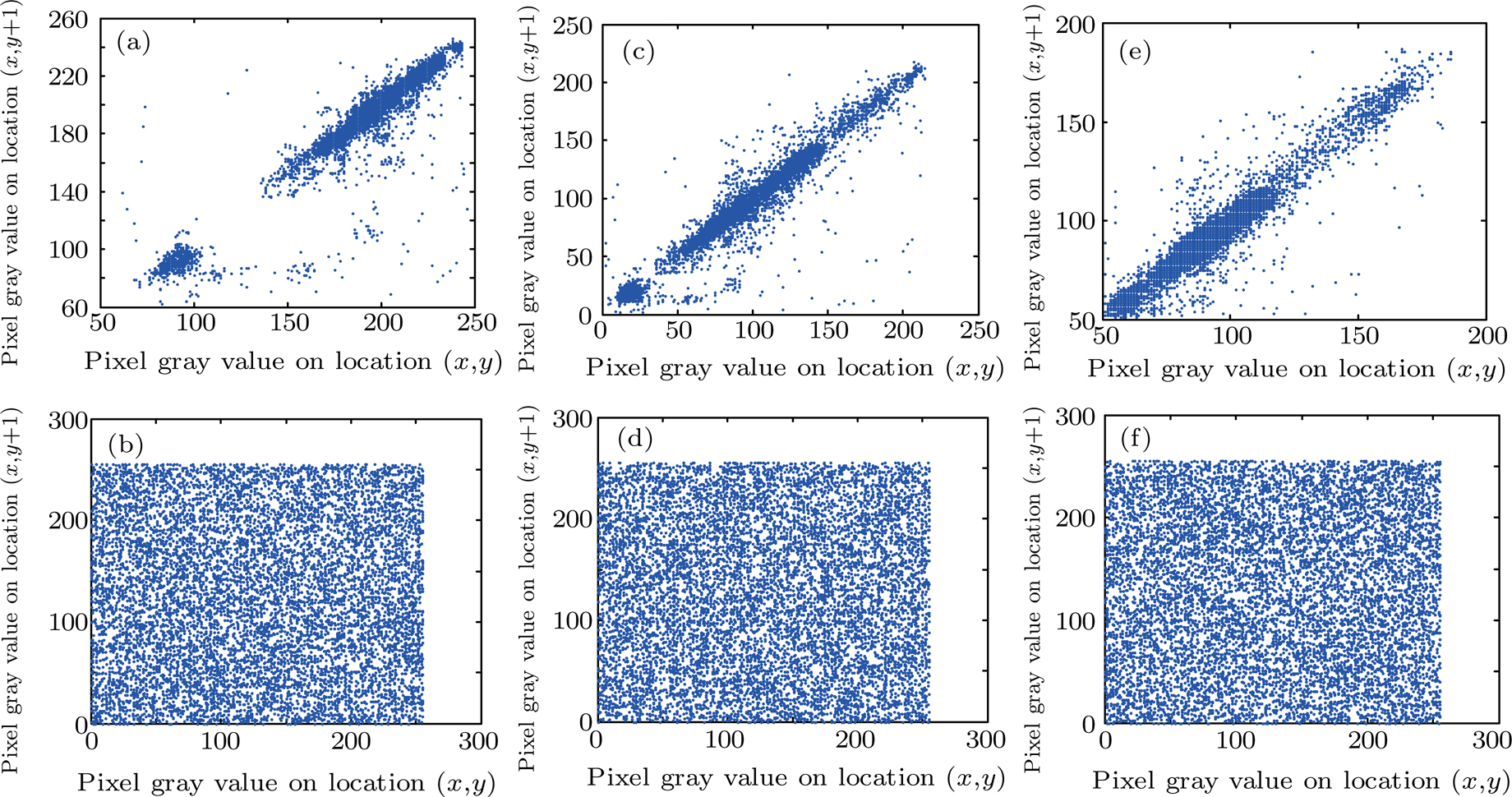
The effectiveness of an encryption algorithm is measured by the correlation of images. The correlation coefficient 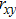
 |
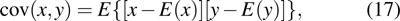 |
 |
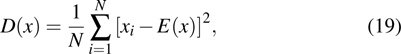 |
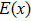
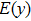
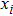
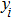
| Table 4.
Correlation coefficients of the original and encrypted images in R, G, B channels. . |
| Table 5.
Identical position correlation coefficients among R, G, and B channels. . |
| Table 6.
Adjacent position correlation coefficients among R, G, and B channels. . |
To demonstrate this result clearly, figure
The randomness of gray value is evaluated by information entropy, and it is defined by
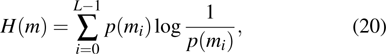 |
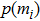
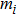
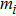
| Table 7.
Information entropy of encrypted images. . |
For an encryption algorithm, the ability of resisting differential attack is connected with the sensitivity to original image. It is evaluated by the number of pixels change rate (NPCR) and unified average changing intensity (UACI). The formula of calculating NPCR and UACI are defined as
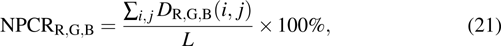 |
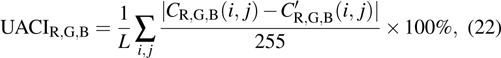 |
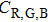
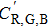
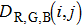
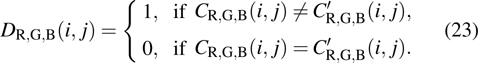 |
In our experiments, we only change the lowest bit of one random pixel of the original image. The average NPCRs and UACIs are obtained as listed in Table
| Table 8.
Mean NPCRs and UACIs of encrypted images. . |
We test the efficiency of this encryption algorithm. The experimental environment is MATLAB R2012a with Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-2350M CPU @ 2.3 GHz and 6.0G RAM on Windows 8 OS. In this experiment, the 256 × 256 color Lena image is encrypted by one round of each algorithm, and the total execution time is 3.4095 s, including 2.5805-s iteration time of fractional-order hyperchaotic system. The convergence rate of the ADM algorithm is faster than others, such as Adams–Bashforth–Moulton (ABM) algorithm and frequency-domain method. Although it is relative slow compared with the algorithm of integer-order chaotic system, ADM algorithm also has excellent convergence speed and accuracy.[30] In addition, if the experiment is implemented on other platform like C/C++, the speed will be faster.
In the key generation of permutation process, the proposed algorithm has low execution time because it only needs 
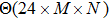
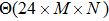
In this paper, based on the fractional-order PWL hyperchaotic map, a novel color image encryption algorithm is proposed combining with DNA sequence operations. The pixel values of the original image are shuffled by DNA sequence addition operation with the key matrix, and the positions of pixels are permuted by the pseudorandom sequences generated from the fractional-order PWL hyperchaotic systems in bidirectional directions. The experiments and security tests show the novel scheme has good encryption effect. It possesses large key space and high sensitive to the key, and can resist common attacks, such as statistical, differential, brute-force, known-plaintext, and chosen-plaintext attacks. Thus, the proposed algorithm has wide application prospect in the future.
| [1] | |
| [2] | |
| [3] | |
| [4] | |
| [5] | |
| [6] | |
| [7] | |
| [8] | |
| [9] | |
| [10] | |
| [11] | |
| [12] | |
| [13] | |
| [14] | |
| [15] | |
| [16] | |
| [17] | |
| [18] | |
| [19] | |
| [20] | |
| [21] | |
| [22] | |
| [23] | |
| [24] | |
| [25] | |
| [26] | |
| [27] | |
| [28] | |
| [29] | |
| [30] |