Water-assisted highly enhanced crystallographic etching of graphene by iron catalysts
Water-assisted highly enhanced crystallographic etching of graphene by iron catalysts |
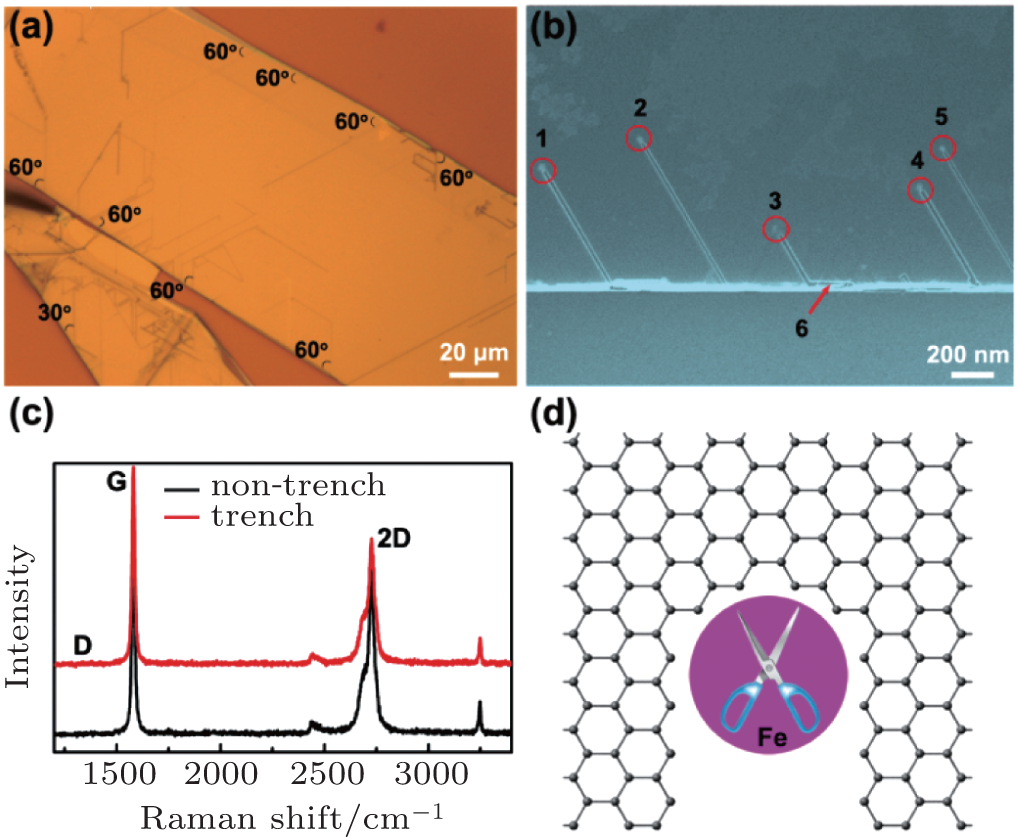
| Nanocutting of graphene by iron catalysts: (a) Experimental visulisation of the nanotrenches at graphite edges by an optical microscope. (b) SEM image of nanotrenches at a graphite edge by changing the etching time to 1 min. It is noted that the cutting tends to start at graphene step edges with angles of 60° and the nanoparticles can be found at the end of the nanotrenches. (c) Raman spectra collected on graphite without (black) and with (red) nanotrenches. (d) Schematic of the crystallographic graphite etching process. As the catalyst directly contacts the graphene edges, it would react with the corresponding active carbon atoms, move forward and break the carbon-carbon bonds in graphene along specific crystallographic directions. |
 |