Shang Xiang-Jun 1, 2, Xu Jian-Xing 1, 2, Ma Ben 1, 2, Chen Ze-Sheng 1, 2, Wei Si-Hang 1, 2, Li Mi-Feng 1, 2, Zha Guo-Wei 1, 2, Zhang Li-Chun 1, 2, Yu Ying 1, 2, Ni Hai-Qiao 1, 2, Niu Zhi-Chuan 1, 2, †,  |
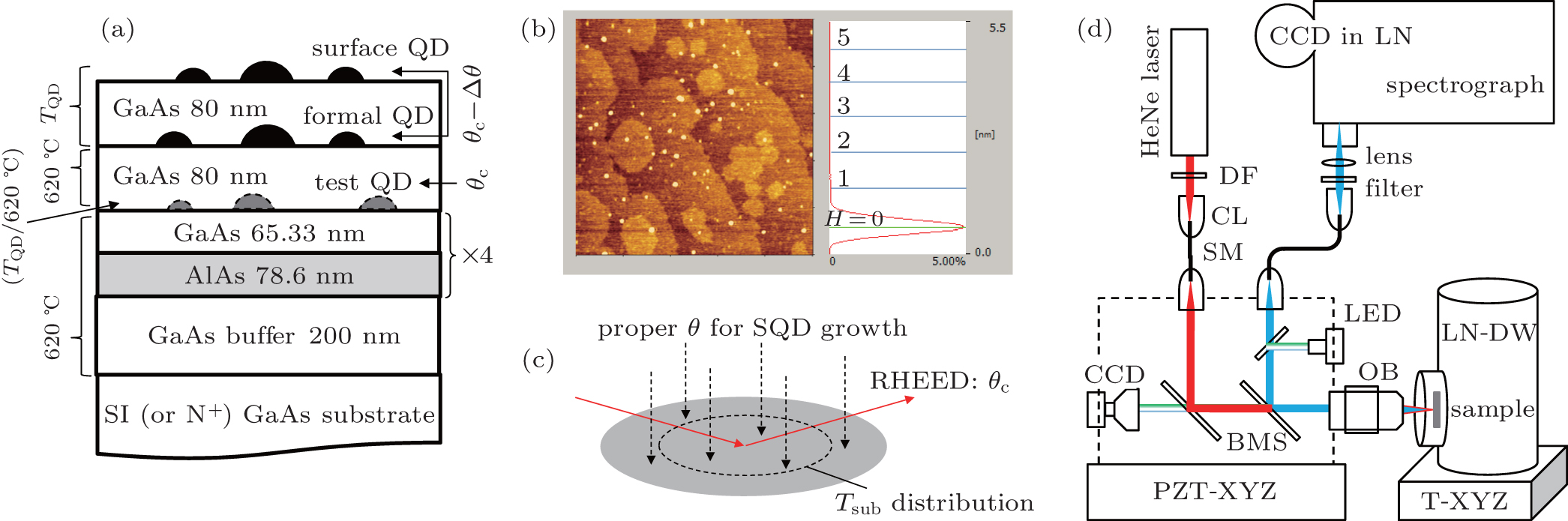
(a) Sample structure with Tsub. (b) QD height statistics (height is leveled into H = 1, 2,…, nm, the baseline (green) is set according to pixel height distribution (red). (c) Test-QD in-situ annealing method. (d) Confocal μPL spectrograph. LN-DW: liquid nitrogen (LN)-cooled Dewa (∼ 80 K); OB: objective (Miltituyo, 100 ×, numerical aperture: 0.55, working distance: 13 mm); LED: white light for CCD imaging; DF: density filter; SM: single-mode fiber; CL: focus tunable collimators (Thorlabs); BMS: 50:50 wideband beamspliter (Thorlabs); Dashed rectangular: cage cubes (Thorlabs); Red: HeNe laser (λ = 632.8 nm) as excitation; Blue: filtered (λ > 800 nm) luminescence; PZT-XYZ: piezoelectric transition stage; T-XYZ: manual one; CCD in LN: PyLon100; Spectrograph: SP2750 (Princeton Intruments). Attenuated by density filters, the focused laser spot on the sample is ∼ 1 μW in power and ∼ 2 μm in diameter. It scans the sample by the transition stages for a fast (t = 1 s) spectrograph to search SQD spectral lines. The luminescence is collected effectively by the objective and then extracted to the spectrograph by a fiber and collimators. |