Structural and robustness properties of smart-city transportation networks
Structural and robustness properties of smart-city transportation networks |
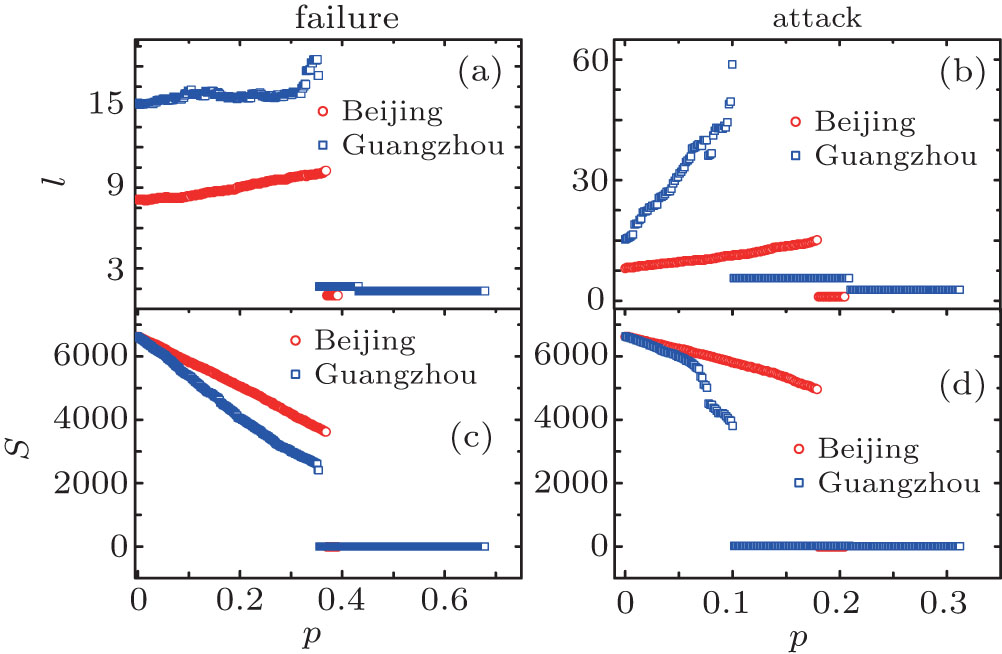
| The transportation network fragmentation under random failures and attacks of nodes. The average path length l and the size of the largest component S as a function of the fraction of removed nodes p for the same systems. (a) and (c) Fragmentation of the network under random failures, l and S change with the increase of p , and the phase transition point is about p ≈ 0.35. (b) and (d) Fragmentation of the network under attack failures, the network breaks down just after several steps at p ≈ 0.1 for Guangzhou, and p ≈ 0.2 for Beijing. |
 |