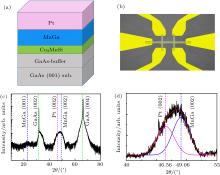
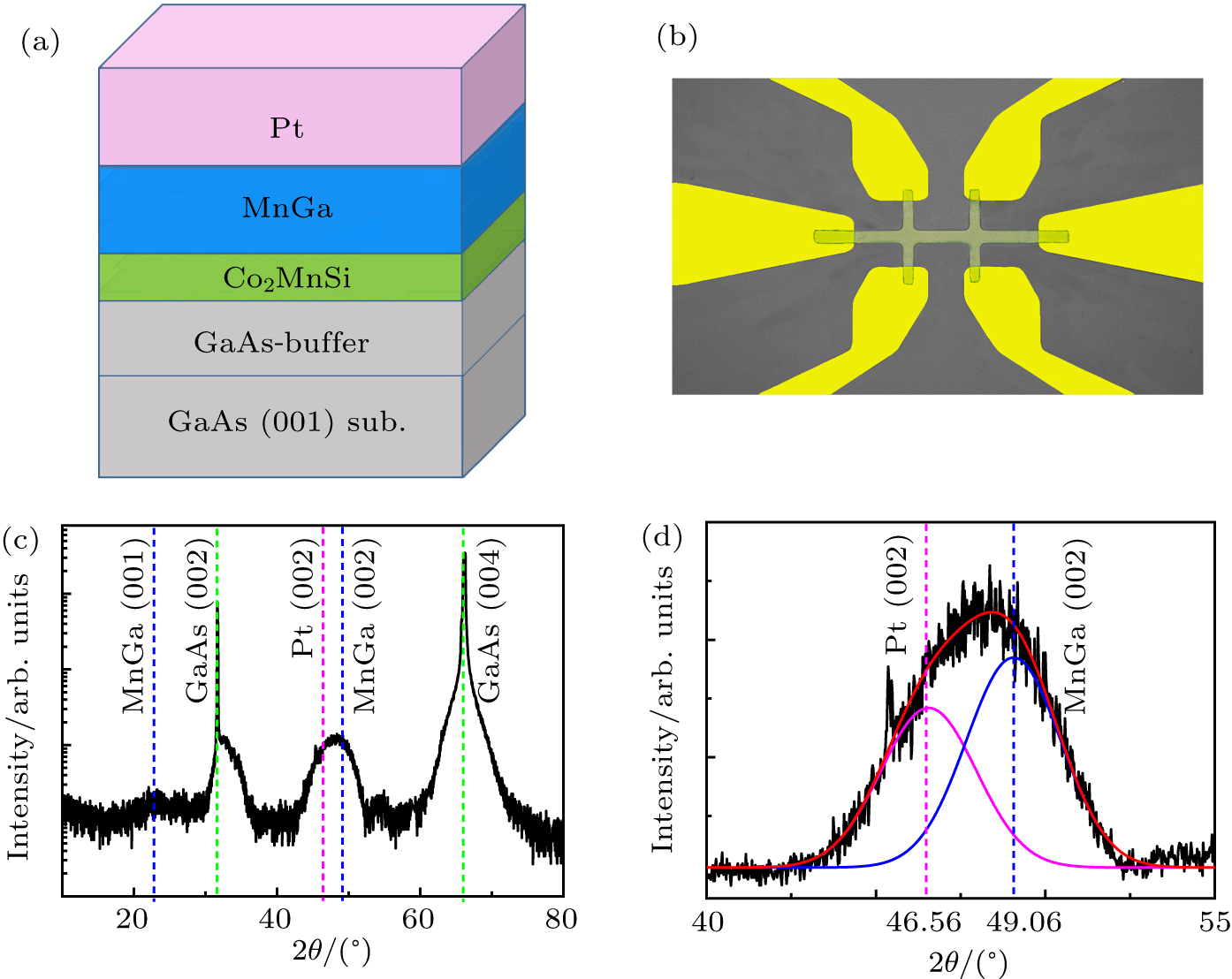
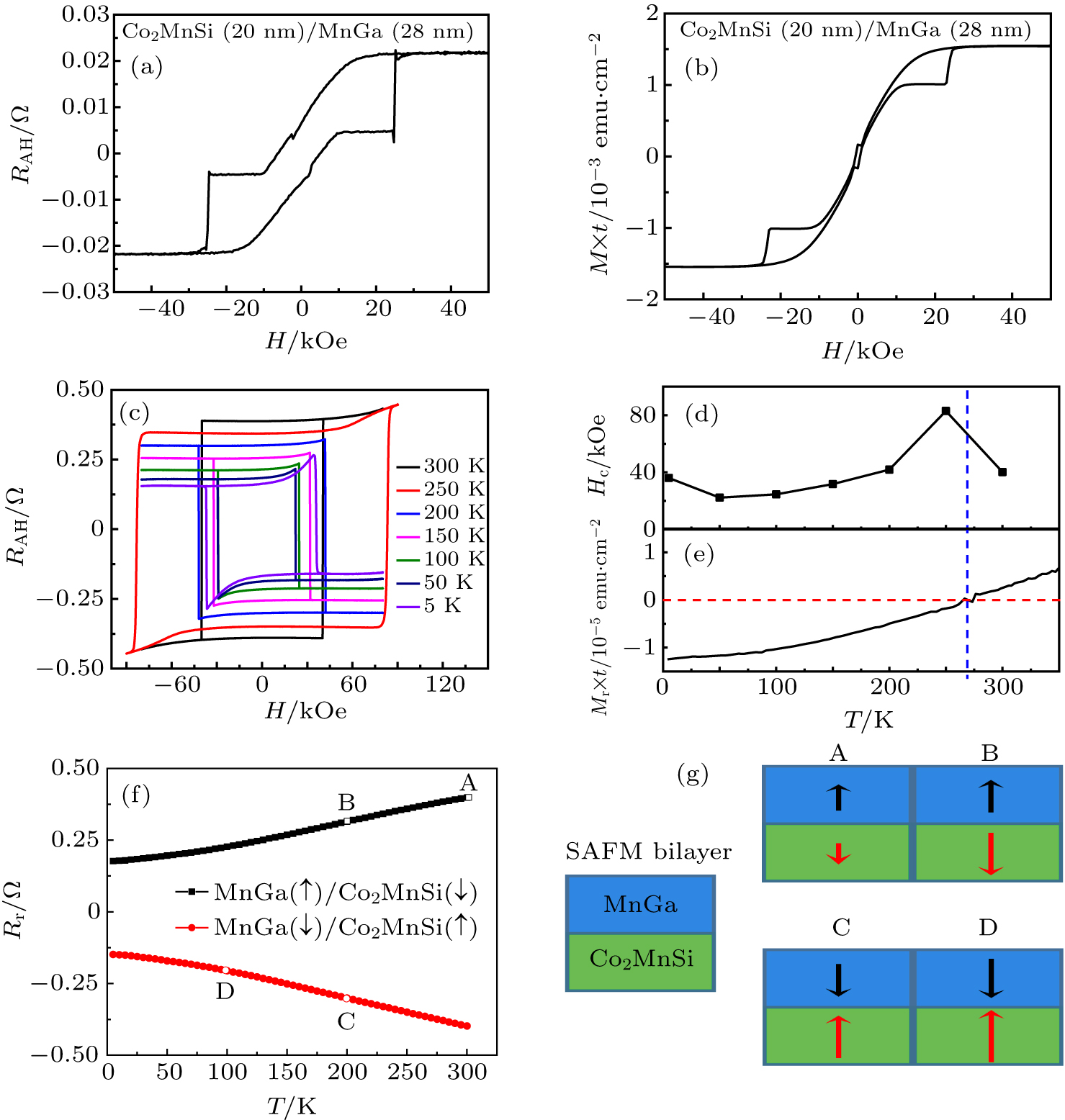
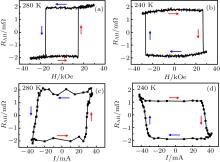
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
Chen R Y, Zhang R Q, Liao L Y, Chen X Z, Zhou Y J, Gu Y D, Saleem M S, Zhou X F, Pan F, Song C 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 115 132403 DOI: 10.1063/1.5118928 |
| [3] |
Fernandez-Pacheco A, Vedmedenko E, Ummelen F, Mansell R, Petit D, Cowburn R P 2019 Nat. Mater. 18 679 DOI: 10.1038/s41563-019-0386-4 |
| [4] |
Han D S, Lee K, Hanke J P, Mokrousov Y, Kim K W, Yoo W, van Hees Y L W, Kim T W, Lavrijsen R, You C Y, Swagten H J M, Jung M H, Klaui M 2019 Nat. Mater. 18 703 DOI: 10.1038/s41563-019-0370-z |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
Shi G Y, Wan C H, Chang Y S, Li F, Zhou X J, Zhang P X, Cai J W, Han X F, Pan F, Song C 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 104435 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.95.104435 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
Bi C, Almasi H, Price K, Newhouse-Illige T, Xu M, Allen S R, Fan X, Wang W 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 104434 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.95.104434 |
| [10] |
Zhang P X, Liao L Y, Shi G Y, Zhang R Q, Wu H Q, Wang Y Y, Pan F, Song C 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 214403 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.97.214403 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
