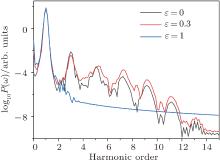
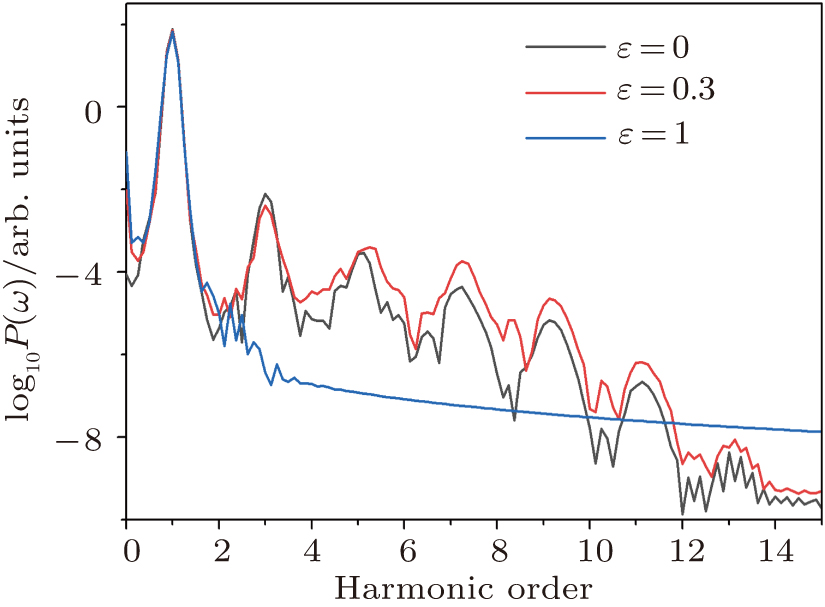
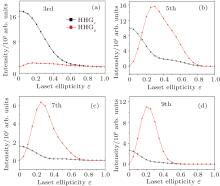
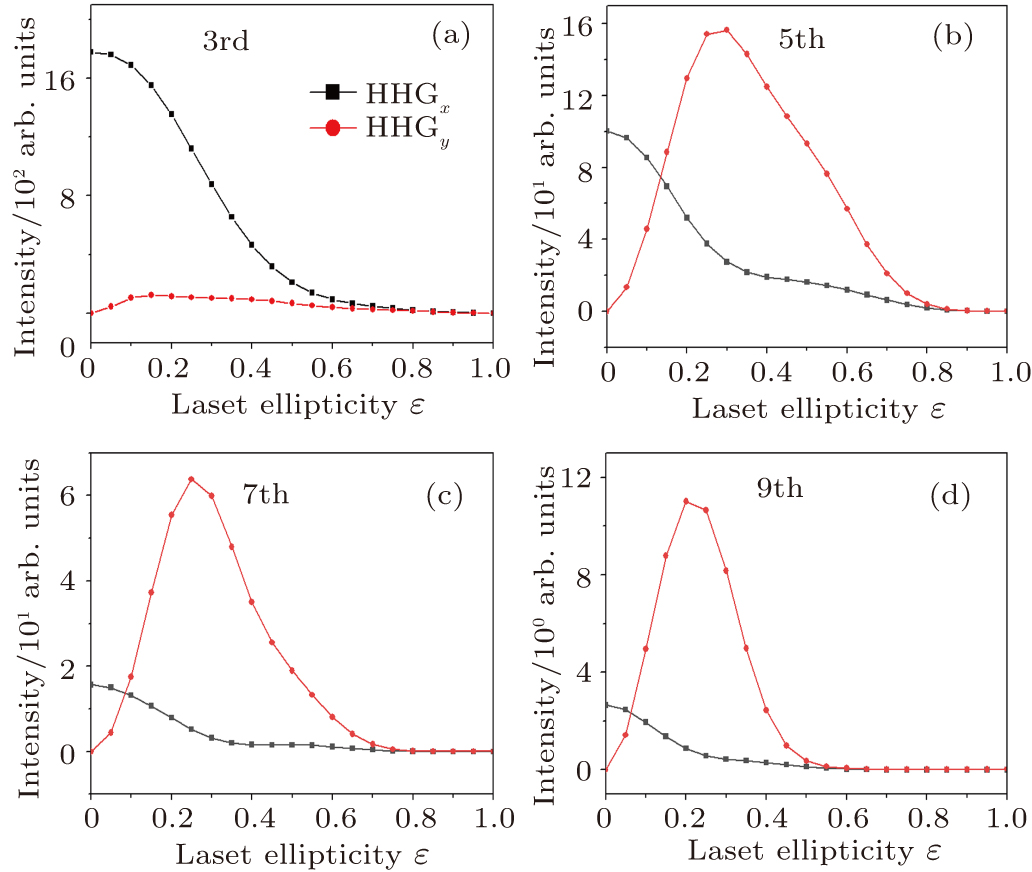
中国物理B ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 104206-.doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/abab76
Zhong Guan(管仲)1, Lu Liu(刘璐)2, Guo-Li Wang(王国利)1,†( ), Song-Feng Zhao(赵松峰)1, Zhi-Hong Jiao(焦志宏)1, Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信)1,‡(
), Song-Feng Zhao(赵松峰)1, Zhi-Hong Jiao(焦志宏)1, Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信)1,‡( )
)
-
收稿日期:2020-04-26修回日期:2020-06-15接受日期:2020-08-01出版日期:2020-10-05发布日期:2020-10-05 -
通讯作者:Guo-Li Wang(王国利), Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信)
An improved method for the investigation of high-order harmonic generation from graphene
Zhong Guan(管仲)1, Lu Liu(刘璐)2, Guo-Li Wang(王国利)1,†, Song-Feng Zhao(赵松峰)1, Zhi-Hong Jiao(焦志宏)1, and Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信)1,‡
- 1
College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Northwest Normal University , Lanzhou 730070,China
2Department of Physics, College of Science, National University of Defense Technology , Changsha 410073,China
-
Received:2020-04-26Revised:2020-06-15Accepted:2020-08-01Online:2020-10-05Published:2020-10-05 -
Contact:†Corresponding author. E-mail:wanggl@nwnu.edu.cn ‡Corresponding author. E-mail:zhouxx@nwnu.edu.cn -
About author:†Corresponding author. E-mail: wanggl@nwnu.edu.cn‡Corresponding author. E-mail: zhouxx@nwnu.edu.cn* Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11764038, 11864037, 11765018, and 11664035) and the Science Foundation of Northwest Normal University, China (Grant No. NWNU-LKQN-17-1).
中图分类号: (Frequency conversion; harmonic generation, including higher-order harmonic generation)
- 42.65.Ky
引用本文
Zhong Guan(管仲), Lu Liu(刘璐), Guo-Li Wang(王国利), Song-Feng Zhao(赵松峰), Zhi-Hong Jiao(焦志宏), Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信). [J]. 中国物理B, 2020, 29(10): 104206-.
Zhong Guan(管仲), Lu Liu(刘璐), Guo-Li Wang(王国利)†, Song-Feng Zhao(赵松峰), Zhi-Hong Jiao(焦志宏), and Xiao-Xin Zhou(周效信)‡. An improved method for the investigation of high-order harmonic generation from graphene[J]. Chin. Phys. B, 2020, 29(10): 104206-.
| [1] |
Xia C L, Lan Y Y, Li Q Q, Miao X Y 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 103203 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab4278
|
| [2] |
Zhang H D, Guo J, Shi Y, Du H, Liu H F, Huang X R, Liu X S, Jun Jing 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 014206 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/34/1/014206
|
| [3] |
Pan Y, Guo F M, Yang Y J, Ding D J 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 113201 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab47f8
|
| [4] |
Guo C X, Jiao Z H, Zhou X X, Li P C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 074203 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.69.20191883
|
| [5] |
Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Popmintchev D, Arpin P, Brown S, Ališauskas S, Andriukaitis G, Balčiunas T, Mücke Q D, Pugzlys A, Baltuška A, Shim B, Schrauth S E, Gaeta A, Hernández-García C, Plaga L, Becker A, Jaron-Becker A, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2012 Science 336 1287 DOI: 10.1126/science.1218497
|
| [6] |
He L X, Lan P F, Le A T, Wang B N, Wang B C, Zhu X S, Lu P X, Lin C D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 163201 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.163201
|
| [7] |
Shiner A D, Schmidt B E, Trallero-Herrero C, Wörner H J, Patchkovskii S, Corkum P B, Kieffer J C, Légaré F, Villeneuve D M 2001 Nat. Phys. 7 464
|
| [8] |
