|
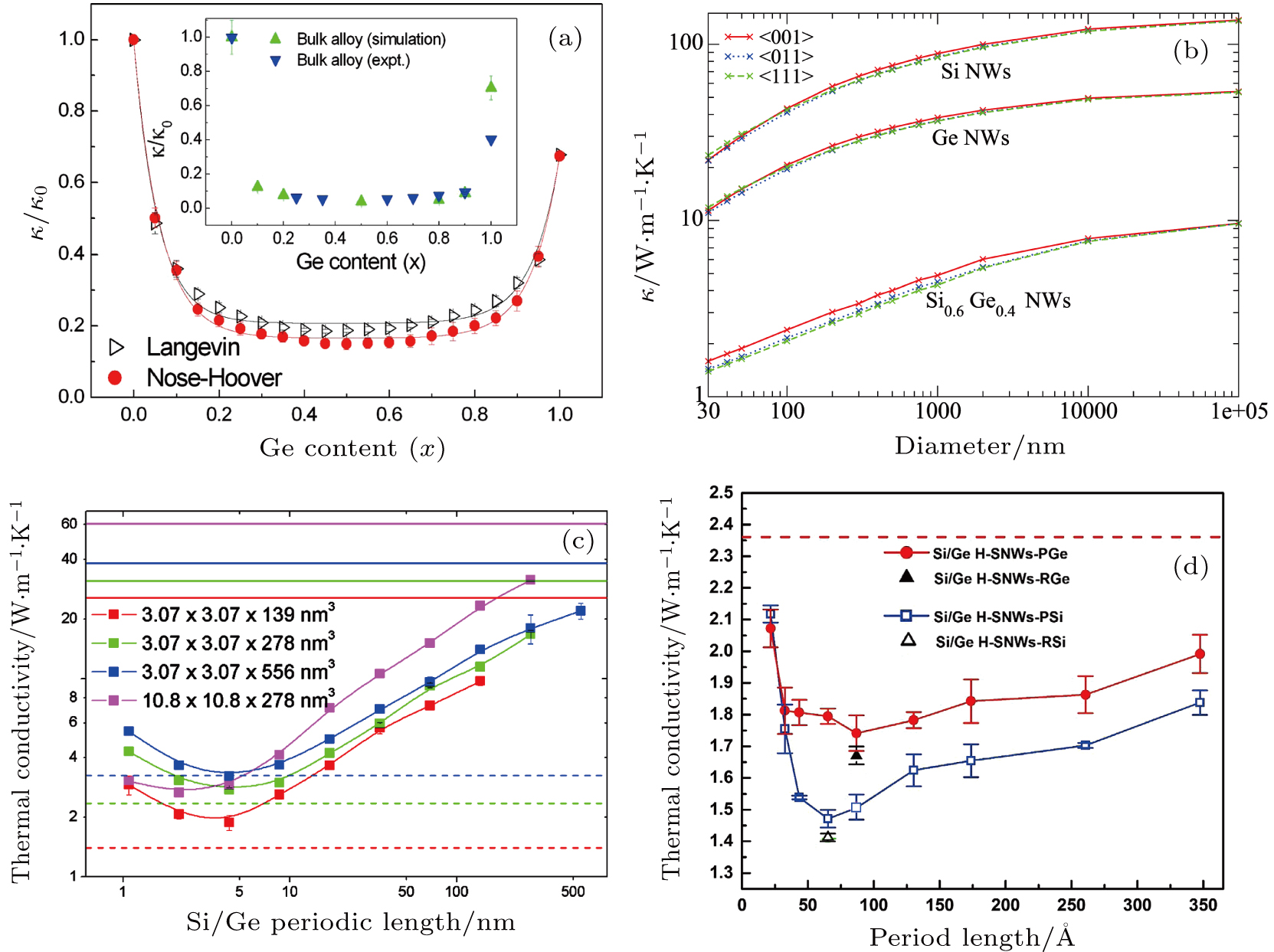
(color online) Thermal conductivity of alloy and superlattice NWs. (a) Room temperature thermal conductivity versus concentration of Ge in Si1−xGex alloy NWs. (b) Room temperature thermal conductivity of Si NWs, Ge NWs, and Si0.6Ge0.4 alloy NWs, as a function of the diameter for
〈
001
〉
,
〈
011
〉
, and
〈
111
〉
growth directions. (c) Periodic length dependence of the thermal conductivity of Si/Ge superlattice NWs for different total lengths. The solid and dashed lines represent the thermal conductivity of pure smooth Si NWs and Si0.5Ge0.5 alloy nanowires with same length and cross-section width, respectively. (d) Room temperature thermal conductivities of Si/Ge H-SNW (hierarchical superlattice nanowires) as a function of their period lengths. Two kinds of Si/Ge H-SNWs: periodically Si- or Ge-defected SNW (denoted as H-SNW-Psi or H-SNW-PGe), and randomly Si- or Ge-defected SNW (denoted as H-SNW-RSi or H-SNW-RGe). The red dashed line represents the thermal conductivity of regular Si/Ge SNW with the period of “AB”. Panels adapted with permission from (a) Ref. [91], © 2009 AIP; (b) Ref. [33], ©2013 AIP; (c) Ref. [35], ©2012 ACS; (d) Ref. [95], ©2015, Macmillan Publishers Limited.
|