Interfacial nanobubbles produced by long-time preserved cold water
Project supported by the Key Laboratory of Interfacial Physics and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Open Research Project of the Large Scientific Facility of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11079050, 11290165, 11305252, 11575281, and U1532260), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant Nos. 2012CB825705 and 2013CB932801), the National Natural Science Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientists, China (Grant No. 11225527), the Shanghai Academic Leadership Program, China (Grant No. 13XD1404400), and the Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos. KJCX2-EW-W09 and QYZDJ-SSW-SLH019)
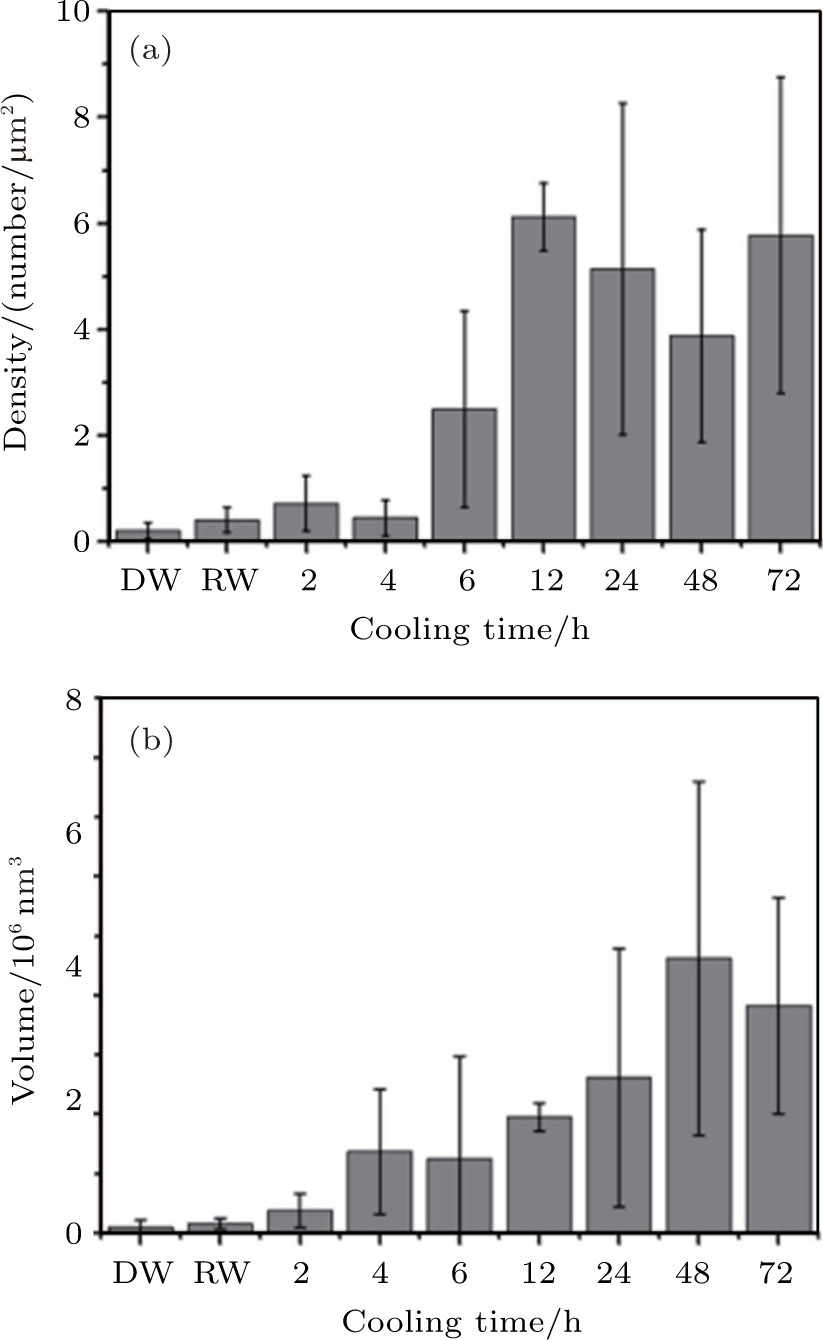
Density and total volume of nanobubbles in the area produced by cold water with different cooling times, room temperature water and degassed water. Error bar is given by analyzing the AFM images scanned at different places on HOPG surface in the experiments. DW: degassed water, RW: room temperature water (0 h).