Wang G L, Jin C, Le A T, Lin C D 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 015401 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.86.015401
|
| [9] |
Wörner H J, Bertrand J B, Fabre B, Higuet J, Ruf H, Dubrouil A, Patchkovskii S, Spanner M, Mairesse Y, Blanchet V, Mevel E, Constant E, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2011 Science 334 208 DOI: 10.1126/science.1208664
|
| [10] |
Itatani J, Levesque J, Zeidler D, Niikura H, Pepin H, Kieffer J, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D 2004 Nature 432 867 DOI: 10.1038/nature03183
|
| [11] |
Baker S, Robinson J, Haworth C, Teng H, Smith R, Chirila C, Lein M, Tisch J, Marangos J 2006 Science 312 424 DOI: 10.1126/science.1123904
|
| [12] |
Smirnova O, Mairesse Y, Patchkovskii S, Dudovich N, Villeneuve D, Corkum P B, Ivanov M Y 2009 Nature 460 972 DOI: 10.1038/nature08253
|
| [13] |
Vodungbo B, Sardinha A B, Gautier J, Lambert G, Lozano M, Sebban S, Meltchakov E, Delmotte 2011 Europhys. Lett. 94 54003 DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/94/54003
|
| [14] |
Corkum P B, Krausz F 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 381 DOI: 10.1038/nphys620
|
| [15] |
Hentschel M, Kienberger R, Spielmann C, Reider G, Milosevic N, Brabec T, Corkum P B, Heinzmann U, Drescher M, Krausz F 2001 Nature 414 509 DOI: 10.1038/35107000
|
| [16] |
Krausz F, Ivanov M 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 163 DOI: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.163
|
| [17] |
Song H, Lü X Y, Zhu R B, Chen G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 184201 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190392
|
| [18] |
Xia C L, Miao X Y 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 043202 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/32/4/043202
|
| [19] |
Lü X Y, Zhu R B, Song H, Su N, Chen G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 214201 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190847
|
| [20] |
Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1994
|
| [21] |
Dou G, Yu Y, Guo M, Zhang Y M, Sun Z, Li Y X 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 038502 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/34/3/038502
|
| [22] |
Huang J J, Su L, Pu S Z, Sun S A, Zhang L Y 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 104204 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/33/10/104204
|
| [23] |
Kang B, Hwang S T 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 057201 DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/33/5/057201
|
| [24] |
Wang L K, Duan F L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 193101 DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190995
|
| [25] |
Liao T J, Lin B H, Wang Y H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 187901 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190882
|
| [26] |
Wang T H, Li A, Han B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 187102 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190859
|
| [27] |
Xu F, Zhang L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 117403 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab478c
|
| [28] |
Hu R X, Ma X L, An C H, Liu J 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 117802 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab4576
|
| [29] |
Ghimire S, DiChiara A D, Sistrunk E, Ndabashimiye G, Szafruga U B, Mohammad A, Agostini P, DiMauro L F, Reis D A 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 043836 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.85.043836
|
| [30] |
Vampa G, McDonald C R, Orlando G, Klug D D, Corkum P B, Brabec T 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 073901 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.073901
