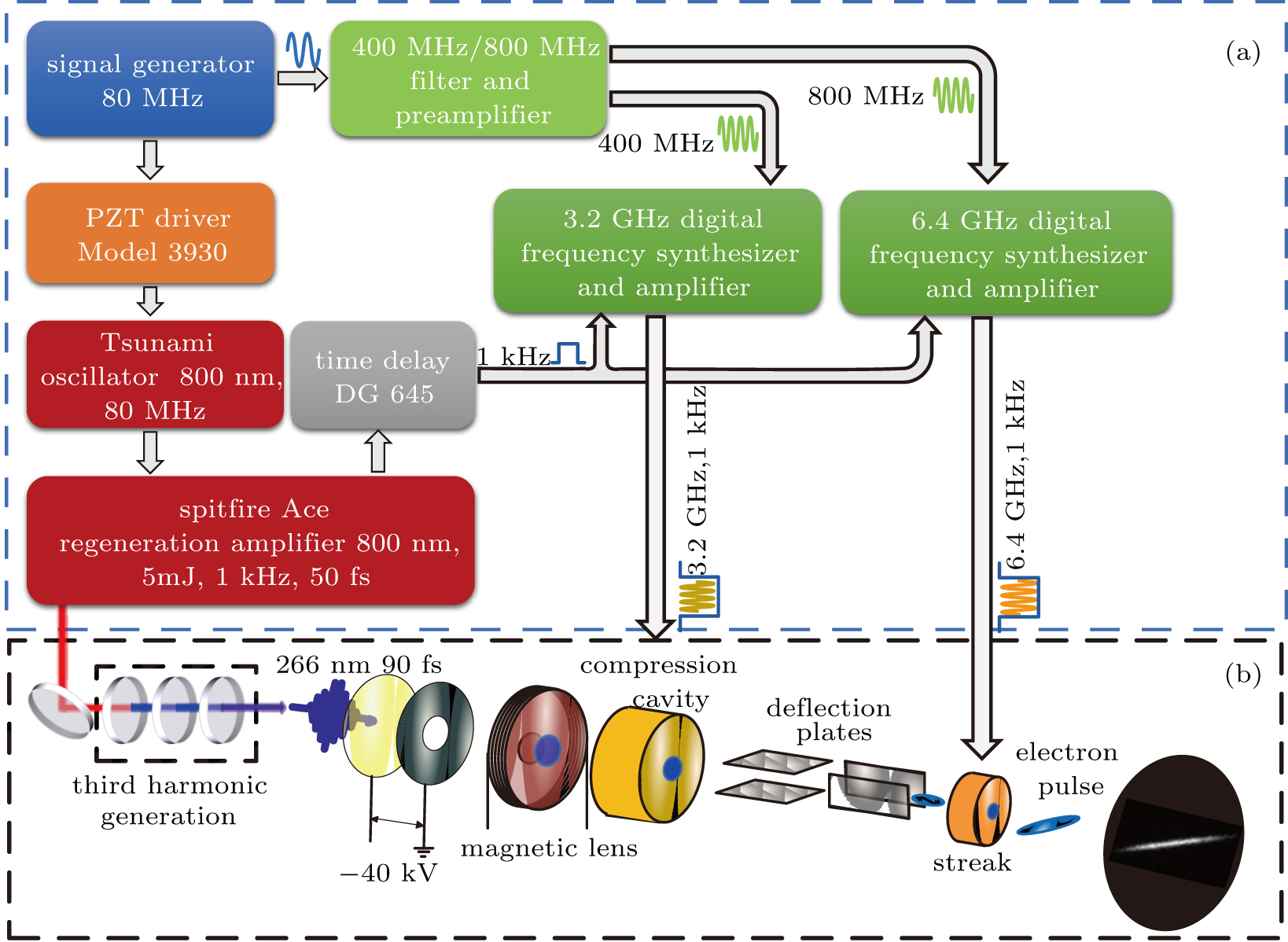
Compressing ultrafast electron pulse by radio frequency cavity
(color online) Experimental arrangement of the ultrafast electron diffraction system based on a radiofrequency compression method. Panel (a) shows the block diagram of the synchronization regime, where the 80-MHz signal generator is used to generate the 3.2-GHz and 6.4-GHz frequency synchronizers by a frequency multiplication and power amplification, and is also used to lock the femtosecond laser system by a phase lock loop; panel (b) displays the schematic diagram of the electron gun, where the electron pulse is generated by back illuminating a 20-nm thick gold film, accelerated to 40 keV by a static electric field, focused by a magnetic lens, and finally compressed by a compression cavity. The electron pulse width is measured by a streak cavity combining with CCD.