Understanding oxygen reactions in aprotic Li-O2batteries
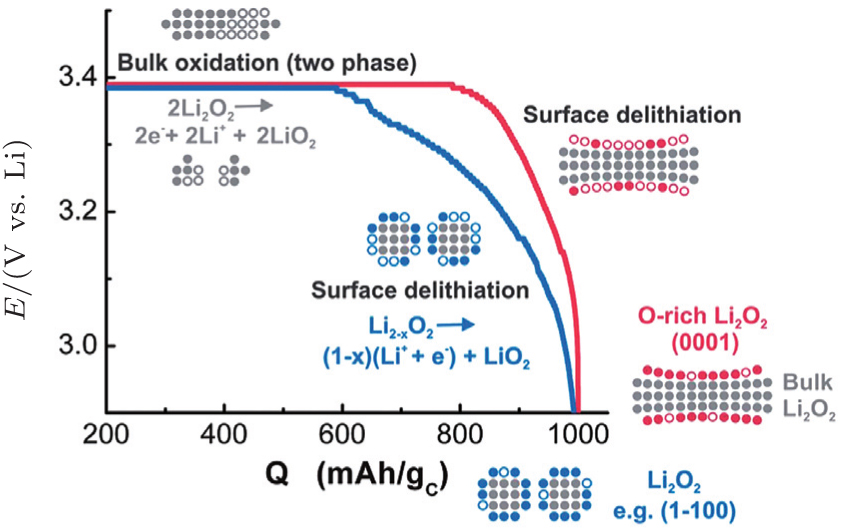
Proposed charging processes for Li2O2, with disc (gray/red, typical dimensions ∼ 50 to 200 nm) or particle (gray/blue, typical dimensions < 20 nm) morphologies overlaid. Discs’ surfaces are largely O-rich (0001) with LiO2-like surface species, while particles consist of less O-rich (more stoichiometric) Li2O2surfaces. During the initial stage of charging (to ∼ 800 mA·h/gCfor discs and to ∼ 600 mA·h/gCfor particles), both discs and particles exhibit a sloping voltage profile attributed to solid solution-like surface de-lithiation. Upon further charging, discs and particles exhibit a voltage plateau at ∼ 3.4 V vs. Li, corresponding to bulk oxidation via a two-phase process, e.g., between Li2O2and LiO2.[