Epitaxial growth and air-stability of monolayer Cu2Te
Project supported by the National Key Research & Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2016YFA0202300 and 2018YF A0305800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61888102, 11604373, 61622116, and 51872284), the CAS Pioneer Hundred Talents Program, China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos. XDB30000000 and XDB28000000), Beijing Nova Program, China (Grant No. Z181100006218023), and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. A portion of the research was performed in the CAS Key Laboratory of Vacuum Physics. Computational resources were provided by the National Supercomputing Center in Tianjin.
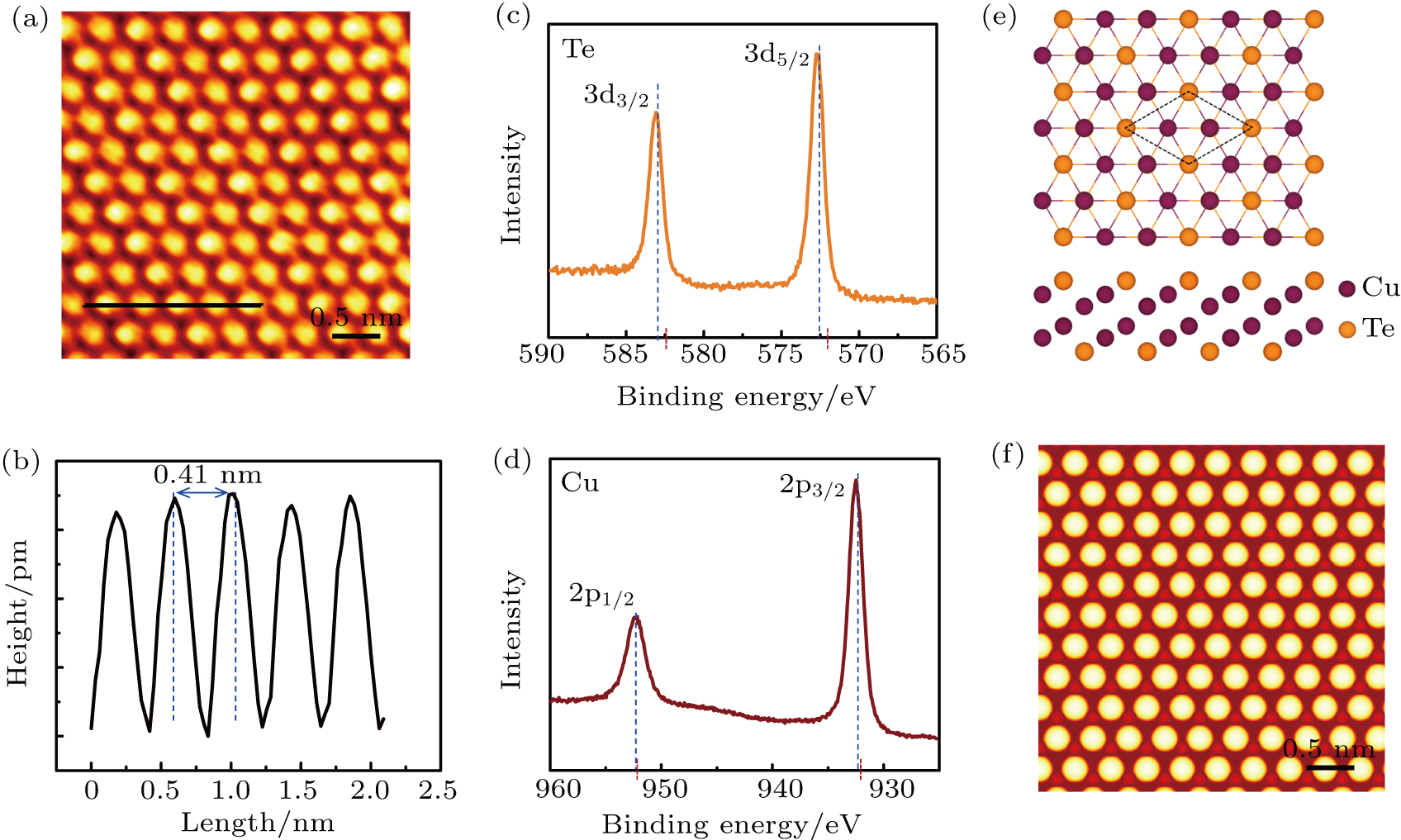
Atomic configuration and the XPS results of the monolayer Cu2Te. (a) An atomic resolution STM image of monolayer Cu2Te. (b) Line profile of the Cu2Te sample corresponding to the black line in (a). The periodicity of the monolayer Cu2Te lattice is ∼ 0.41 nm. (c) The XPS core-level spectrum of Te. The peak positions are 583.1 eV (3d3/2) and 572.8 eV (3d5/2). (d) The Cu 2p XPS spectrum. The peak positions are 952.6 eV (2p1/2) and 932.8 eV (2p3/2). (e) The atomic model of the monolayer Cu2Te. The dotted rhombus indicates the unit cell of the Cu2Te monolayer. (f) Simulated STM image of the monolayer Cu2Te.