Jin C, Song C, Wang J, Liu Q 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 182404 DOI: 10.1063/1.4967006 |
| [14] |
Lee J C T, Chess J J, Montoya S A, Shi X, Tamura N, Mishra S K, Fischer P, McMorran B J, Sinha S K, Fullerton E E, Kevan S D, Roy S 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 022402 DOI: 10.1063/1.4955462 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
Caretta L, Mann M, Buttner F, Ueda K, Pfau B, Gunther C M, Hessing P, Churikova A, Klose C, Schneider M, Engel D, Marcus C, Bono D, Bagschik K, Eisebitt S, Beach G S D 2018 Nat. Nanotechnol. 13 1154 DOI: 10.1038/s41565-018-0255-3 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
Hirata Y, Kim D H, Kim S K, Lee D K, Oh S H, Kim D Y, Nishimura T, Okuno T, Futakawa Y, Yoshikawa H, Tsukamoto A, Tserkovnyak Y, Shiota Y, Moriyama T, Choe S B, Lee K J, Ono T 2019 Nat. Nanotechnol. 14 232 DOI: 10.1038/s41565-018-0345-2 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
Fache T, Tarazona H S, Liu J, L’vova G, Applegate M J, Rojas-Sanchez J C, Petit-Watelot S, Landauro C V, Quispe-Marcatoma J, Morgunov R, Barnes C H W, Mangin S 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 064410 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.98.064410 |
| [25] |
