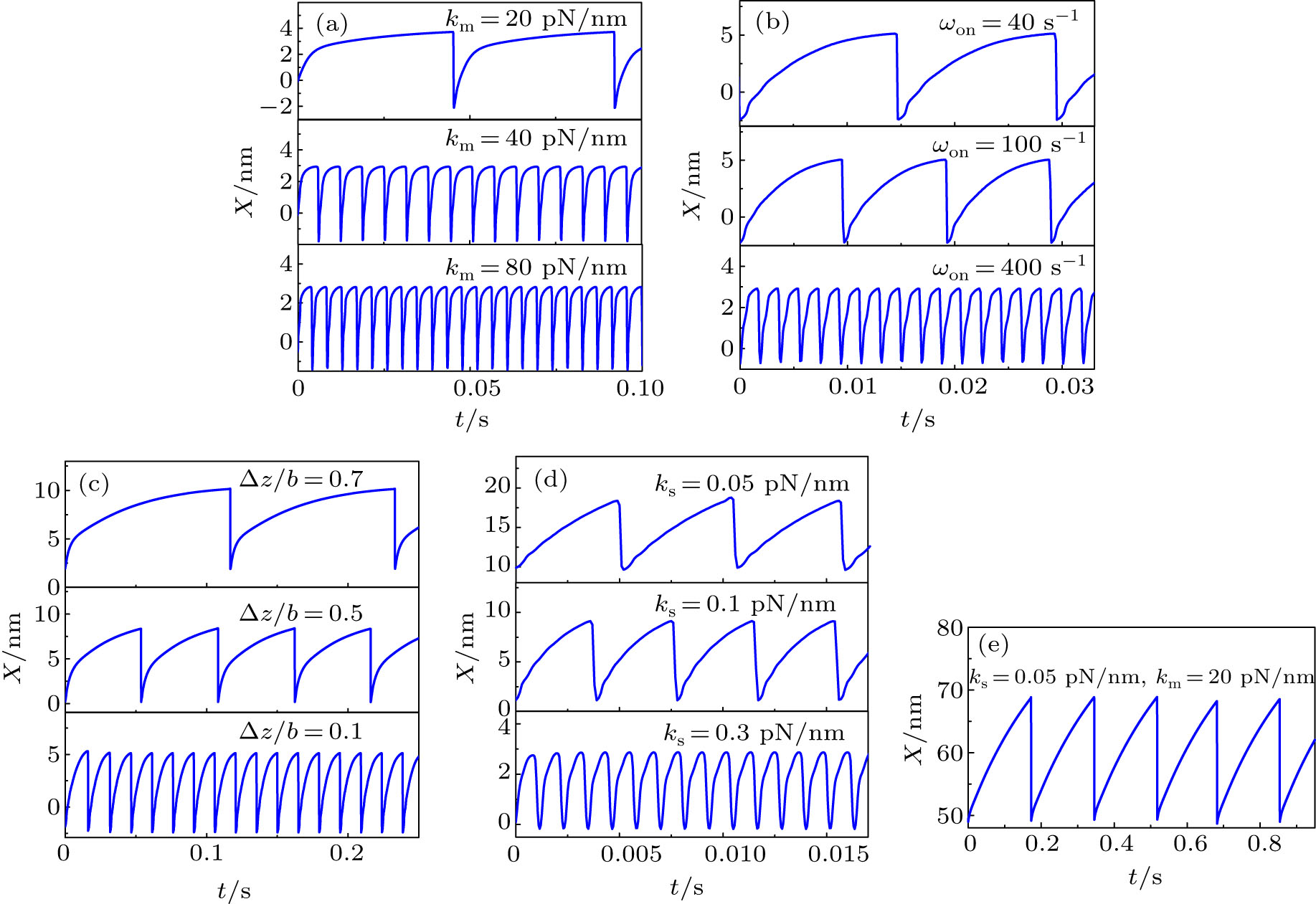
The oscillation frequency is related to some parameters. (a) The oscillation frequency increases with motor stiffness km, where ks = 1.0 pN/nm per motor, ωon = 40 s−1, and Δz/b = 0.1. (b) The oscillation frequency increases with motor binding rate ωon, where ks = 0.5 pN/nm per motor, km = 80 pN/nm, and Δz/b = 0.1. (c) The oscillation frequency increases with the decrease of Δz/b, where ks = 0.5 pN/nm per motor, km = 80 pN/nm, and ωon = 40 s−1. (d) The oscillation frequency increases with spring stiffness ks, where km = 80 pN/nm, ωon = 1000 s−1, and Δ z/b = 0.1. (e) The oscillation frequency is a few Hz when ks = 0.05 pN/nm per motor, km = 20 pN/nm, ωon = 40 s−1, and Δz/b = 0.1. The other parameters are the same as those in Fig. 2. |