|
| [31] |
Wu M, Browne D A, Schafer K J, Gaarde M B 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 063403 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.063403
|
| [32] |
Wu M, Ghimire S, Reis D A, Schafer K J, Gaarde M B 2015 Phys. Rev. A 94 043839 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.043839
|
| [33] |
Ghimire S, Reis D A 2019 Nature 15 10 DOI: 10.1038/s41567-018-0315-5
|
| [34] |
McDonald C R, Vampa G, Corkum P B, Brabec T 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 033845 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.92.033845
|
| [35] |
Vampa G, McDonald C R, Orlando G, Corkum P B, Brabec T 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 064302 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.064302
|
| [36] |
Tamaya T, Ishikawa A, Ogawa T, Tanaka K 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 016601 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.016601
|
| [37] |
Ikemachi T, Shinohara Y, Sato T, Yumoto J, Kuwata-Gonokami M, Ishikawa K L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 043416 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.95.043416
|
| [38] |
McDonald C R, Vampa G, Corkum P B, Brabec T 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 173601 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.173601
|
| [39] |
Vampa G, Hammond T G, Thiré N, Schmidt B E, Légaré F, McDonald C R, Brabec T, Klug D D, Corkum P B 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 193603 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.193603
|
| [40] |
Vampa G, McDonald C R, Orlando G, Klug D D, Corkum P B, Brabec T 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 073901 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.073901
|
| [41] |
Guan Z, Zhou X X, Bian X B 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 033852 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.93.033852
|
| [42] |
Jin J Z, Xiao X R, Liang H, Wang M X, Chen S G, Gong Q, Peng L Y 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 043420 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.97.043420
|
| [43] |
Tancogne D N, Mücke O D, K?rtner F X, Rubio A 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 087403 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.087403
|
| [44] |
Luu T T, Garg M, Kruchinin S Y, Moulet A, Hassan M T, Goulielmakis E 2015 Nature 521 498 DOI: 10.1038/nature14456
|
| [45] |
Ndabashimiye G, Ghimire S, Wu M, Browne D A, Schafer K J, Gaarde M B, Reis D A 2017 Nat. Phys. 13 345 DOI: 10.1038/nphys3955
|
| [46] |
Sivis M, Taucer M, Vampa G, Johnston K, Staudte A, Naumov A Y, Villeneuve D M, Ropers C, Corkum P B 2017 Science 357 330
|
| [47] |
Tancogne D N, Mücke O D, Kärtner F X, Rubio A 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 745 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00764-5
|
| [48] |
Taucer M, Hammond T J, Corkum P B, Vampa G, Couture C, Thiré N, Schmidt B E, Légaré F, Selvi H, Unsuree N, Hamilton B, Echtermeyer T J, Denecke M A 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 195420 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.195420
|
| [49] |
Yang J L, Yuan Q C, Chen R F, Fang H L, Xiao F J, Li J T, Jiang B Q, Zhao J L, Gan X T 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 214207 in Chinese DOI: 10.7498/aps.68.20190789
|
| [50] |
Liu L, Zhao J, Yuan J M, Zhao Z X 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 114205 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab47f7
|
| [51] |
Li L, Lan P F, Zhu X S, Huang T F, Zhang Q B, Lein M, Lu P X 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 193901 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.193901
|
| [52] |
