Heo Jino 1, 2, Hong Chang-Ho 1, 2, Lee Dong-Hoon 1, 2, Yang Hyung-Jin 1, 3, †,  |
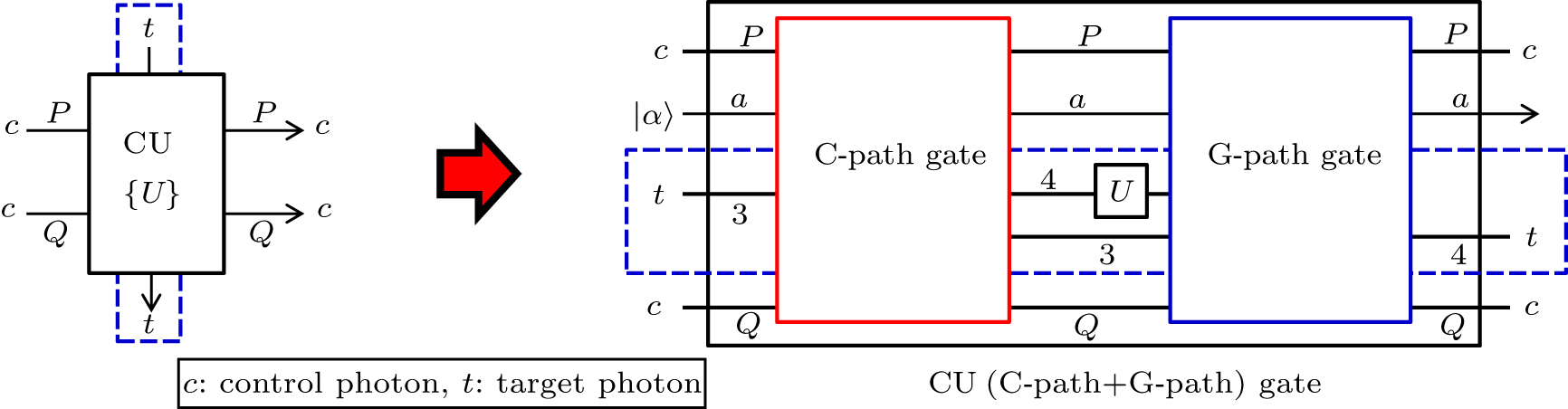
Photon T is used as a control qubit, and the photons A, 2, and B are used as target qubits in the CU operations. These CU operations are implemented by the CU gates, in which the C-path and G-path gates are consecutively performed by XKNLs, the qubus beams, the QND (PNR) measurements, and feed-forwards, as described in Section 2. If the unitary operator U in the middle between the C-path and G-path gates is σX the CU gate will become a CNOT, whereas if the operator is σZ the CU gate will become a CZ. For the BTQI scheme, the details of this CU gate are presented in Appendix A. |