Ranjbar R, Suzuki K Z, Sugihara A, Ando Y, Miyazaki T, Mizukami S 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 433 195 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.03.018 |
| [26] |
Ranjbar R, Suzuki K, Sugihara A, Miyazaki T, Ando Y, Mizukami S 2015 Materials (Basel) 8 6531 DOI: 10.3390/ma8095320 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
Mao S W, Lu J, Zhao X P, Wang X L, Wei D H, Liu J, Xia J B, Zhao J H 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 43064 DOI: 10.1038/srep43064 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
Zhu L J, Pan D, Nie S H, Lu J, Zhao J H 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 132403 DOI: 10.1063/1.4799344 |
| [33] |
Matsuno J, Ogawa N, Yasuda K, Kagawa F, Koshibae W, Nagaosa N, Tokura Y, Kawasaki M 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1600304 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1600304 |
| [34] |
Kan D, Moriyama T, Kobayashi K, Shimakawa Y 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 18048(R) http://dx.doi.org/ |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
Wang W H, Ren X B, Wu G H, Przybylski M, Barthel J, Kirschner J 2005 IEEE Trans. Magn. 41 2805 DOI: 10.1109/TMAG.2005.854833 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
 ), Si-Wei Mao(毛思玮)1,2, Da-Hai Wei(魏大海)1,2,3, Jian-Hua Zhao(赵建华)1,2,3
), Si-Wei Mao(毛思玮)1,2, Da-Hai Wei(魏大海)1,2,3, Jian-Hua Zhao(赵建华)1,2,3