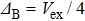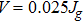(color online) (a) Schematic diagram of the superexchange and inter-orbital spin-exchange interactions. The
 atoms are independently trapped in the shallow (deep) superlattice, whose nuclear spin states are marked by
atoms are independently trapped in the shallow (deep) superlattice, whose nuclear spin states are marked by
 and
and
 . The superexchange process (green arrow) happens between AFM states (
. The superexchange process (green arrow) happens between AFM states (
 ) via virtual tunneling (black dashed arrows), while two-orbital spin-exchange interaction (red arrows) couples
) via virtual tunneling (black dashed arrows), while two-orbital spin-exchange interaction (red arrows) couples
 with the magnetic state
with the magnetic state
 . (b) Time evolution of the spin imbalance Ngz of the g atoms (black) and the population of the state
. (b) Time evolution of the spin imbalance Ngz of the g atoms (black) and the population of the state
 (blue) for a small magnetic field (the resulting differential Zeeman shift can be ignored) and the initial state
(blue) for a small magnetic field (the resulting differential Zeeman shift can be ignored) and the initial state
 . The envelope of Ngz is given by
. The envelope of Ngz is given by
 (red). The collapse and revival happen at
(red). The collapse and revival happen at
 and
and
 , respectively. (c) Energy levels of the perturbation model (left) and the eigenstates (right).
, respectively. (c) Energy levels of the perturbation model (left) and the eigenstates (right).
 .
.
 are the coupling matrix elements. δ is the energy shift. The red solid and blue dashed arrows indicate the near-resonant coupling and far-off-resonant coupling, respectively. (d) Time evolution of the spin-imbalance of g atoms with
are the coupling matrix elements. δ is the energy shift. The red solid and blue dashed arrows indicate the near-resonant coupling and far-off-resonant coupling, respectively. (d) Time evolution of the spin-imbalance of g atoms with
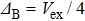 (black line). The envelope (red solid) corresponds to
(black line). The envelope (red solid) corresponds to
 . The parameters are
. The parameters are
 ,
,
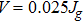 ,
,
 in panels (b) and (d).
in panels (b) and (d).
|