Transient thermal analysis as measurement method for IC package structural integrity
Transient thermal analysis as measurement method for IC package structural integrity |
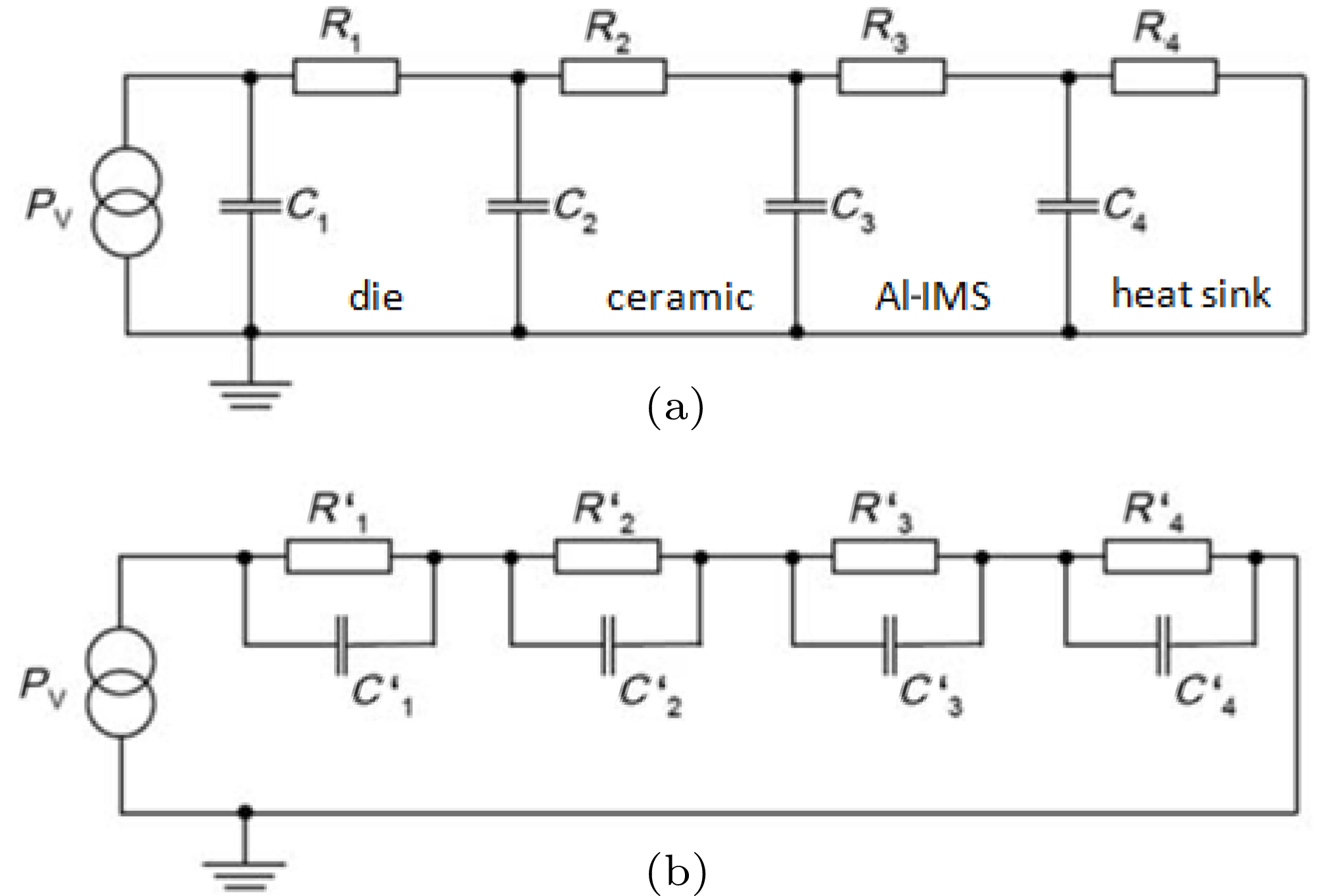
| Simplified equivalent network of the ceramic LED package of Al-IMS. In panel (a) the physical Cauer Network is represented. The physical thermal masses are “charged” with heat in reference to the ambient temperature, which is equivalent with the ground. Four main capacities are approximated: C 1 = C die, C 2 = C ceramic, C 3 = C Al-core, C 4 = C heat sink. The thermal masses of the electric layer and the solder joint are included in C 2. The thermal resistances are approximated: R 1 contains the thermal resistance of the die and the interconnect of the die to the ceramic ( R 1 = R die + R interconnect), R 2 contains the thermal resistance of the ceramic (small), the solder joint (medium) and the electric copper layer (small) and the dielectric layer of the IMS (large), R 3 contains the thermal resistance of the Al-core (small) of the IMS and the TIM (large) to the heat sink, R 4 contains the thermal resistance of the heat sink and the thermal resistance of the heat sink to the ambient air temperature. (b) The physical Cauer network can be transformed by partial fraction decomposition into the Foster network. |
 |