Controlled mutual quantum entity authentication using entanglement swapping
Controlled mutual quantum entity authentication using entanglement swapping |
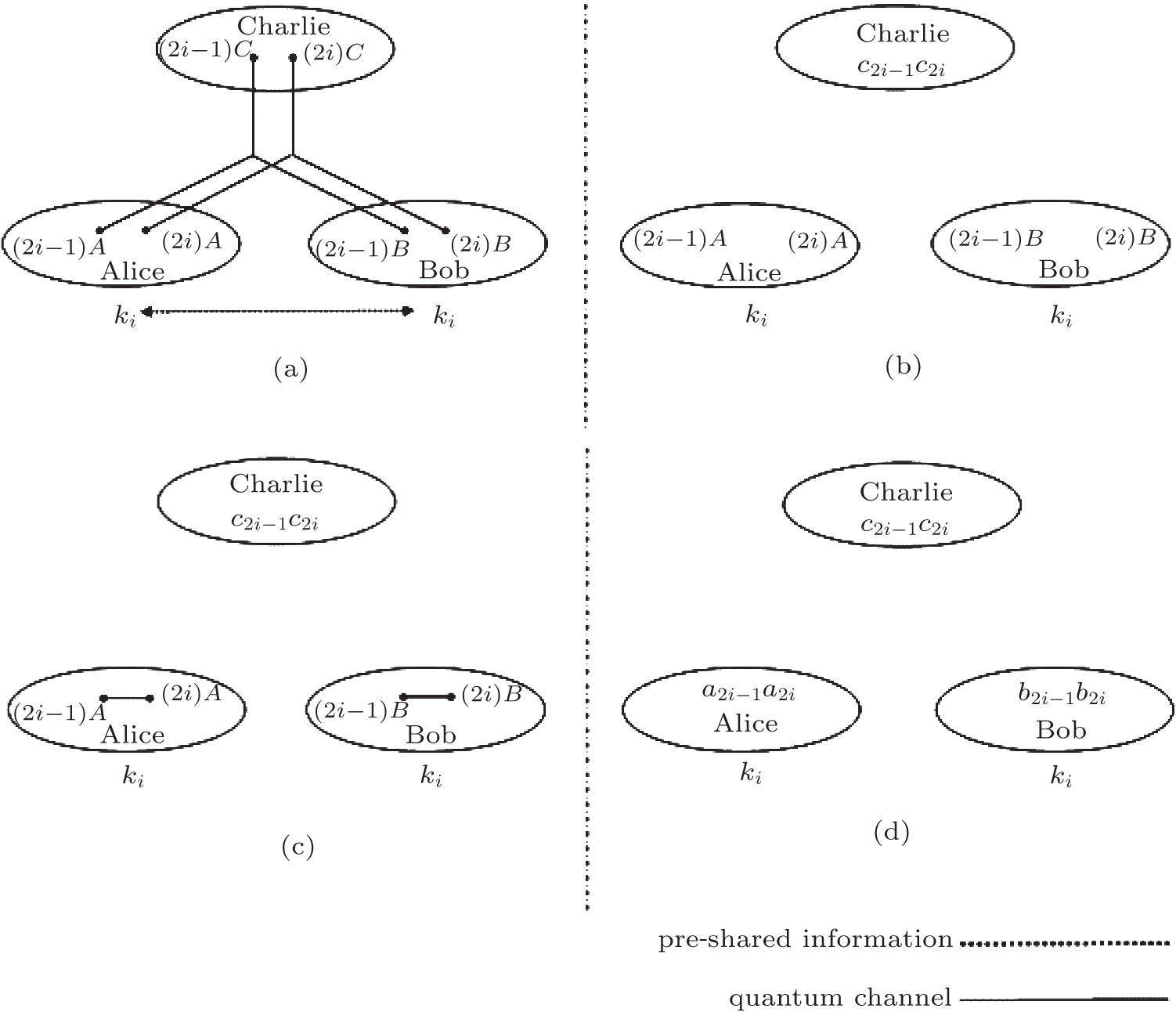
| Schematic representation of controlled mutual quantum entity authentication. (a) Alice and Bob share secret information k i for entity authentication. Alice, Bob, and Charlie share the GHZ-like states , which Charlie prepared in advance. (b) Charlie gains the classical bit, c 2 i − 1 c 2 i , which corresponds to the measurement outcome by the von Neumann measurement. Alice and Bob share one pair of Bell states with Charlie’s measurement. (c) and (d) Alice and Bob swap one pair of the shared entangled states and, respectively, gain classical bit a 2 i − 1 a 2 i and b 2 i −1 b 2 i as measurement outcomes. Subsequently, as shown in phase E4, Alice and Bob carry out mutual entity authentication under Charlie’s control. |
 |