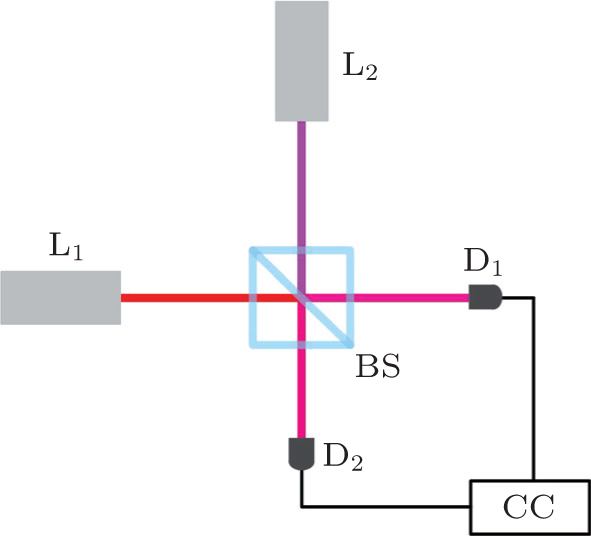
Second-order interference of two independent and tunable single-mode continuous-wave lasers
Second-order interference of two independent lasers. Two independent laser light beams are incident to two adjacent input ports of a 1:1 non-polarizing beam splitter (BS), respectively. L1 and L2 are two single-mode continuous-wave lasers. D1 and D2 are two single-photon detectors. CC is two-photon coincidence count detection system. The mean frequencies of photons emitted by L1 and L2 are