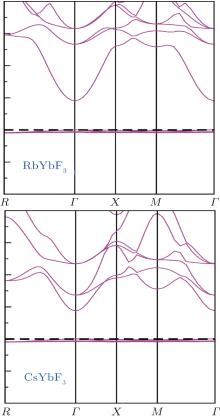
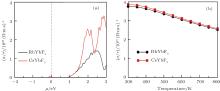
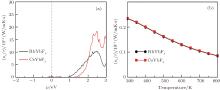
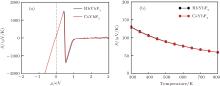
| [1] |
Mathur N, andwood P L 2003 Phys. Today 56 25
|
| [2] |
Moskvin S, Makhnev A A, Nomerovannaya L V, Loshkareva N N, Balbashov A M 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 035106 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.035106 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
Klauk H 2000 Phys. World 13 18
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
Scott J F 2006 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18 R361
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
Huang K, Feng M, Goodenough J, Milliken C 1997 J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 3620 DOI: 10.1149/1.1838058 |
| [12] |
Rao K, Yoon K 2003 J. Mater. Sci. 383 91
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
Murtaza G, Ahmad I, Maqbool M, Rahnamaye-Aliabad H A, Afaq A 2011 Chin. Phys. Lett. 281 17803
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
Erickson E M, Ghanty C, Aurbach D 2014 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5 3313 DOI: 10.1021/jz501387m |
| [19] |
Bai Y, Yu H, Zhu Z, Jiang K, Zhang T, Zhao N, Yang S, Yan H 2015 J. Mater. Chem. A 3 9098 DOI: 10.1039/C4TA05309E |
| [20] |
Moreira R L, Dias A 2007 Phys. Chem. Solids 681 617
|
| [21] |
Wu G Q, Hoppe R 1983 Z. Anorp;. Allg. Chemie 504 55
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
Zhao L D, Berardan D, Pei Y L, Byl C, Pinsard-Gaudart L, Dragoe N 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 092118 DOI: 10.1063/1.3485050 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
Amin B, Singh N, Tritt T M, Alshareef H N, Schwingenschlögl U 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 031907 DOI: 10.1063/1.4815928 |
| [32] |
Li H, Tang X, Zhang Q, Uher C 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 10114
|
| [33] |
Nam W H, Kim B B, Seo S G, Lim Y S, Kim J Y, Seo W S, Choi W K, Park H H, Lee J Y 2014 Nano Lett. 14 5104 DOI: 10.1021/nl5018089 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Madsen G K, Kvasnicka D, Luitz J 2001 Wien2k An augmented plane wave+ local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Sorantin P, Trickey S K 1990 Comput. Phys. Commun. 59 339
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
Ullah R, Ali M A, Murad S, Khan A, Dar S A, Mahmood I, Laref A 2019 Mater. Res. Express 6 125901 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab540e |
| [43] |
Hautier G, Fischer C, Ehrlacher V, Jain A, Ceder G 2019 Inorganic chemistry 17 656
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
Sabir B, Murtaza G, Mahmood Q, Ahmad R, Bhamu K C 2017 Current Appl. Phys. 17 1539
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
Scheidemantel T J, Ambrosch-Draxl C, Thonhauser T, Badding J V, Sofo J O 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 125210 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.125210 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
Mahmood Q, Hassan M, Ahmed S H A, Shahid A, Laref A 2018 J. Phys. Chem. Solid 20 87
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
 ), N A Noor3, T Ghrib1,2, Nessrin A Kattan4, Asif Mahmood5,‡(
), N A Noor3, T Ghrib1,2, Nessrin A Kattan4, Asif Mahmood5,‡( ), Shahid M Ramay6
), Shahid M Ramay6