Zeng A W, Bian X B 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 203901 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.203901
|
| [53] |
Wang X Q, Xu Y, Huang X H, Bian X B 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 023427 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.98.023427
|
| [54] |
Jiang S C, Chen J G, Wei H, Yu C, Lu R F, Lin C D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 253201 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.253201
|
| [55] |
Jiang S C, Wei H, Chen J G, Yu C, Lu R F, Lin C D 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 053850 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.96.053850
|
| [56] |
Li J B, Zhang X, Fu S L, Feng Y K, Hu B T, Du H C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 043404 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.100.043404
|
| [57] |
Wang H Q, Feng Y K, Fu S L, Li J B, Zhang X, Du H C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 023406 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.99.023406
|
| [58] |
Kelardeh H K, Apalkov V, Stockman M I 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 045439 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.045439
|
| [59] |
Liu C, Zheng Y, Zeng Z, Li R 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 063412 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.97.063412
|
| [60] |
Zurrón Ó, Picón A, Plaja L 2018 New J. Phys. 20 053033 DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/aabec7
|
| [61] |
Zurrón Ó, Boyero-García R, Hernández-García C, Picón A, Plaja L 2019 Opt. Express 27 7776 DOI: 10.1364/OE.27.007776
|
| [62] |
Ishikawa K L 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 201402 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.201402
|
| [63] |
Wallace P R 1947 Phys. Rev. 71 622 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRev.71.622
|
| [64] |
Slonczewski J C, Weiss P R 1958 Phys. Rev. 109 272 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRev.109.272
|
| [65] |
Saito R, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus M 1999 Physical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes London Imperial College Press 17 29
|
| [66] |
Ishikawa K L 2013 New J. Phys 15 055021 DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/15/5/055021
|
| [67] |
Higuchi T, Heide C, Ullmann K, Weber H B, Hommelhoff P 2017 Nature 550 224 DOI: 10.1038/nature23900
|
| [68] |
Dimitrovski D, Madsen L, Pedersen T 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 035405 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.95.035405
|
| [69] |
Naib I, Sipe J E, Dignam M M 2016 Phys. Rev. B 90 245423 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.90.245423
|
| [70] |
Chizhova L A, Libisch F, Burgdörfe J 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 075412 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.94.075412
|
| [71] |
Yoshikawa N, Tamaya T, Tanaka K 2017 Science 356 736 DOI: 10.1126/science.aam8861
|
| [72] |
Budil K S, Salières P, L’Huillier A, Ditmire T, Perry M D 2003 Phys. Rev. A 48 R3437 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.48.R3437
|
| [73] |
Schubert O, Hohenleutner M, Langer F, Urbanek B, Lange C, Huttner U, Golde D, Meier T, Kira M, Koch S W, Huber R 2014 Nat. Photon. 8 119 DOI: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.349
|
| [74] |
Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045 DOI: 10.1103/RevModPhys.82.3045
|
| [75] |
Chen L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 117304 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab478e
|
