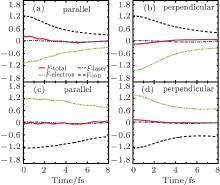
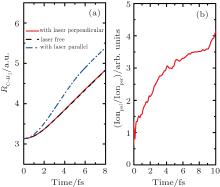
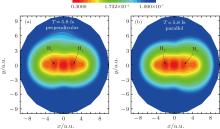
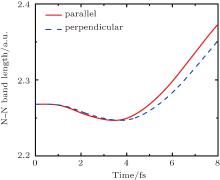
中国物理B ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 113202-.doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/abb3de
Ji-Gen Chen(陈基根)1, Gang-Tai Zhang(张刚台)2, Ting-Ting Bai(白婷婷)3, Jun Wang(王俊)4,†( ), Ping-Ping Chen(陈平平)5,‡(
), Ping-Ping Chen(陈平平)5,‡( ), Wei-Wei Yu(于伟威)6,§, Xi Zhao(赵曦)7,8,9,¶
), Wei-Wei Yu(于伟威)6,§, Xi Zhao(赵曦)7,8,9,¶
Nonadiabatic molecular dynamics simulation of ${{\rm{C}}}_{2}{{\rm{H}}}_{2}^{2+}$ in a strong laser field
Ji-Gen Chen(陈基根)1, Gang-Tai Zhang(张刚台)2, Ting-Ting Bai(白婷婷)3, Jun Wang(王俊)4, †, Ping-Ping Chen(陈平平)5,, ‡, Wei-Wei Yu(于伟威)6,§, and Xi Zhao(赵曦)7,8,9,¶
- 1 Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Cutting Tools, Taizhou University, Taizhou 225300, China
2 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Technology, Baoji University of Arts and Sciences, Baoji 721016, China
3 College of Mathematics and Information Science, Baoji University of Arts and Sciences, Baoji 721013, China
4 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
5 Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS 66506, USA
6 School of Physics and Electronic Technology, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian 116029, China
7 School of Physics and Information Technology, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710062, China
8 School of Physics and Electronics, Qiannan Normal College For Nationalities, Guizhou Province, Duyun 558000, China
9 Department of Physics, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS 66506, USA