Physical mechanism of mind changes and tradeoffs among speed, accuracy, and energy cost in brain decision making: Landscape, flux, and path perspectives
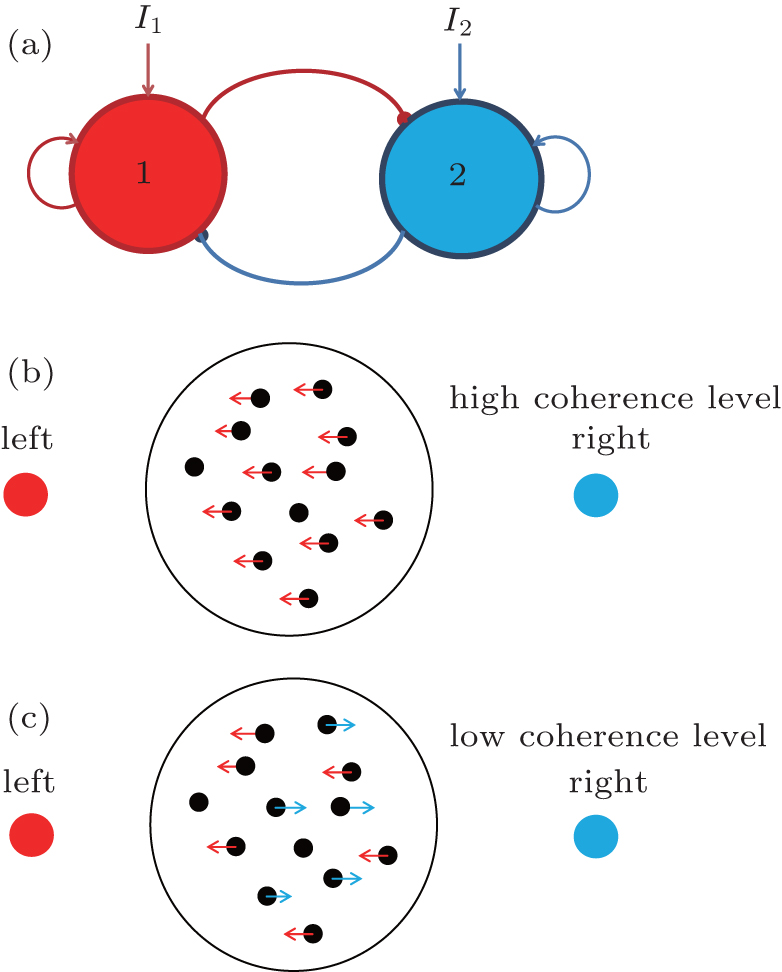
(a) The schematic diagram of the reduced two-population decision-making model. This reduced model consists of two competing neural populations that are selective for leftward or rightward directions, respectively. The arrows represent excitatory connections, and the lines with solid circles represent inhibition. (b) and (c) The schematic representation of the random dots motion. For higher motion coherence, most dots move in one direction, whereas the dots move with no directional bias at a low motion coherence level.