|
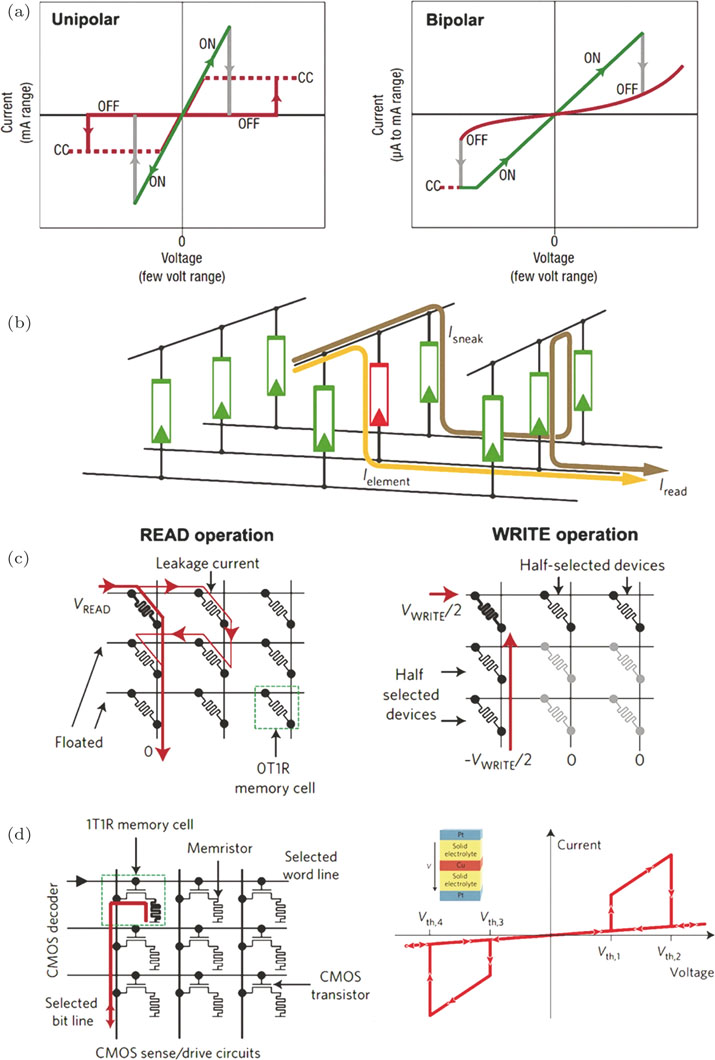
(color online) (a) Classification of the switching characteristics based on the set/reset voltage polar.[54] Left: unipolar switching. The set voltage is higher than the reset voltage, and the reset current is higher than the compliance current (CC) during set operation. Right: bipolar switching. The set voltage and reset voltage have the opposite polarity. (b) Crossbar array and the sneak leakage path issue.[18] When we try to read/write the selected element, the sneak leakage current will affect the operations. (c) Schematic shows the effect of sneak leakage path to read/write operations.[2] Left: read operation. When trying to read the state of the addressed element, the leakage current from adjacent elements in the low resistance state will degrade the output signal. Right: write operation. During the write operation, the extra voltage drop along half-selected elements will lead to an insufficient voltage at the selected element. (d) The solutions for sneak leakage path problem.[2,18] Left: 1-transistor/1-resistor (1T1R) cell architecture which only enables read/write to a particular row. Right: using complementary structure to produce a complementary switching characteristics.
|