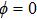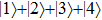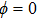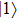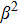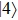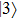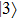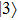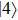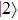|
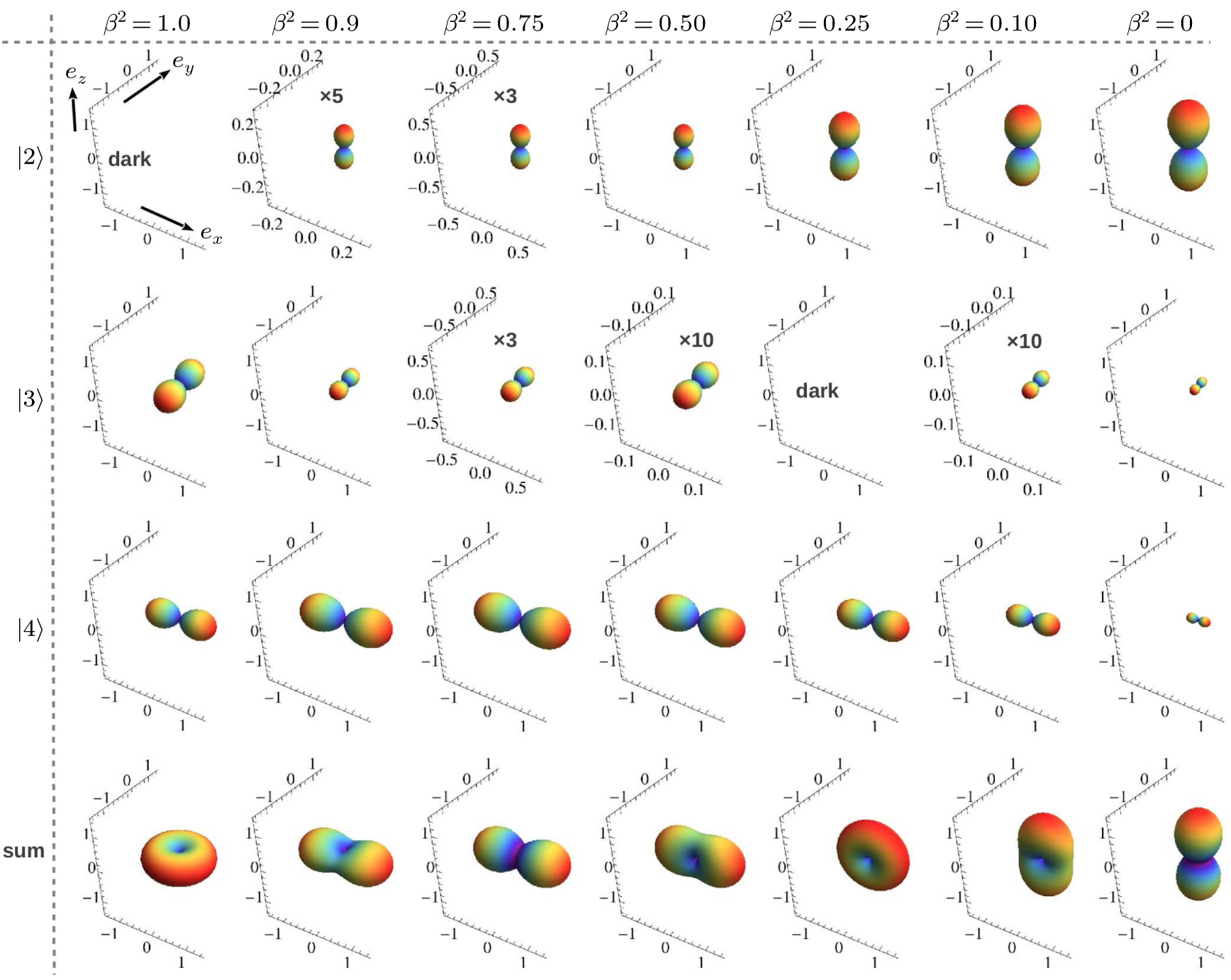
(color online) Three-dimensional polar plots of transition dipole moments of different states of ground state exciton for different magnitudes of LH–HH mixing with 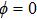 in a QD. The sum represents the total oscillator strength of
in a QD. The sum represents the total oscillator strength of 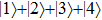 . In the case of
. In the case of 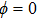 , the state
, the state 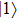 is always dark for any value of
is always dark for any value of 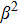 . The state
. The state 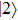 becomes bright with the direction of polarization along the growth direction of the QD for a nonzero value of the LH character in the hole states. The intensity of this state increases with an increase in the LH character. The
becomes bright with the direction of polarization along the growth direction of the QD for a nonzero value of the LH character in the hole states. The intensity of this state increases with an increase in the LH character. The 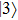 and
and 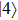 states are equally bright with directions of polarization in the growth-plane of the QD. However, for the case of mixed HH-LH hole states the intensity of
states are equally bright with directions of polarization in the growth-plane of the QD. However, for the case of mixed HH-LH hole states the intensity of  decreases, while that of
decreases, while that of 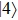 increases with an increase in LH character. Eventually the
increases with an increase in LH character. Eventually the 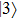 becomes dark for about 75% LH character in the hole state. For further increase in LH character the
becomes dark for about 75% LH character in the hole state. For further increase in LH character the 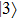 becomes bright again. For pure LH the
becomes bright again. For pure LH the 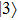 and
and 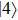 are equally bright with the directions of polarization normal to each other in the growth-plane, while
are equally bright with the directions of polarization normal to each other in the growth-plane, while 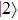 is strongly bright with the direction of polarization along the growth direction of the QD.
is strongly bright with the direction of polarization along the growth direction of the QD.
|