Bloom’s syndrome protein unfolding G-quadruplexes in two pathways
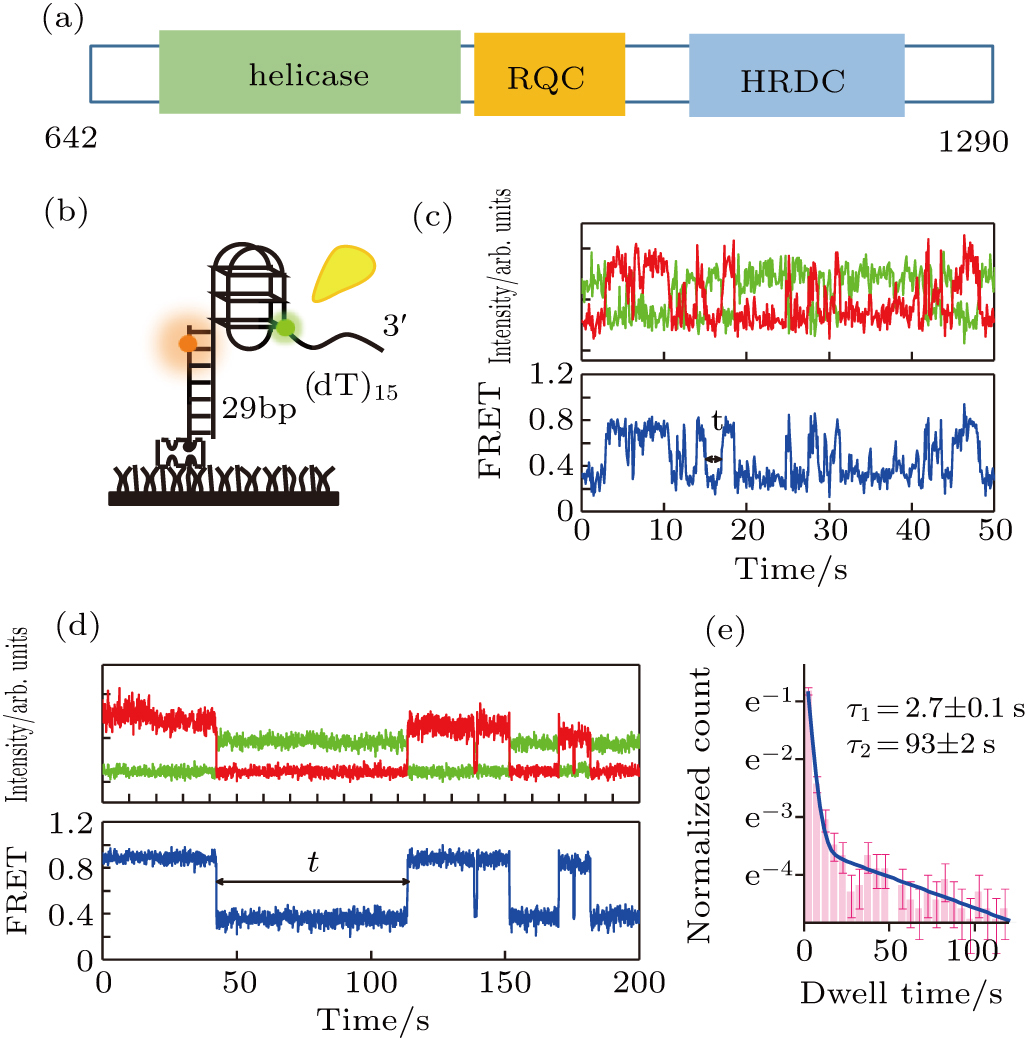
(color online) BLM unfolds G4 at 200-μM ATP. (a) BLM protein functional domains used in this study. (b) Schematic diagram of Cy3 (green)- and Cy5 (red)-labeled DNA construct (G4) with G4 having three G-quartet planes. G4 strand and complementary stem strand are annealed to form a duplex stem. Biotin is used to immobilize the DNA to a streptavidin-coated coverslip surface. (c) and (d) Traces of fluorescence intensities of Cy3 and Cy5 (upper panel) and FRET trace (lower panel) with 2-nM BLM and 200-μM ATP. The dwelling time of the completely unfolded state is denoted as t. (e) Histograms of the dwelling times for the completely unfolded G4. Error bar = s.e.m.