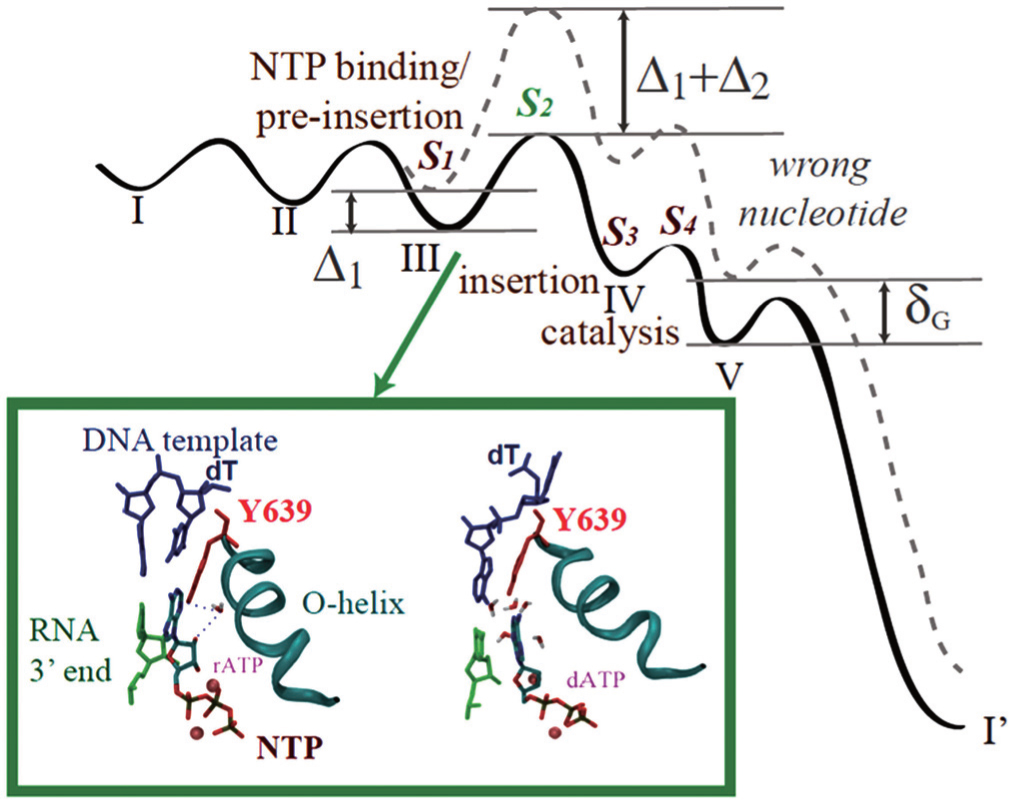
The nucleotide selection scheme in T7 RNAP elongation. (Top) The free energy landscape for incorporating the right (solid line) and wrong (dashed) nucleotides in the five-state kinetic scheme. Four selection checkpoints (S1toS4) are labeled. Δ1and Δ2are differentiation free energies between the right and wrong nucleotides at the first two checkpoints. δGis an overall free energy differentiation without polymerase. See Ref. [71] for details. (Bottom) Comparing the active site configurations when the right and wrong NTP bind respectively to the pre-insertion site.[72]Y639 (red) is located on the C-term end of the Ohelix (cyan) to assist the nucleotide selection. Left: rATP (right) forms the Watson–Crick base pairing with the template. The recognition is assisted by water bridging HB interactions with Y639-OH and 2’-OH of rNTP. Right: dATP cannot base pair with the template due to the Y639 interference, which associates with dATP and stacks well with the DNA–RNA hybrid end, under water collision.[72] |