| [1] | Chang-Tong Liang(梁畅通), Jing-Jing Zhang(张晶晶), and Peng-Cheng Li(李鹏程). Phase-coherence dynamics of frequency-comb emission via high-order harmonic generation in few-cycle pulse trains[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(3): 33201-033201. |
| [2] | Dong-Dong Cao(曹冬冬), Xue-Fei Pan(潘雪飞), Jun Zhang(张军), and Xue-Shen Liu(刘学深). Spectral shift of solid high-order harmonics from different channels in a combined laser field[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(3): 34204-034204. |
| [3] | Yining Zhu(朱奕宁), Zixu Zhu(朱子虚), Anbang Pei(裴安邦), and Yong-Pan Gao(高永潘). Optomagnonically tunable whispering gallery cavity laser wavelength conversion[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(2): 24206-024206. |
| [4] | Shu-Shan Zhou(周书山), Yu-Jun Yang(杨玉军), Yang Yang(杨扬), Ming-Yue Suo(索明月), Dong-Yuan Li(李东垣), Yue Qiao(乔月), Hai-Ying Yuan(袁海颖), Wen-Di Lan(蓝文迪), and Mu-Hong Hu(胡木宏). High-order harmonic generation of the cyclo[18]carbon molecule irradiated by circularly polarized laser pulse[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(1): 13201-013201. |
| [5] | Yanbo Chen(陈炎波), Baochang Li(李保昌), Xuhong Li(李胥红), Xiangyu Tang(唐翔宇), Chi Zhang(张弛), and Cheng Jin(金成). Effect of laser focus in two-color synthesized waveform on generation of soft x-ray high harmonics[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(1): 14203-014203. |
| [6] | Xiaoyu Liu(刘晓宇), Yong Zhang(张勇), Haoran Wang(王皓冉), Haomiao Wei(魏浩淼),Jingtao Zhou(周静涛), Zhi Jin(金智), Yuehang Xu(徐跃杭), and Bo Yan(延波). High frequency doubling efficiency THz GaAs Schottky barrier diode based on inverted trapezoidal epitaxial cross-section structure[J]. 中国物理B, 2023, 32(1): 17305-017305. |
| [7] | Dong Tang(唐栋) and Xue-Bin Bian(卞学滨). Multiple collisions in crystal high-order harmonic generation[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(12): 123202-123202. |
| [8] | Lixin He(何立新), Xiaosong Zhu(祝晓松), Wei Cao(曹伟), Pengfei Lan(兰鹏飞), and Peixiang Lu(陆培祥). Attosecond spectroscopy for filming the ultrafast movies of atoms, molecules and solids[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(12): 123301-123301. |
| [9] | Xiaofan Zhang(张晓凡) and Xiaosong Zhu(祝晓松). Yield enhancement of elliptical high harmonics driven by bicircular laser pulses[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(11): 114209-114209. |
| [10] | Ping Li(李萍), Na Gao(高娜), Rui-Xian Yu(蔚瑞贤), Jun Wang(王俊), Su-Yu Li(李苏宇), Fu-Ming Guo(郭福明), and Yu-Jun Yang(杨玉军). Amplitude and rotation of the ellipticity of harmonicsfrom a linearly polarized laser field[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(10): 103303-103303. |
| [11] | Xiao-Zhuo Qi(祁晓卓), and Xi-Feng Ren(任希锋). Enhancement of the second harmonic generation from monolayer WS2 coupled with a silica microsphere[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(10): 104203-104203. |
| [12] | Zheng Ge(葛正), Chen Yang(杨琛), Yin-Hai Li(李银海), Yan Li(李岩), Shi-Kai Liu(刘世凯), Su-Jian Niu(牛素俭), Zhi-Yuan Zhou(周志远), and Bao-Sen Shi(史保森). Up-conversion detection of mid-infrared light carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(10): 104210-104210. |
| [13] | Ming-Wei Qiu(邱明伟), Chao-Qun Cai(蔡超群), and Zu-Xing Zhang(张祖兴). Spatiotemporal mode-locked multimode fiber laser with dissipative four-wave mixing effect[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(10): 104207-104207. |
| [14] | Long Lin(林龙), Tong-Gang Jia(贾铜钢), Zhi-Bin Wang(王志斌), and Peng-Cheng Li(李鹏程). Probing subcycle spectral structures and dynamics of high-order harmonic generation in crystals[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(9): 93202-093202. |
| [15] | Ce Bian(边策), Jianwei Shi(史建伟), Xinfeng Liu(刘新风), Yang Yang(杨洋), Haitao Yang(杨海涛), and Hongjun Gao(高鸿钧). Optical second-harmonic generation of Janus MoSSe monolayer[J]. 中国物理B, 2022, 31(9): 97304-097304. |
|
||