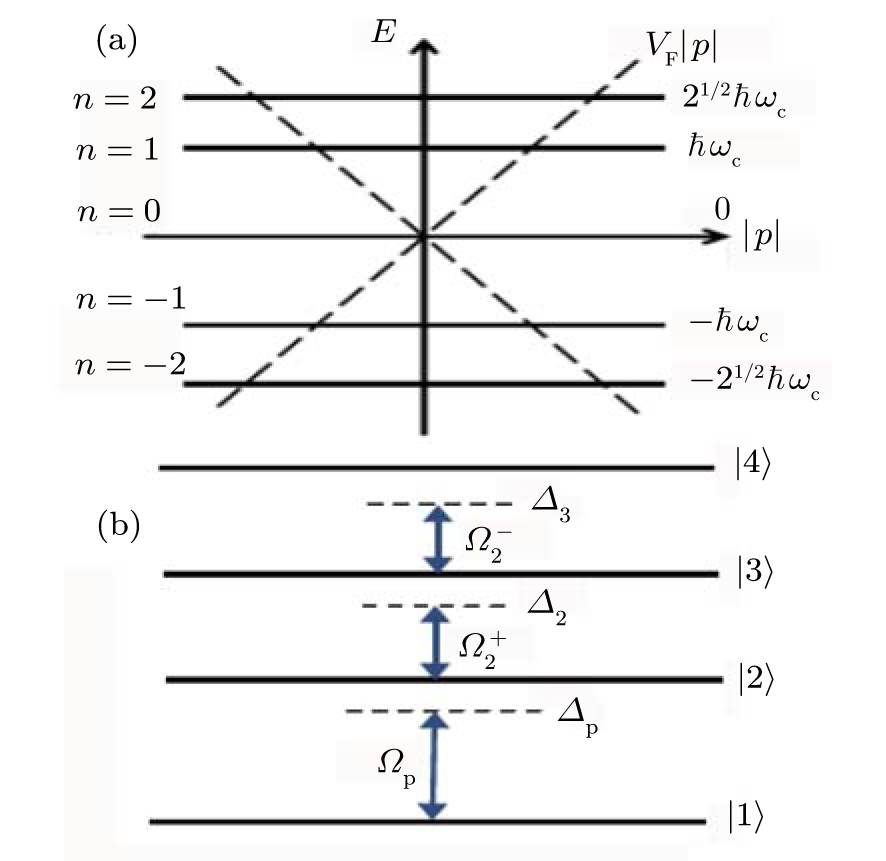
(a) LLs near the K point superimposed on the electronic energy dispersion without a magnetic field E = ±vF |p|. The magnetic field condenses the original states in the Dirac cone into discrete energies. The LLs in graphene are unequally spaced: (b) Energy level diagram and optical transitions in graphene interacting with two continuous-wave control fields, a cycling coupling field, and a weak pulsed probe field. The states |1〉, |2〉, |3〉, and |4〉 correspond to the LLs with energy quantum numbers n = −2,−1, 0, and 1, respectively. Graphene monolayer is a one-atom-thick monolayer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, which we will treat as a perfect two-dimensional (2D) crystal structure in the x–y plane. |